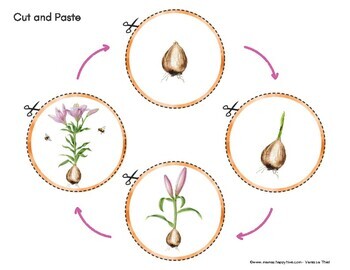
Understanding the Life Cycle of Lily Bulbs
Lily bulbs, like all living organisms, go through a series of stages in their life cycle. Understanding these stages is crucial for gardeners who want to successfully grow and care for their lily plants. The life cycle of a lily bulb consists of three main stages: dormancy, sprouting, and blooming.
During the dormancy stage, the lily bulb is in a state of rest, and its growth is slowed down. This stage is crucial for the bulb’s survival, as it allows the bulb to conserve energy and prepare for the next growing season. The length of the dormancy stage varies depending on the type of lily and environmental factors, but it typically lasts from a few weeks to several months.
As the weather warms up and daylight hours increase, the lily bulb begins to sprout. This stage is characterized by the emergence of green shoots and the development of roots. The sprouting stage is a critical period in the life cycle of a lily bulb, as it determines the plant’s ability to grow and bloom. Factors such as temperature, light, water, and soil quality can affect the sprouting time of lily bulbs, and gardeners can optimize these conditions to promote healthy growth.
Once the lily plant has reached its full height and the flowers have bloomed, the blooming stage begins. This stage is the most visible and spectacular part of the life cycle, as the flowers bloom and produce seeds. The blooming stage typically lasts from a few weeks to several months, depending on the type of lily and environmental factors.
Understanding the life cycle of lily bulbs is essential for gardeners who want to provide the best possible care for their plants. By recognizing the different stages of the life cycle, gardeners can optimize growing conditions, prevent common problems, and enjoy the beauty and fragrance of their lily flowers. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just starting out, knowing how long it takes for lily bulbs to sprout and bloom can help you plan and care for your garden with confidence.
Factors Affecting Lily Bulb Sprouting Time
Several factors can influence the time it takes for lily bulbs to sprout, and understanding these factors can help gardeners optimize growing conditions for faster germination. Temperature is one of the most critical factors, as lily bulbs typically require a period of cold temperatures to break dormancy. A temperature range of 35°F to 45°F (2°C to 7°C) is ideal for most lily varieties.
Light is another essential factor, as lily bulbs need adequate light to produce the energy required for growth. However, too much light can be detrimental, so it’s essential to provide filtered or indirect light during the germination period. Water is also crucial, as lily bulbs need consistent moisture to sprout. However, overwatering can lead to rot and poor germination, so it’s essential to maintain a balance.
Soil quality is also a critical factor, as lily bulbs prefer well-draining, fertile soil with a pH between 6.0 and 7.0. Poor soil quality can lead to slow germination, so it’s essential to test the soil and amend it if necessary. Other factors, such as humidity, wind, and pests, can also affect the sprouting time of lily bulbs.
To optimize the sprouting time of lily bulbs, gardeners can take several steps. First, choose a location with the right temperature and light conditions. Next, prepare the soil by adding organic matter and fertilizers. Plant the bulbs at the correct depth and water them consistently. Finally, provide ongoing care, including fertilization and pest management, to promote healthy growth.
By understanding the factors that affect lily bulb sprouting time, gardeners can take steps to optimize growing conditions and promote faster germination. This can help reduce the time it takes for lily bulbs to sprout, allowing gardeners to enjoy the beauty and fragrance of their flowers sooner. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just starting out, knowing how to optimize growing conditions can make a significant difference in the success of your lily bulbs.
How to Plant Lily Bulbs for Optimal Germination
Planting lily bulbs requires careful attention to detail to ensure optimal germination and growth. The first step is to choose a location with the right conditions for lily bulbs. Look for a spot that receives partial shade to full sun, depending on the variety, and has well-draining soil. Avoid planting in areas with standing water or where water tends to collect.
Next, prepare the soil by loosening it to a depth of about 12 inches. Add a 2-inch layer of compost or well-rotted manure to improve soil fertility and drainage. If your soil is heavy clay or sandy, mix in some organic matter to improve its structure.
