The Benefits of Composting Coffee Grounds
Composting coffee grounds is a simple yet effective way to reduce waste, create nutrient-rich soil, and support sustainable gardening practices. By incorporating coffee grounds into your compost pile, you can divert a significant amount of organic waste from landfills and create a valuable resource for your garden. Composted coffee grounds are rich in nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, making them an excellent natural fertilizer for plants. Additionally, composting coffee grounds can help to improve soil structure, increase the water-holding capacity of soil, and support the growth of beneficial microorganisms.
One of the most significant benefits of composting coffee grounds is the reduction of waste. Coffee grounds are a common household waste product, with millions of pounds of coffee grounds being thrown away each year. By composting coffee grounds, you can reduce the amount of waste sent to landfills and create a valuable resource for your garden. Furthermore, composting coffee grounds can help to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers and minimizing the production of methane in landfills.
Composting coffee grounds is also a great way to support sustainable gardening practices. By using composted coffee grounds as a natural fertilizer, you can reduce your reliance on synthetic fertilizers and create a more sustainable gardening practice. Composted coffee grounds can also help to improve soil health, increase crop yields, and support the growth of beneficial microorganisms. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just starting out, composting coffee grounds is a simple and effective way to create a more sustainable and productive garden.
So, how to compost coffee grounds? It’s easier than you think. Simply collect your coffee grounds in a designated container, add them to your compost pile, and mix well. You can also add other organic materials, such as leaves, grass clippings, and vegetable scraps, to create a nutrient-rich compost. With a little patience and effort, you can create a valuable resource for your garden and support sustainable gardening practices.
Preparing Your Coffee Grounds for Composting
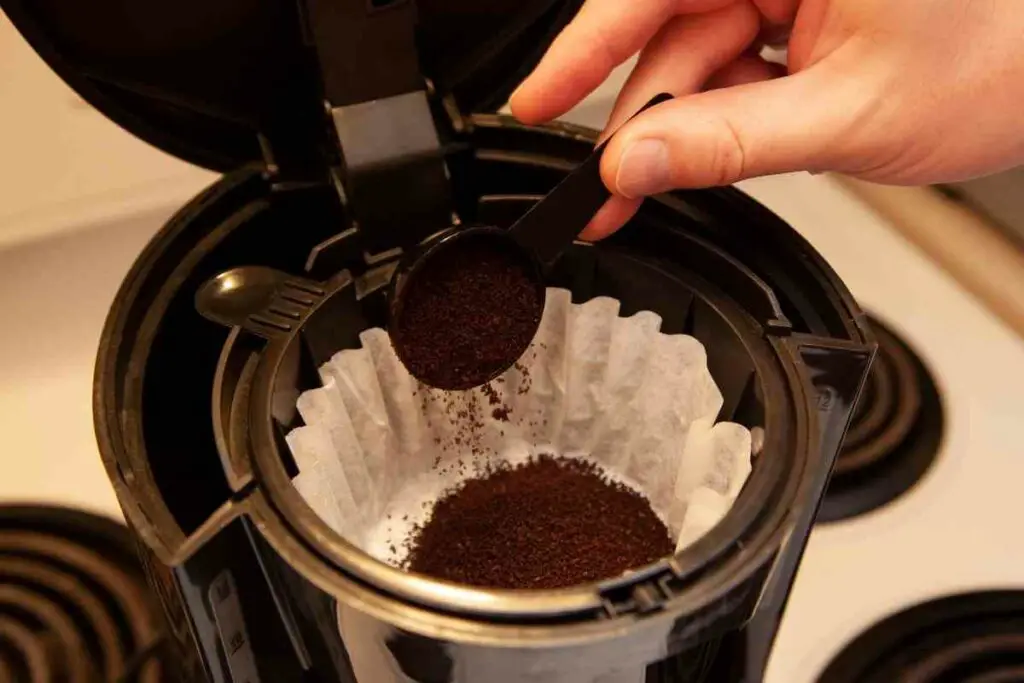
To ensure successful composting of coffee grounds, it’s essential to prepare them properly. The first step is to dry the coffee grounds thoroughly. This can be done by spreading them out in a single layer on a baking sheet or tray and allowing them to air dry for a few days. Alternatively, you can dry them in a low-temperature oven (150°F – 200°F) for a few hours. Drying the coffee grounds helps to reduce the risk of mold and pests in the compost pile.
Once the coffee grounds are dry, you can grind them into a finer texture using a coffee grinder or mortar and pestle. Grinding the coffee grounds increases their surface area, allowing them to break down more easily in the compost pile. However, be careful not to grind them too finely, as this can create a dense, anaerobic environment that can lead to unpleasant odors and pest problems.
Next, mix the ground coffee with other compost materials, such as leaves, grass clippings, or vegetable scraps. Aim for a mix of 2/3 “brown” materials (e.g., leaves, straw) and 1/3 “green” materials (e.g., coffee grounds, grass clippings). This balance of carbon-rich and nitrogen-rich materials will help to create a healthy, thriving compost pile.
