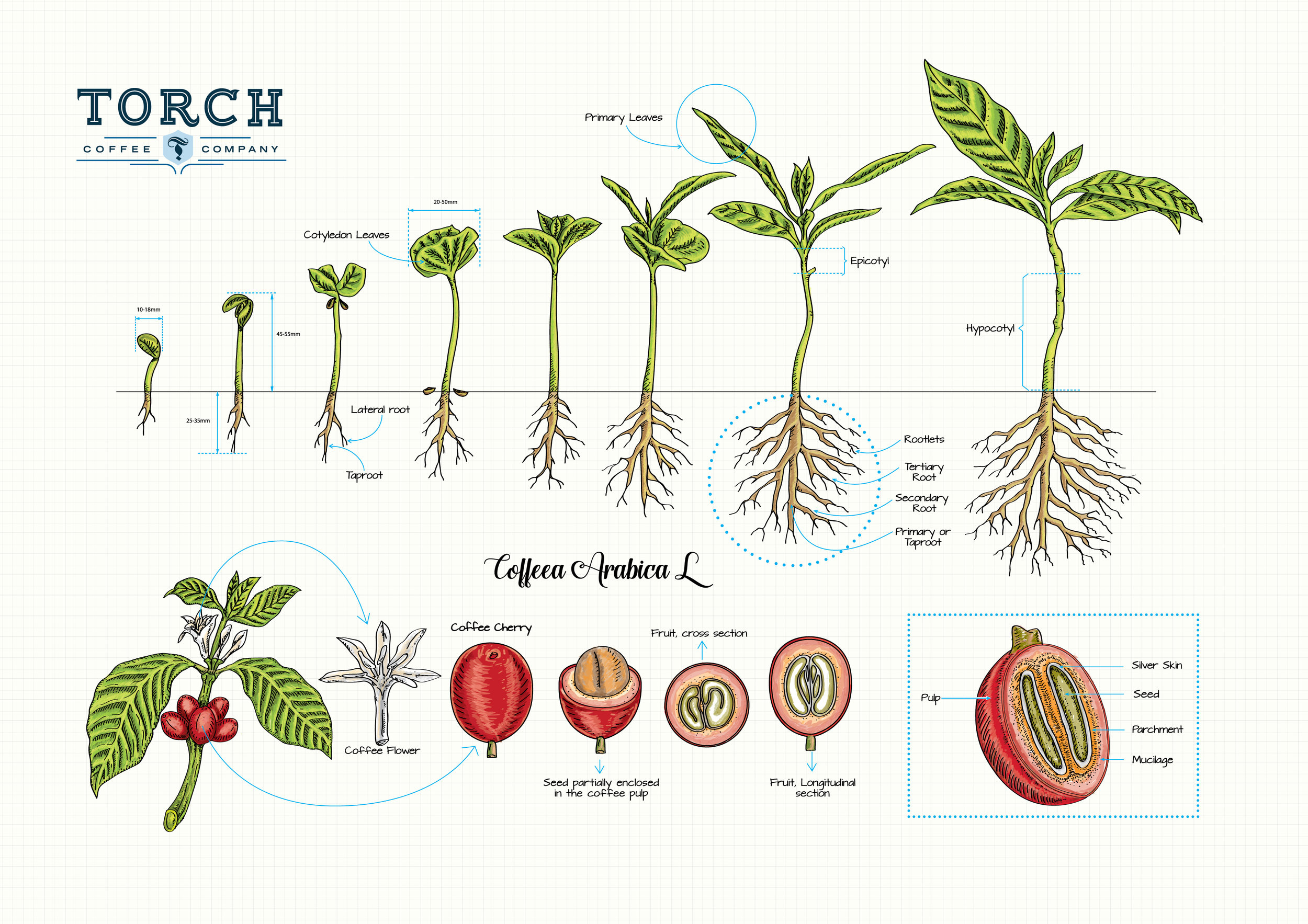
Understanding the Coffee Plant: A Brief Overview
Coffee plants are the foundation of the coffee industry, and understanding their unique characteristics is essential to appreciating the journey of coffee beans from seed to cup. Native to tropical regions of Africa and Asia, coffee plants belong to the genus Coffea, with over 100 species identified. However, only two main species, Arabica (Coffea arabica) and Robusta (Coffea canephora), account for approximately 98% of global coffee production.
