Deciphering the Code: What Do NPK Values Mean?
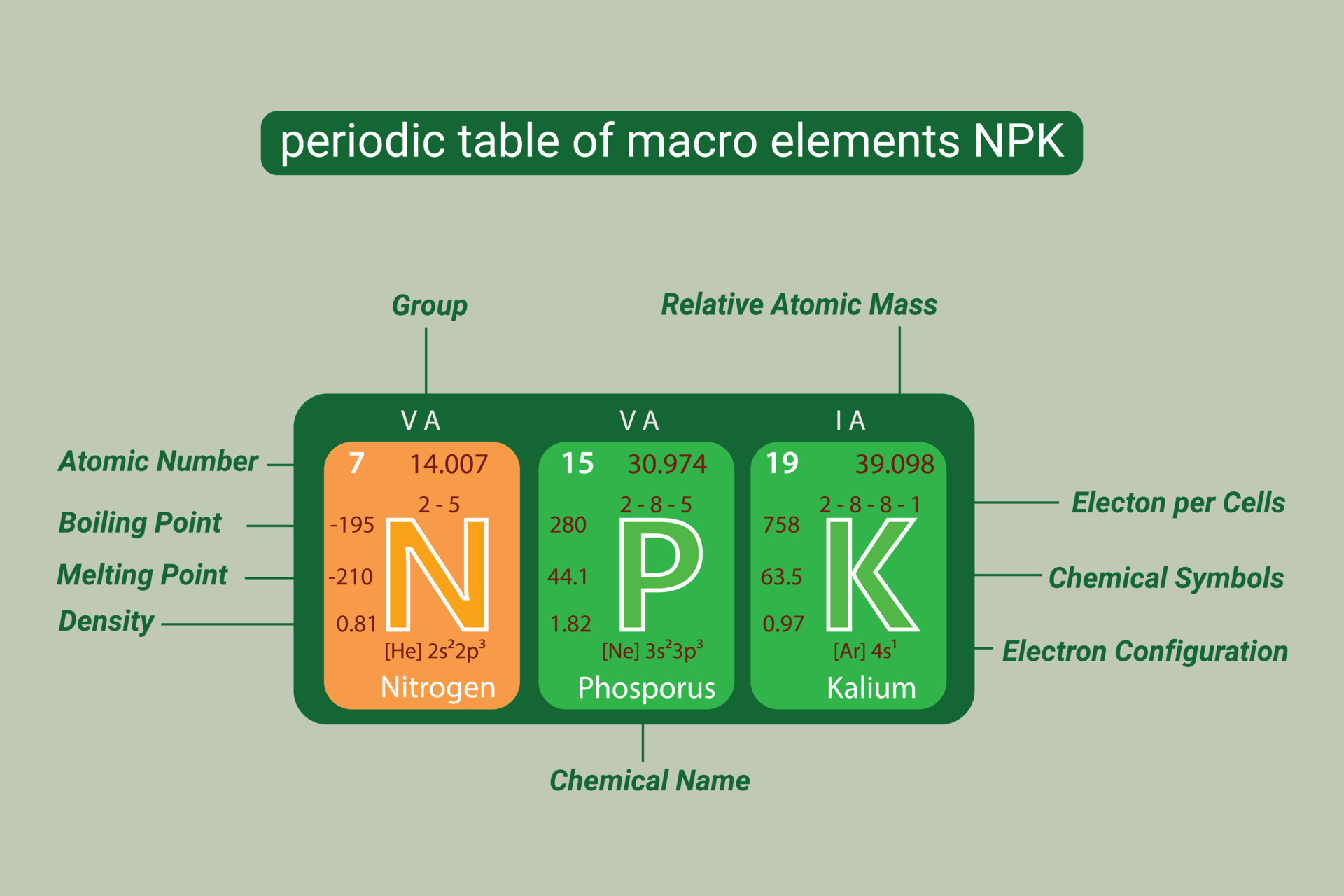
NPK stands for Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium, three essential macronutrients that play a vital role in plant growth and development. Understanding what NPK values mean is crucial for gardeners and farmers to provide their plants with the necessary nutrients for optimal growth. The NPK values are usually displayed on fertilizer labels as a series of three numbers, representing the percentage of each nutrient in the product.
For instance, a fertilizer with an NPK value of 10-10-10 contains 10% nitrogen, 10% phosphorus, and 10% potassium. The remaining 70% consists of other ingredients, such as fillers and micronutrients. Knowing what these numbers represent can help you make informed decisions when selecting fertilizers for your plants.