When adding coffee grounds to your compost pile, it’s essential to mix them in thoroughly to avoid creating a dense, coffee-ground-only layer. This can lead to anaerobic conditions, unpleasant odors, and pest problems. Instead, mix the coffee grounds in with other materials, and turn the pile regularly to ensure adequate aeration and decomposition.
By following these simple steps, you can prepare your coffee grounds for composting and create a nutrient-rich soil amendment for your garden. Remember to always follow proper composting practices, including maintaining a balanced carbon-to-nitrogen ratio, monitoring temperature and moisture, and turning the pile regularly. With a little patience and effort, you can turn your coffee grounds into a valuable resource for your garden.
Choosing the Right Composting Method for Your Coffee Grounds
When it comes to composting coffee grounds, there are several methods to choose from, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The right method for you will depend on your specific needs and circumstances. Here are three common composting methods that can be used for coffee grounds: hot composting, cold composting, and vermicomposting.
Hot composting is a fast and efficient method that involves actively managing the compost pile to speed up the decomposition process. This method is ideal for large quantities of coffee grounds and can produce finished compost in as little as 1-2 months. To hot compost coffee grounds, create a pile with a mix of “green” materials (e.g., coffee grounds, grass clippings) and “brown” materials (e.g., leaves, straw). The pile should be at least 3-4 feet high and 3-4 feet wide. Turn the pile regularly to maintain aeration and monitor temperature, which should reach 130-140°F within a few days.
Cold composting, on the other hand, is a slower and more passive method that involves simply adding materials to a pile and letting them break down over time. This method is ideal for small quantities of coffee grounds and can produce finished compost in 6-12 months. To cold compost coffee grounds, create a pile with a mix of “green” and “brown” materials, but do not actively manage the pile. Instead, let it sit for several months, turning it occasionally to maintain aeration.
Vermicomposting, also known as worm composting, is a method that uses worms to break down organic materials. This method is ideal for small quantities of coffee grounds and can produce finished compost in as little as 1-2 months. To vermicompost coffee grounds, create a worm bin with a mix of “green” and “brown” materials, and add red wiggler worms. The worms will break down the materials over time, producing a nutrient-rich compost.
When choosing a composting method for your coffee grounds, consider factors such as space, time, and desired outcome. Hot composting is ideal for large quantities and fast results, while cold composting is better suited for small quantities and a more passive approach. Vermicomposting is a great option for those who want to produce a high-quality compost with minimal space and effort.
Adding Coffee Grounds to Your Compost Pile
Once you’ve prepared your coffee grounds for composting, it’s time to add them to your compost pile. The key to successful composting is to maintain a balanced carbon-to-nitrogen ratio. Coffee grounds are high in nitrogen, so they should be balanced with carbon-rich materials such as leaves, straw, or shredded newspaper.
A general rule of thumb is to mix 2/3 “brown” materials (e.g., leaves, straw) with 1/3 “green” materials (e.g., coffee grounds, grass clippings). This will help to create a balanced compost pile that breaks down efficiently. When adding coffee grounds to your compost pile, start with a small amount (about 1-2 cups) and mix well with other materials.
It’s also important to consider the moisture level of your compost pile. Coffee grounds can be quite dry, so you may need to add some water to the pile to maintain a consistent moisture level. Aim for a pile that is moist but not soggy, like a damp sponge.
When adding coffee grounds to your compost pile, it’s also a good idea to mix in some bulking agents such as straw or shredded newspaper. These materials will help to absorb excess moisture and odors, and will also provide a source of carbon to balance out the nitrogen-rich coffee grounds.
Finally, be sure to turn your compost pile regularly to maintain aeration and speed up the decomposition process. This will help to prevent anaerobic conditions and odors, and will ensure that your compost pile breaks down efficiently.
By following these tips, you can successfully add coffee grounds to your compost pile and create a nutrient-rich soil amendment for your garden. Remember to always maintain a balanced carbon-to-nitrogen ratio, monitor moisture levels, and turn your compost pile regularly to ensure optimal decomposition.
Managing Odors and Pests in Your Coffee Grounds Compost
As with any composting process, managing odors and pests is crucial to maintaining a healthy and thriving compost pile. Coffee grounds can be particularly prone to odors and pests due to their high nitrogen content and moisture levels. However, with the right techniques and strategies, you can minimize these issues and create a nutrient-rich compost for your garden.
One of the most effective ways to manage odors in your coffee grounds compost is to turn the pile regularly. This helps to aerate the materials, reduce moisture levels, and prevent anaerobic conditions that can lead to unpleasant odors. Aim to turn your compost pile every 7-10 days, or whenever you notice a strong odor.
Another way to manage odors is to add bulking agents such as straw or shredded newspaper to your compost pile. These materials will help to absorb excess moisture and odors, and will also provide a source of carbon to balance out the nitrogen-rich coffee grounds.
Pests can also be a problem in coffee grounds compost, particularly fruit flies and rodents. To manage pests, make sure to cover your compost pile with a lid or tarp to prevent them from accessing the materials. You can also add natural pest control methods such as diatomaceous earth or neem oil to your compost pile to deter pests.
