Unlocking the Potential of Loquat Seeds
The loquat tree, also known as Eriobotrya japonica, is a popular evergreen tree native to Asia. Its sweet and juicy fruit has made it a favorite among gardeners and fruit enthusiasts alike. Growing loquat trees from seed can be a rewarding experience, but it requires careful attention to detail and proper cultivation techniques. With the right approach, loquat seeds can be coaxed into thriving trees that produce delicious fruit for years to come.
One of the main benefits of growing loquat trees from seed is the ability to control the growing conditions from the very beginning. By starting with high-quality seeds and providing optimal care, gardeners can increase the chances of successful germination and healthy growth. Additionally, growing from seed allows for greater flexibility in terms of tree selection and breeding, making it an attractive option for those looking to experiment with new varieties.
However, growing loquat trees from seed can also be a challenging and time-consuming process. It requires patience, dedication, and a willingness to learn and adapt. With the right guidance and techniques, however, anyone can successfully grow loquat trees from seed and enjoy the many benefits they have to offer.
For those looking to grow loquat trees from seed, it is essential to understand the basics of loquat cultivation. This includes selecting high-quality seeds, preparing the soil, and providing optimal growing conditions. By following these steps and staying committed to proper care and maintenance, gardeners can unlock the full potential of their loquat seeds and enjoy a bountiful harvest of delicious fruit.
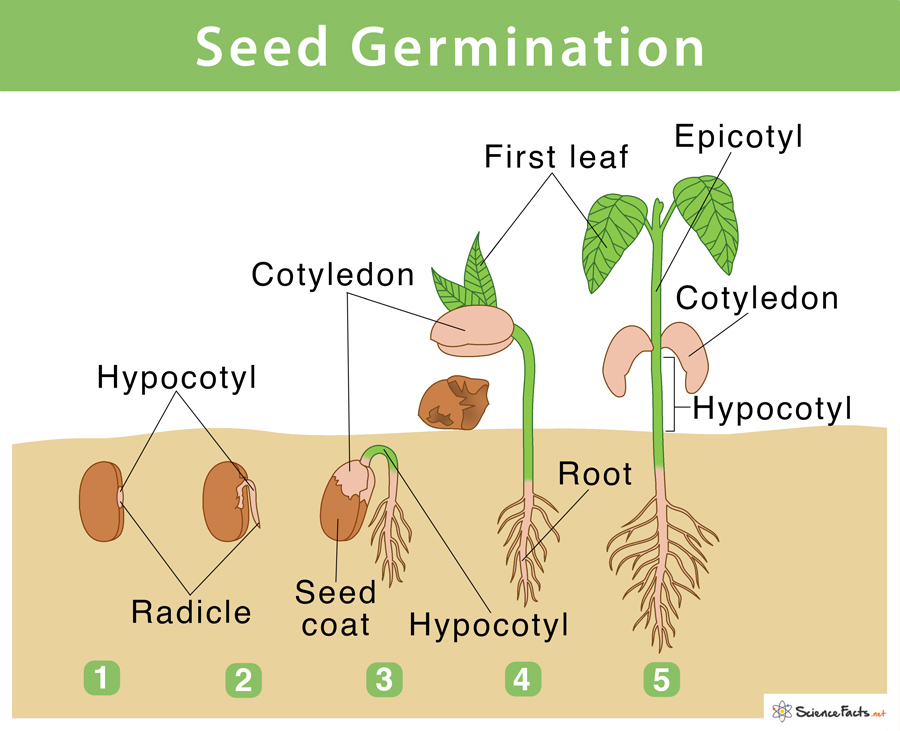
Preparing the Perfect Environment for Germination
Creating an optimal environment for loquat seed germination is crucial for successful growth. Loquat seeds require a warm and humid climate to germinate, with temperatures ranging from 65°F to 75°F (18°C to 24°C). A consistent temperature above 60°F (15°C) is essential for breaking seed dormancy and promoting germination.
Humidity is also a critical factor in loquat seed germination. A humid environment helps to maintain seed moisture, which is essential for germination. To create a humid microclimate, gardeners can cover the seed tray or container with a clear plastic bag or a cloche. This will help to maintain a consistent level of humidity and promote germination.
Light is another important factor to consider when preparing the environment for loquat seed germination. Loquat seeds require indirect light to germinate, as direct sunlight can cause overheating and inhibit germination. A south-facing window or a grow light with a low intensity setting can provide the necessary light for germination.