Coffee plants are evergreen shrubs or small trees that thrive in regions with mild temperatures, high altitudes, and well-defined wet and dry seasons. They require specific conditions to grow, including average temperatures between 15°C and 25°C (59°F and 77°F), annual rainfall of at least 1,500 mm (60 in), and altitudes between 600 and 2,500 meters (2,000 and 8,200 ft) above sea level.
Coffee plants are typically cultivated on plantations or smallholder farms, where they are carefully nurtured to optimize yields and quality. Farmers employ various techniques to promote healthy growth, including pruning, fertilization, and pest management. By understanding the unique needs and characteristics of coffee plants, farmers can optimize their growing conditions, ultimately affecting the flavor and quality of the coffee beans.
As we explore the journey of coffee beans, it’s essential to recognize the significance of coffee plants as the starting point. By grasping the basics of coffee plant cultivation, we can better appreciate the complexities involved in growing high-quality coffee beans. Whether you’re a coffee connoisseur or simply interested in learning more about the coffee-making process, understanding the coffee plant is a crucial step in discovering how are coffee beans grown.
How to Grow Coffee: The Ideal Climate and Conditions
Coffee plants require a specific set of climate and environmental conditions to thrive. The ideal temperature for coffee production ranges from 15°C to 25°C (59°F to 77°F), with average temperatures between 18°C and 22°C (64°F to 72°F) being optimal. Temperatures above 30°C (86°F) can lead to stress, while temperatures below 10°C (50°F) can cause damage to the plant.
Altitude also plays a crucial role in coffee production, with most coffee plants grown at high altitudes between 600 and 2,500 meters (2,000 and 8,200 ft) above sea level. High altitudes provide the necessary cooler temperatures, well-defined wet and dry seasons, and rich soil conditions that coffee plants require. However, high altitudes can also lead to slower maturation rates and lower yields.
Rainfall is another critical factor in coffee production, with most coffee plants requiring annual rainfall of at least 1,500 mm (60 in). Well-distributed rainfall throughout the year ensures consistent growth and development, while droughts can lead to stress and reduced yields. In regions with inadequate rainfall, irrigation systems are often used to supplement the water needs of the coffee plants.
Understanding the ideal climate and conditions required for growing coffee plants is essential to appreciating how are coffee beans grown. By replicating these conditions, coffee farmers can optimize yields, improve quality, and reduce the environmental impact of coffee production. Whether you’re a coffee enthusiast or simply interested in learning more about the coffee-making process, recognizing the importance of climate and conditions is a crucial step in understanding the journey of coffee beans from seed to cup.
In addition to temperature, altitude, and rainfall, other factors such as soil type, sunlight, and wind also play a role in coffee production. Coffee plants prefer well-draining, acidic soils with a pH between 5.5 and 6.5. Adequate sunlight is also essential, with most coffee plants requiring at least 1,000 hours of direct sunlight per year. Wind can also impact coffee production, with strong winds potentially damaging the plants and reducing yields.