In addition to these strategies, it’s also important to maintain a balanced carbon-to-nitrogen ratio in your compost pile. This will help to prevent odors and pests, and will ensure that your compost breaks down efficiently. Aim for a mix of 2/3 “brown” materials (e.g., leaves, straw) and 1/3 “green” materials (e.g., coffee grounds, grass clippings).
By following these tips, you can effectively manage odors and pests in your coffee grounds compost and create a nutrient-rich soil amendment for your garden. Remember to always turn your compost pile regularly, add bulking agents as needed, and maintain a balanced carbon-to-nitrogen ratio to ensure optimal decomposition.
Using Composted Coffee Grounds in Your Garden
Composted coffee grounds are a nutrient-rich soil amendment that can be used to improve soil structure, increase nutrient availability, and support healthy plant growth. When used in gardening, composted coffee grounds can provide a range of benefits, including improved soil fertility, increased water retention, and reduced soil erosion.
One of the main benefits of using composted coffee grounds in gardening is their ability to improve soil structure. Composted coffee grounds are high in organic matter, which can help to improve soil porosity, aeration, and water infiltration. This can lead to healthier plant growth, improved root development, and increased crop yields.
Composted coffee grounds are also a rich source of nutrients, including nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. These nutrients are essential for plant growth and can help to promote healthy plant development. Additionally, composted coffee grounds can help to support beneficial microorganisms in the soil, which can help to break down organic matter and make nutrients more available to plants.
When using composted coffee grounds in gardening, it’s best to mix them into the soil at a rate of 10-20% of the total soil volume. This can help to ensure that the composted coffee grounds are evenly distributed throughout the soil and can provide maximum benefits to plants.
Composted coffee grounds can be used in a variety of gardening applications, including vegetable gardens, flower gardens, and container gardens. They can also be used as a mulch or top dressing to help retain moisture and suppress weeds.
Overall, composted coffee grounds are a valuable resource for gardeners, providing a range of benefits that can help to promote healthy plant growth and improve soil fertility. By incorporating composted coffee grounds into your gardening routine, you can create a more sustainable and productive garden that benefits both you and the environment.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with Composting Coffee Grounds
While composting coffee grounds can be a rewarding and beneficial process, there are some common issues that may arise. In this section, we’ll address some of the most common problems and provide solutions to help you overcome them.
One of the most common issues with composting coffee grounds is slow decomposition. This can be caused by a lack of oxygen, inadequate moisture, or insufficient carbon-rich materials. To overcome this issue, make sure to turn your compost pile regularly to aerate the materials, add more carbon-rich materials such as leaves or straw, and maintain a consistent moisture level.
Another common issue is mold growth. This can be caused by excessive moisture, inadequate aeration, or the presence of contaminants. To prevent mold growth, make sure to maintain a consistent moisture level, turn your compost pile regularly, and add more carbon-rich materials to absorb excess moisture.
Pests can also be a problem when composting coffee grounds. Fruit flies, rodents, and other pests may be attracted to the coffee grounds and can cause problems. To prevent pests, make sure to cover your compost pile with a lid or tarp, add more carbon-rich materials to absorb excess moisture, and use natural pest control methods such as diatomaceous earth or neem oil.
Finally, some people may experience issues with odors when composting coffee grounds. This can be caused by inadequate aeration, excessive moisture, or the presence of contaminants. To prevent odors, make sure to turn your compost pile regularly, maintain a consistent moisture level, and add more carbon-rich materials to absorb excess moisture.
By following these tips and troubleshooting common issues, you can ensure a healthy and thriving compost pile with coffee grounds. Remember to always monitor your compost pile’s temperature, moisture, and carbon-to-nitrogen ratios to ensure optimal decomposition.
Maintaining a Healthy Compost Pile with Coffee Grounds
Maintaining a healthy compost pile with coffee grounds requires regular monitoring and maintenance. This includes monitoring temperature, moisture, and carbon-to-nitrogen ratios to ensure optimal decomposition.
Temperature is an important factor in composting, as it can affect the rate of decomposition and the quality of the finished compost. Ideally, the temperature of the compost pile should be between 130°F and 140°F, which is hot enough to kill off pathogens and weed seeds, but not so hot that it kills off beneficial microorganisms.
Moisture is also crucial, as it helps to support the growth of microorganisms and facilitate decomposition. The compost pile should be kept moist, but not soggy, with a consistency similar to a damp sponge.
Carbon-to-nitrogen ratios are also important, as they affect the balance of the compost pile and the quality of the finished compost. Ideally, the carbon-to-nitrogen ratio should be around 25:1, with a mix of 25 parts carbon-rich materials (such as leaves or straw) to 1 part nitrogen-rich materials (such as coffee grounds or grass clippings).
Regular turning of the compost pile is also essential, as it helps to aerate the materials, speed up decomposition, and prevent anaerobic conditions. The compost pile should be turned every 7-10 days, or whenever it becomes compacted or develops an unpleasant odor.
By monitoring temperature, moisture, and carbon-to-nitrogen ratios, and regularly turning the compost pile, you can ensure a healthy and thriving compost pile with coffee grounds. This will help to produce a high-quality compost that is rich in nutrients and beneficial microorganisms, and can be used to support healthy plant growth and sustainable gardening practices.