Plant the lily bulbs at the correct depth, which is usually 2-3 times the height of the bulb. For example, if the bulb is 2 inches tall, plant it 4-6 inches deep. Space the bulbs 6-12 inches apart, depending on the variety, and water them well after planting.
It’s also essential to plant the bulbs at the right time. In most regions, the best time to plant lily bulbs is in the fall, about 6-8 weeks before the first frost. This allows the bulbs to establish themselves in the soil over the winter, and then send up green shoots and flowers in the spring.
Proper planting techniques are crucial for successful germination and growth of lily bulbs. By following these steps, you can give your lily bulbs the best chance to thrive and enjoy their beautiful flowers for years to come. Remember, the key to successful germination is to provide the right conditions, including temperature, light, water, and soil quality. With a little care and attention, you can enjoy the beauty and fragrance of your lily bulbs and wonder how long it takes for them to sprout.
The Waiting Game: What to Expect During Germination
After planting lily bulbs, the waiting game begins. It’s essential to understand what to expect during the germination process to ensure optimal growth and development. The first sign of germination is usually the emergence of green shoots, which can take anywhere from 2-6 weeks, depending on the variety and growing conditions.
As the shoots grow, they will begin to develop roots, which will anchor the plant in the soil. This is a critical period, as the roots will provide the necessary nutrients and water for the plant to grow. It’s essential to keep the soil consistently moist during this period to promote healthy root development.
During the germination period, it’s also important to provide the right amount of light. Most lily varieties require partial shade to full sun, depending on the variety. Make sure to provide the right amount of light to promote healthy growth and development.
Another critical aspect of germination is temperature. Lily bulbs typically require a period of cold temperatures to break dormancy. If the temperature is too high, it can delay or prevent germination. Make sure to provide the right temperature conditions to promote healthy germination.
It’s also essential to be patient during the germination period. Germination can take anywhere from 2-6 weeks, depending on the variety and growing conditions. Keep the soil consistently moist, provide the right amount of light, and maintain the right temperature conditions to promote healthy germination.
By understanding what to expect during the germination process, you can provide the right conditions to promote healthy growth and development. Remember, the key to successful germination is to provide the right conditions, including temperature, light, water, and soil quality. With a little care and attention, you can enjoy the beauty and fragrance of your lily bulbs and wonder how long it takes for them to sprout.
Common Challenges and Solutions for Slow-Germinating Lily Bulbs
Despite proper care and attention, some lily bulbs may experience delayed or failed germination. There are several common challenges that can cause slow germination, including pests, diseases, and inadequate care. In this section, we will discuss some of the most common issues and provide troubleshooting tips and solutions to help readers overcome these challenges.
Pests, such as aphids, slugs, and snails, can cause significant damage to lily bulbs and delay germination. To prevent pest infestations, use organic pest control methods, such as neem oil or insecticidal soap, and keep the soil clean and free of debris. Regularly inspect the bulbs for signs of pests and take action promptly if you notice any issues.
Diseases, such as fungal infections and bacterial rot, can also cause slow germination. To prevent diseases, use clean and sterile equipment when handling the bulbs, and avoid overwatering, which can create an ideal environment for disease to develop. If you notice any signs of disease, such as yellowing or blackening of the leaves, remove the affected areas and treat the bulbs with a fungicide.
Inadequate care, such as insufficient light or water, can also cause slow germination. Make sure to provide the right amount of light and water for the specific variety of lily bulb you are growing. Check the soil regularly to ensure it is consistently moist but not waterlogged.
Other common challenges that can cause slow germination include poor soil quality, inadequate fertilization, and extreme temperatures. To overcome these challenges, use high-quality potting soil, fertilize the bulbs regularly, and provide protection from extreme temperatures.
By understanding the common challenges that can cause slow germination and taking steps to prevent them, you can help ensure successful germination and growth of your lily bulbs. Remember, patience and proper care are key to unlocking the full potential of your lily bulbs and enjoying their beautiful flowers.
How Long Does it Take for Lily Bulbs to Sprout?
The germination timeline for lily bulbs can vary depending on several factors, including the specific variety, growing conditions, and care. On average, it can take anywhere from 2-6 weeks for lily bulbs to sprout, with some varieties taking longer than others.