The Coffee Bean Growing Process: From Flowering to Harvesting
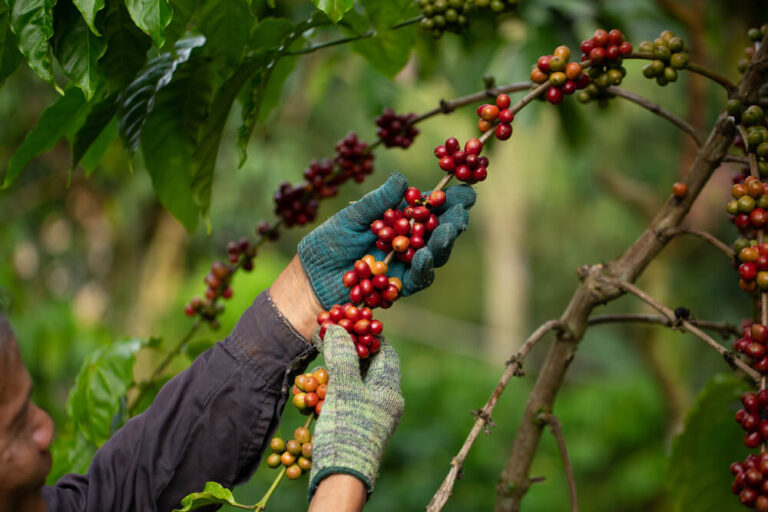
Coffee plants produce small, white, fragrant flowers that last for a few days. After flowering, the plants produce coffee cherries, which are small, red or yellow fruits that contain two seeds – the coffee beans. The coffee cherry is the fruit of the coffee plant, and it’s the seeds inside that are harvested and processed to become the coffee beans we use to make coffee.
The coffee cherry grows and matures over the next several months, turning from green to yellow, orange, and finally red. The cherries are typically ready to be harvested between 7 and 9 months after flowering. There are several methods of harvesting coffee cherries, including strip picking, where all the cherries are removed from the plant at once, and selective picking, where only the ripe cherries are picked.
After harvesting, the coffee cherries are processed to extract the coffee beans. This involves removing the outer skin and pulp of the cherry, and then washing and drying the beans to remove any remaining moisture. The beans are then hulled to remove the parchment layer, leaving just the green coffee bean.
Understanding the coffee bean growing process is essential to appreciating how are coffee beans grown. From flowering to harvesting, the coffee plant requires careful attention and nurturing to produce high-quality coffee beans. By recognizing the importance of each stage of the process, coffee farmers and producers can optimize yields, improve quality, and reduce the environmental impact of coffee production.
The processing stage is critical in determining the flavor and quality of the coffee beans. Different processing methods, such as washed, natural, or honey processing, can result in distinct flavor profiles and aromas. The processing method used can also impact the environmental sustainability of coffee production, with some methods requiring more water and energy than others.
Coffee Farming Methods: Traditional vs. Modern Techniques
Coffee farming methods have evolved over the years, with traditional and modern techniques being used to cultivate coffee plants. Traditional coffee farming methods involve growing coffee plants under a canopy of shade trees, which provides a natural habitat for the plants and helps to maintain soil health. This method is often referred to as shade-grown coffee.
Modern coffee farming methods, on the other hand, involve growing coffee plants in full sun, without the use of shade trees. This method is often referred to as sun-grown coffee. Sun-grown coffee is more common in regions with high altitudes and cooler temperatures, where the risk of disease and pests is lower.
Another distinction between traditional and modern coffee farming methods is the use of organic vs. conventional farming practices. Organic coffee farming involves using natural methods to control pests and diseases, and to fertilize the soil. Conventional coffee farming, on the other hand, involves using synthetic fertilizers and pesticides to control pests and diseases.
The choice of coffee farming method can have a significant impact on the flavor and quality of the coffee beans. Shade-grown coffee, for example, is often described as having a more complex flavor profile, with notes of fruit and chocolate. Sun-grown coffee, on the other hand, is often described as having a brighter, more acidic flavor.
Understanding the different coffee farming methods is essential to appreciating how are coffee beans grown. By recognizing the pros and cons of each method, coffee farmers and producers can make informed decisions about which method to use, and how to optimize their yields and quality.
In addition to the flavor and quality of the coffee beans, the choice of coffee farming method can also have a significant impact on the environment. Organic coffee farming, for example, is often more environmentally friendly, as it avoids the use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides. Shade-grown coffee, on the other hand, can help to maintain biodiversity and protect the natural habitat of the coffee plants.