In addition to temperature, humidity, and light, the quality of the potting mix is also crucial for loquat seed germination. A well-draining potting mix with a pH between 6.0 and 7.0 is ideal for loquat seeds. Gardeners can also add a small amount of organic matter, such as compost or peat moss, to the potting mix to improve its water-holding capacity and fertility.
By creating an optimal environment for germination, gardeners can increase the chances of successful loquat seed germination and promote healthy growth. This includes providing the right temperature, humidity, light, and potting mix conditions, as well as maintaining a consistent level of care and attention.
How to Sow Loquat Seeds for Successful Germination
Sowing loquat seeds requires careful attention to detail to ensure successful germination. To start, select high-quality seeds that are fresh and have not been stored for too long. Loquat seeds can be obtained from a reputable nursery or online supplier.
Before sowing, prepare the seeds by soaking them in water for 24 hours. This will help to soften the seed coat and encourage germination. After soaking, plant the seeds about ¼ inch deep in a seed starting mix. The sowing depth is critical, as seeds that are planted too deeply may not germinate.
Space the seeds about 1-2 inches apart, depending on the size of the seeds. This will give the seedlings enough room to grow without becoming overcrowded. Cover the seeds with a thin layer of the seed starting mix, and gently firm the soil to ensure good contact.
Water the seeds gently but thoroughly after sowing. Make sure the soil is consistently moist but not waterlogged, as this can lead to rot and poor germination. Provide the seeds with the optimal environment for germination, including warm temperatures, high humidity, and indirect light.
It’s also essential to maintain good hygiene when sowing loquat seeds. Use clean and sterile equipment, and avoid touching the seeds or soil to prevent contamination. By following these steps and providing the right conditions, gardeners can increase the chances of successful loquat seed germination and promote healthy growth.
When growing loquat trees from seed, it’s essential to be patient and not rush the process. Germination can take anywhere from 1-3 months, depending on the conditions. Keep the soil consistently moist and provide the seedlings with the right environment, and they will eventually emerge and start growing.
Nourishing Your Loquat Seedlings: Essential Care Tips
Once loquat seedlings have germinated, they require careful nourishment to promote healthy growth. Watering is a critical aspect of loquat seedling care, as these plants prefer consistently moist soil. However, overwatering can be detrimental, so it’s essential to strike a balance. Water the seedlings when the top inch of soil feels dry to the touch, and avoid getting water on the leaves to prevent fungal diseases.
Fertilization is also crucial for loquat seedlings. Use a balanced, water-soluble fertilizer (20-20-20) and follow the manufacturer’s instructions for application rates. Feed the seedlings once a month, taking care not to overfertilize, which can cause more harm than good.
Pruning is another essential care tip for loquat seedlings. Prune the seedlings to maintain a strong, central leader and encourage a balanced, symmetrical shape. Remove any weak or spindly growth, and cut back the tips of the branches to encourage branching.
Loquat seedlings are also susceptible to pests and diseases, such as aphids, whiteflies, and root rot. Monitor the seedlings regularly for signs of infestation or infection, and take action promptly to prevent the problem from spreading.
Common challenges when growing loquat seedlings include nutrient deficiencies, pests, and diseases. To address these issues, provide the seedlings with a balanced fertilizer, use integrated pest management techniques, and maintain good hygiene practices.
By following these essential care tips, gardeners can promote healthy growth and development in their loquat seedlings. With proper care and attention, loquat seedlings can thrive and eventually produce delicious fruit.
Transplanting Loquat Seedlings: A Critical Step in Their Development
Transplanting loquat seedlings is a critical step in their development, as it allows them to grow and thrive in a more spacious environment. When transplanting, choose a container that is at least 1-2 sizes larger than the original pot, and use a well-draining potting mix to prevent waterlogged soil.
Before transplanting, water the seedlings thoroughly to make the soil easier to handle. Gently remove the seedlings from their pots, taking care not to disturb the roots. If the roots have become pot-bound, gently tease them apart with your fingers or a blunt instrument.
Plant the seedlings at the same depth as they were previously, and water them well after transplanting. Provide the seedlings with bright, indirect light, and maintain a consistent temperature between 65-75°F (18-24°C).
To minimize transplant shock, avoid transplanting seedlings during extreme weather conditions, such as intense heat or cold. Also, avoid over-handling the seedlings, as this can cause stress and lead to transplant shock.
After transplanting, monitor the seedlings closely for signs of stress or disease. Adjust their care accordingly, and provide them with the necessary nutrients and support to promote healthy growth.
Transplanting loquat seedlings directly into the ground can also be a viable option, provided the soil is well-draining and rich in organic matter. Choose a location with full sun to partial shade, and water the seedlings regularly to ensure establishment.