Temperature is one of the most significant factors that can influence the germination time of lily bulbs. Most lily varieties require a period of cold temperatures to break dormancy, typically between 35°F and 45°F (2°C and 7°C). If the temperature is too high, it can delay or prevent germination.
Light is also an essential factor in the germination process. Lily bulbs typically require partial shade to full sun, depending on the variety. If the light is too intense, it can cause the bulbs to become scorched, leading to delayed or failed germination.
Water and soil quality are also critical factors that can influence the germination time of lily bulbs. Consistent moisture and well-draining soil can help promote healthy germination, while overwatering or poor soil quality can lead to delayed or failed germination.
It’s essential to note that some lily varieties can take longer to germinate than others. For example, Asiatic lilies typically germinate within 2-3 weeks, while Oriental lilies can take 4-6 weeks. By understanding the specific germination requirements of your lily variety, you can provide the best possible care and conditions for optimal growth and blooming.
Patience and proper care are key to successful germination and growth of lily bulbs. By providing the right conditions, including temperature, light, water, and soil quality, you can help ensure that your lily bulbs sprout and grow into healthy, thriving plants. Remember, the time it takes for lily bulbs to sprout can vary, but with the right care and attention, you can enjoy the beauty and fragrance of your lily flowers for years to come.
Post-Germination Care: Tips for Healthy Lily Plant Growth
After germination, lily plants require ongoing care to promote healthy growth and blooming. One of the most critical aspects of post-germination care is fertilization. Feed your lily plants with a balanced fertilizer, such as a 10-10-10 formula, once a month during the growing season. This will provide essential nutrients for optimal growth and blooming.
Pruning is another essential aspect of post-germination care. Remove any dead or damaged leaves or flowers to promote healthy growth and prevent the spread of disease. Cut back the flower stalks after blooming to encourage the plant to focus its energy on re-growing and storing energy for next year’s bloom.
Pest management is also crucial for healthy lily plant growth. Keep an eye out for common pests, such as aphids, slugs, and snails, and take action promptly if you notice any issues. Use organic pest control methods, such as neem oil or insecticidal soap, to minimize harm to the environment and your plants.
Soil quality is also essential for healthy lily plant growth. Add a layer of compost or well-rotted manure to the soil around your lily plants to improve soil fertility and drainage. This will help promote healthy root growth and prevent waterlogged soil.
Finally, make sure to provide your lily plants with the right amount of water. Lily plants prefer well-draining soil and consistent moisture, but overwatering can lead to root rot and other problems. Check the soil regularly to ensure it is consistently moist but not waterlogged.
By following these tips, you can provide your lily plants with the care they need to thrive and bloom beautifully. Remember, the key to successful growth and blooming is to provide the right conditions, including temperature, light, water, and soil quality. With a little care and attention, you can enjoy the beauty and fragrance of your lily flowers for years to come.
Conclusion: Unlocking the Full Potential of Your Lily Bulbs
Germinating lily bulbs can be a rewarding experience, but it requires patience, proper care, and attention to detail. By understanding the life cycle of lily bulbs, the factors that affect sprouting time, and the importance of proper planting techniques, you can unlock the full potential of your lily bulbs and enjoy their beautiful flowers for years to come.
Remember, the key to successful germination is to provide the right conditions, including temperature, light, water, and soil quality. By following the tips and advice provided in this article, you can optimize these conditions and promote healthy growth and blooming.
Additionally, be aware of common challenges that may cause delayed or failed germination, such as pests, diseases, and inadequate care. By troubleshooting these issues and taking action promptly, you can overcome these challenges and achieve successful germination.
Finally, don’t forget to provide ongoing care for your lily plants after germination, including fertilization, pruning, and pest management. This will help promote healthy growth and blooming, and ensure that your lily plants continue to thrive for years to come.
By applying the knowledge and tips provided in this article, you can unlock the full potential of your lily bulbs and enjoy their beauty and fragrance for years to come. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just starting out, germinating lily bulbs can be a fun and rewarding experience. So why not give it a try and see the amazing results for yourself?






/GettyImages-153342142-56a75f045f9b58b7d0e9bee6.jpg)