The Role of Coffee Farmers: Challenges and Opportunities
Coffee farmers play a vital role in the coffee production process, and their work is essential to the quality and flavor of the coffee beans. However, coffee farmers face numerous challenges, including climate change, pests, and diseases, which can impact the yield and quality of their crops.
Climate change is one of the biggest challenges facing coffee farmers today. Rising temperatures and changing weather patterns can lead to droughts, floods, and other extreme weather events that can damage coffee crops. Additionally, climate change can also lead to the spread of pests and diseases, which can further impact coffee yields.
Despite these challenges, there are also opportunities for coffee farmers to improve their livelihoods and contribute to sustainable coffee production. One way to do this is through sustainable farming practices, such as shade-grown coffee and organic farming. These practices can help to reduce the environmental impact of coffee production, while also improving the quality and flavor of the coffee beans.
Another opportunity for coffee farmers is to participate in fair trade and sustainable coffee certification programs. These programs can provide coffee farmers with a higher price for their coffee, as well as access to training and technical assistance to improve their farming practices.
Understanding the role of coffee farmers and the challenges they face is essential to appreciating how are coffee beans grown. By recognizing the importance of coffee farmers and the challenges they face, we can work to support sustainable and equitable coffee production, and ensure that coffee farmers receive a fair price for their coffee.
In addition to the challenges and opportunities facing coffee farmers, it’s also important to recognize the impact of coffee production on the environment. Coffee production can have a significant impact on the environment, including deforestation, water pollution, and soil degradation. However, sustainable coffee production practices can help to reduce this impact, and promote environmental sustainability.
Processing and Exporting Coffee Beans: The Next Steps
After harvesting, coffee beans undergo a series of processing steps to prepare them for export. The first step is pulping, which involves removing the outer skin and pulp of the coffee cherry. This is typically done using a machine, which helps to speed up the process and improve efficiency.
Next, the coffee beans are fermented, which involves breaking down the mucilage (a sticky substance) that covers the beans. This process can take anywhere from a few hours to a few days, depending on the type of coffee and the desired flavor profile.
After fermentation, the coffee beans are washed to remove any remaining pulp and mucilage. This helps to improve the flavor and aroma of the coffee, and also makes it easier to dry the beans.
The coffee beans are then dried to a moisture level of around 11%, either by machine or by sun drying. Sun drying is a traditional method that involves spreading the coffee beans out in the sun, while machine drying uses a machine to speed up the process.
Once the coffee beans are dry, they are hulled to remove the parchment layer, leaving just the green coffee bean. The beans are then sorted and graded according to size and quality, and packaged for export.
There are several types of coffee beans, each with its own unique characteristics and flavor profile. Arabica beans, for example, are known for their mild and nuanced flavor, while Robusta beans are often used as a base for instant coffee.
Understanding the processing and exporting steps involved in coffee production is essential to appreciating how are coffee beans grown. By recognizing the importance of each step, coffee producers can optimize their processes and improve the quality of their coffee.
In addition to the processing and exporting steps, it’s also important to consider the role of certifications and standards in the coffee industry. Certifications such as Fairtrade and Organic can help to ensure that coffee is produced in a sustainable and equitable way, while standards such as ISO 9001 can help to ensure that coffee is produced to a high quality.
From Bean to Cup: The Journey of Specialty Coffee
Specialty coffee is a term used to describe high-quality coffee beans that have been carefully selected, roasted, and brewed to bring out their unique flavor and aroma. The journey of specialty coffee from the farm to the cup is a complex one, involving several steps that require great care and attention to detail.
The first step in the journey of specialty coffee is the selection of high-quality coffee beans. This involves carefully evaluating the beans for their flavor, aroma, and acidity, as well as their origin and processing methods. Specialty coffee beans are typically grown at high altitudes, where the cooler temperatures and well-defined wet and dry seasons allow for a slower maturation process, resulting in a more complex flavor profile.