Nitrogen is responsible for leaf growth and development, phosphorus promotes root growth and flower/fruit production, while potassium helps with overall plant health and resistance to disease. A balanced NPK ratio is essential to ensure that plants receive the necessary nutrients for optimal growth.
When searching for answers to “what does NPK stand for,” it’s essential to consider the specific needs of your plants. Different plants have varying NPK requirements, and using a fertilizer with the wrong ratio can lead to nutrient deficiencies or over-fertilization. By understanding the basics of NPK and its importance in plant growth, you can take the first step towards creating a thriving garden or crop.
In the next section, we’ll delve deeper into the functions of each macronutrient, exploring the roles of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium in plant growth and development.
Breaking Down the Components: Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium Explained
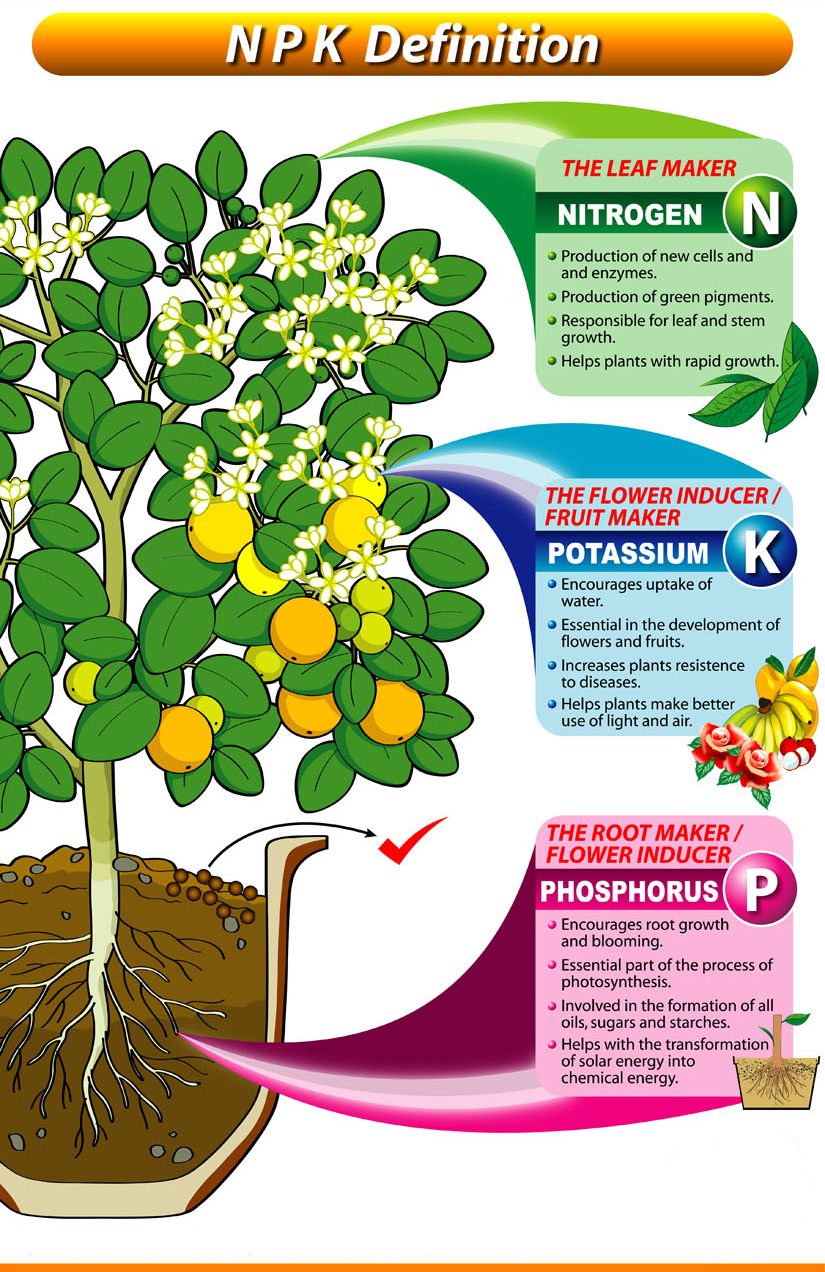
Nitrogen is a critical component of plant growth, playing a key role in the development of leaves, stems, and roots. It is a major building block of amino acids, which are the foundation of proteins. Nitrogen deficiency can lead to stunted growth, yellowing leaves, and reduced yields. On the other hand, excessive nitrogen can cause an overgrowth of foliage, making plants more susceptible to disease and pests.