By following these tips and taking the necessary precautions, gardeners can successfully transplant their loquat seedlings and set them on the path to becoming healthy, productive trees.
Pest and Disease Management: Protecting Your Loquat Trees
Loquat trees are susceptible to various pests and diseases that can impact their health and productivity. To maintain the health and vigor of your loquat trees, it’s essential to implement integrated pest management (IPM) strategies.
Common pests that can affect loquat trees include aphids, whiteflies, and scales. These pests can be controlled using insecticidal soap, neem oil, or horticultural oil. Regularly inspect your trees for signs of infestation, and take action promptly to prevent the problem from spreading.
Loquat trees are also susceptible to various diseases, including root rot, leaf spot, and powdery mildew. These diseases can be caused by fungal, bacterial, or viral pathogens, and can be controlled using fungicides, bactericides, or other disease management strategies.
To prevent pest and disease problems, maintain good hygiene practices, such as removing weeds, debris, and infested plants. Regularly inspect your trees for signs of stress or disease, and take action promptly to prevent the problem from spreading.
Biological control methods, such as introducing beneficial insects or using microorganisms, can also be effective in managing pest and disease problems. For example, introducing lady beetles or lacewings can help control aphid populations, while using Trichoderma harzianum can help control fungal diseases.
Cultural control methods, such as pruning, watering, and fertilizing, can also help prevent pest and disease problems. Prune your loquat trees regularly to promote air circulation, reduce humidity, and remove diseased or damaged branches.
By implementing IPM strategies, you can protect your loquat trees from pests and diseases, and maintain their health and productivity.
Pruning and Training Loquat Trees for Optimal Fruit Production
Pruning and training are essential practices for loquat trees to promote healthy growth, maximize fruit production, and maintain tree longevity. Pruning involves removing select branches or stems to control the tree’s shape, size, and fruiting habits.
There are several pruning techniques that can be applied to loquat trees, including thinning, reduction, and pinching. Thinning involves removing select branches to allow more sunlight to penetrate the tree’s canopy, while reduction involves cutting back branches to control the tree’s size. Pinching involves removing the tips of new growth to encourage branching and promote fruiting.
Training loquat trees involves providing support and guidance to the tree’s growth habits. This can be achieved through the use of trellises, stakes, or other support systems. Training can help to promote a strong, central leader and encourage the tree to grow in a desired shape or direction.
Regular maintenance is crucial for promoting healthy growth and fruiting in loquat trees. This includes pruning, training, and fertilizing the tree on a regular basis. By following these practices, gardeners can optimize fruit production and enjoy a bountiful harvest of delicious loquats.
When pruning loquat trees, it’s essential to make clean cuts and avoid damaging the tree’s bark or underlying tissues. Use sharp, sterile pruning tools and make cuts at a 45-degree angle to promote healthy healing. Remove any diseased, damaged, or dead branches to prevent the spread of disease and encourage healthy growth.
By pruning and training loquat trees, gardeners can promote optimal fruit production and enjoy a long-lasting harvest of delicious loquats. With proper care and maintenance, loquat trees can thrive and provide a bountiful supply of fresh fruit for years to come.
Harvesting and Enjoying Your Homegrown Loquats
Loquats are typically ready to harvest in late spring to early summer, depending on the variety and growing conditions. To determine if your loquats are ripe, gently tug on the fruit. If it comes off the tree easily, it’s ready to eat.
When harvesting loquats, handle the fruit carefully to avoid bruising or damaging the skin. Use scissors or a sharp knife to cut the fruit from the tree, leaving a small piece of stem attached to the fruit.
Loquats can be enjoyed fresh, used in cooking and baking, or preserved through canning or freezing. They’re a delicious addition to salads, smoothies, and desserts, and can be used to make jams, jellies, and preserves.
One popular way to enjoy loquats is to make a loquat jam or jelly. This can be done by cooking the fruit with sugar and pectin, then canning or freezing the resulting jam or jelly.
Loquats can also be used in savory dishes, such as stir-fries and salads. They pair well with ingredients like chicken, pork, and tofu, and can add a sweet and tangy flavor to a variety of dishes.
For those who want to preserve their loquats for later use, freezing is a great option. Simply wash and chop the fruit, then spread it out on a baking sheet and place it in the freezer. Once frozen, transfer the loquats to airtight containers or freezer bags and store them in the freezer for up to 6 months.
By following these tips and techniques, you can enjoy your homegrown loquats at their best and make the most of your harvest.