Once the coffee beans have been selected, they are roasted to bring out their unique flavor and aroma. Roasting involves heating the beans to a high temperature, which causes them to expand in size and change color. The roasting process can greatly affect the flavor of the coffee, with lighter roasts having a more acidic and fruity flavor, and darker roasts having a richer and more bitter flavor.
After roasting, the coffee beans are ground and brewed to create the perfect cup of coffee. The brewing process involves extracting the flavors and oils from the coffee beans using hot water, and can be done using a variety of methods, including pour-over, French press, and espresso.
The final step in the journey of specialty coffee is the serving and enjoyment of the coffee. This involves carefully pouring the coffee into a cup, and adding any desired sweeteners or creamers. The flavor and aroma of the coffee can be greatly affected by the serving method, with some methods bringing out the nuances of the coffee more than others.
Understanding the journey of specialty coffee from the farm to the cup is essential to appreciating how are coffee beans grown. By recognizing the importance of each step in the process, coffee producers and consumers can work together to create high-quality coffee that is both delicious and sustainable.
In addition to the steps involved in the journey of specialty coffee, it’s also important to consider the role of certifications and standards in the specialty coffee industry. Certifications such as Fairtrade and Organic can help to ensure that coffee is produced in a sustainable and equitable way, while standards such as the Specialty Coffee Association’s Cupping Protocol can help to ensure that coffee is evaluated and graded in a consistent and fair manner.
Sustainable Coffee Production: The Future of Coffee
Sustainable coffee production is crucial for the long-term viability of the coffee industry. As the world’s demand for coffee continues to grow, it is essential to adopt practices that minimize the environmental impact of coffee production, ensure fair labor conditions, and promote social responsibility. Sustainable coffee production not only benefits the environment and farmers but also contributes to the quality and flavor of the coffee beans.
One of the primary concerns in sustainable coffee production is the environmental impact of coffee farming. Coffee plants require large amounts of water, fertilizers, and pesticides, which can lead to soil degradation, water pollution, and loss of biodiversity. To mitigate these effects, many coffee farmers are adopting sustainable practices such as shade-grown coffee, organic farming, and rainwater harvesting. These methods not only reduce the environmental footprint of coffee production but also promote ecosystem services and biodiversity.
Another critical aspect of sustainable coffee production is social responsibility. Coffee farmers, particularly small-scale producers, often face challenges such as low prices, limited access to markets, and poor working conditions. Sustainable coffee production initiatives, such as Fairtrade and Organic certifications, aim to address these issues by providing fair prices, improving working conditions, and promoting social justice.
In addition to environmental and social benefits, sustainable coffee production also contributes to the quality and flavor of the coffee beans. Sustainable farming practices, such as using natural fertilizers and pest control methods, can result in more complex and nuanced flavor profiles. Moreover, sustainable coffee production often involves careful processing and handling methods, which can enhance the overall quality of the coffee beans.
Several initiatives and certifications promote sustainable coffee production, including the Rainforest Alliance, 4C Association, and UTZ Certified. These programs provide guidelines and standards for sustainable coffee production, ensuring that coffee farmers adhere to environmentally friendly and socially responsible practices.
As consumers become increasingly aware of the environmental and social impact of their purchasing decisions, the demand for sustainable coffee is growing. By choosing sustainable coffee, consumers can contribute to a more equitable and environmentally friendly coffee industry. Moreover, sustainable coffee production can help ensure the long-term viability of the coffee industry, providing a secure future for coffee farmers and the environment.
In the context of how coffee beans are grown, sustainable production methods play a vital role in maintaining the quality and flavor of the coffee beans. By adopting sustainable practices, coffee farmers can reduce their environmental footprint, promote social responsibility, and contribute to the overall quality of the coffee beans. As the coffee industry continues to evolve, sustainable coffee production will become increasingly important for ensuring a bright future for coffee lovers around the world.