Phosphorus is essential for root development, flower and fruit production, and overall plant maturation. It plays a crucial role in the transfer of energy within the plant, facilitating the conversion of sunlight into chemical energy. Phosphorus deficiency can lead to stunted root growth, reduced flower and fruit production, and increased susceptibility to disease.
Potassium, also known as potash, is vital for overall plant health and resistance to disease. It helps regulate water balance, maintains cell turgor pressure, and facilitates the transport of nutrients and sugars throughout the plant. Potassium deficiency can lead to weakened plant defenses, increased susceptibility to disease, and reduced yields.
Understanding the functions of each macronutrient is crucial for answering the question “what does NPK stand for” and making informed decisions about fertilizer applications. By recognizing the unique roles of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, gardeners and farmers can optimize their fertilizer blends to meet the specific needs of their plants.
In the next section, we’ll explore the importance of selecting the right NPK ratio for different types of plants, including lawns, flowers, and vegetables.
How to Choose the Right NPK Ratio for Your Plants
Choosing the right NPK ratio for your plants can be a daunting task, especially for those new to gardening or agriculture. However, understanding the specific needs of your plants is crucial for optimal growth and productivity. When selecting a fertilizer, consider the type of plant, soil type, climate, and plant age to determine the ideal NPK ratio.
For lawns, a balanced NPK ratio of 10-10-10 or 20-5-10 is often recommended. This provides the necessary nutrients for healthy grass growth and development. For flowers and vegetables, a slightly higher phosphorus content (such as 15-30-15) can promote blooming and fruiting.
Soil type is also an important factor to consider when selecting an NPK ratio. For example, plants growing in sandy soils may require a higher potassium content to compensate for the soil’s low water-holding capacity. In contrast, plants growing in clay soils may require a lower potassium content to avoid over-fertilization.
Climate is another critical factor to consider when choosing an NPK ratio. In areas with high temperatures and low rainfall, plants may require a higher nitrogen content to promote healthy growth. In areas with cool temperatures and high rainfall, plants may require a lower nitrogen content to avoid over-fertilization.
Plant age is also an important consideration when selecting an NPK ratio. Young seedlings may require a higher phosphorus content to promote root development, while mature plants may require a higher potassium content to promote overall health and resistance to disease.
By considering these factors and choosing the right NPK ratio for your plants, you can optimize their growth and productivity. Remember, understanding what NPK stands for is just the first step – applying this knowledge to your gardening or agricultural practices is key to achieving optimal results.
NPK in Organic vs. Synthetic Fertilizers: What’s the Difference?
When it comes to fertilizers, gardeners and farmers have two main options: organic and synthetic. Both types of fertilizers provide essential nutrients for plant growth, but they differ significantly in terms of their composition, environmental impact, and effects on plant health.
Organic fertilizers are derived from natural sources, such as animal waste, compost, and green manure. These fertilizers release nutrients slowly, providing a steady supply of NPK to plants. Organic fertilizers also promote soil health by increasing the population of beneficial microorganisms and improving soil structure.
Synthetic fertilizers, on the other hand, are manufactured using chemical processes. These fertilizers provide a quick release of NPK, promoting rapid plant growth. However, synthetic fertilizers can also have negative environmental impacts, such as water pollution and soil degradation.
One of the main differences between organic and synthetic fertilizers is their NPK ratio. Organic fertilizers often have a lower NPK ratio, as they release nutrients slowly and promote soil health. Synthetic fertilizers, by contrast, often have a higher NPK ratio, as they provide a quick release of nutrients.
When choosing between organic and synthetic fertilizers, it’s essential to consider the specific needs of your plants and the environmental impact of your choice. Organic fertilizers may be a better option for gardeners and farmers who prioritize soil health and sustainability. Synthetic fertilizers, on the other hand, may be a better option for those who need a quick release of nutrients.
Understanding the differences between organic and synthetic fertilizers can help you make informed decisions about your fertilizer choices. By considering the NPK ratio and environmental impact of your fertilizer, you can promote healthy plant growth and minimize your environmental footprint.
Common NPK Ratios for Popular Plants: A Quick Guide
When it comes to choosing the right NPK ratio for your plants, it can be overwhelming with the numerous options available. To help you get started, here’s a quick guide to common NPK ratios for popular plants:
For lawns, a balanced NPK ratio of 10-10-10 or 20-5-10 is often recommended. This provides the necessary nutrients for healthy grass growth and development.
For flowers, a slightly higher phosphorus content (such as 15-30-15) can promote blooming and fruiting. This is especially true for plants like roses, which require a lot of phosphorus to produce plenty of blooms.
For vegetables, a balanced NPK ratio of 10-10-10 or 20-20-20 is often recommended. This provides the necessary nutrients for healthy plant growth and development.
Some popular fertilizers and their corresponding NPK ratios include:
- Miracle-Gro: 24-8-16
- Scotts Osmocote: 14-14-14
- Espoma Organic Bloom!: 5-3-4
Keep in mind that these are just general guidelines, and the specific NPK ratio required by your plants may vary depending on factors like soil type, climate, and plant age.
By using these common NPK ratios as a starting point, you can customize your fertilizer blend to meet the specific needs of your plants. Remember to always read the label and follow the instructions carefully to ensure optimal results.
Maximizing NPK Uptake: Tips for Efficient Fertilizer Use
To maximize NPK uptake and ensure efficient fertilizer use, it’s essential to consider several factors. Here are some expert tips to help you optimize your fertilizer application:
Soil Preparation: Before applying fertilizer, make sure the soil is well-prepared. This includes loosening the soil to a depth of 8-10 inches, removing any debris or rocks, and incorporating organic matter like compost or manure.
Application Timing: The timing of fertilizer application is critical. For most plants, it’s best to apply fertilizer during the growing season when the plant is actively producing new growth. Avoid applying fertilizer during periods of drought or extreme weather conditions.
Complementary Nutrient Use: In addition to NPK, other nutrients like calcium, magnesium, and sulfur are also essential for plant growth. Consider using complementary nutrients to provide a balanced fertilizer program.
Soil pH Management: Soil pH can significantly impact NPK uptake. Most plants prefer a slightly acidic to neutral soil pH (between 6.0 and 7.0). Adjusting the soil pH can help optimize NPK uptake and ensure efficient fertilizer use.
Water Management: Adequate water supply is essential for NPK uptake. Ensure that the soil is consistently moist but not waterlogged, as this can lead to nutrient leaching and reduced fertilizer efficiency.
By following these tips, you can maximize NPK uptake and ensure efficient fertilizer use. Remember to always read the label and follow the instructions carefully to ensure optimal results.
Monitoring and Adjusting NPK Levels: A Key to Healthy Plant Growth
Regular soil testing and NPK level monitoring are crucial for maintaining healthy plant growth. By monitoring NPK levels, you can adjust fertilizer applications to ensure optimal plant nutrition.
Soil testing can be done using a variety of methods, including laboratory analysis and DIY soil testing kits. These tests can provide valuable information on soil pH, nutrient levels, and other factors that affect plant growth.
When interpreting soil test results, look for the following:
- Nitrogen levels: Aim for a nitrogen level between 10-20 ppm (parts per million) for most plants.
- Phosphorus levels: Aim for a phosphorus level between 5-10 ppm for most plants.
- Potassium levels: Aim for a potassium level between 10-20 ppm for most plants.
Based on the test results, adjust fertilizer applications to ensure optimal NPK levels. For example, if the soil test reveals low nitrogen levels, consider applying a nitrogen-rich fertilizer.
Plant responses can also provide valuable information on NPK levels. Look for signs of nutrient deficiency or excess, such as:
- Yellowing leaves (nitrogen deficiency)
- Purple or red leaves (phosphorus deficiency)
- Weak or spindly growth (potassium deficiency)
By monitoring NPK levels and adjusting fertilizer applications accordingly, you can ensure optimal plant growth and maximize yields.
Conclusion: Mastering NPK for a Thriving Garden or Crop
Understanding NPK and its role in plant growth is crucial for achieving optimal results in gardening and agriculture. By grasping the basics of NPK and its importance in plant nutrition, you can make informed decisions about fertilizer applications and ensure healthy plant growth.
Remember, NPK is just one part of the equation. Other factors like soil type, climate, and plant age also play a significant role in determining the optimal NPK ratio for your plants.
By applying the knowledge and tips outlined in this article, you can unlock the secrets of fertilizer labels and take your gardening or agricultural practices to the next level. Whether you’re a seasoned pro or just starting out, mastering NPK is key to achieving a thriving garden or crop.
So, the next time you’re faced with a fertilizer label, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge to decipher the code and make informed decisions about NPK applications. Happy gardening!