Understanding Pomegranate Tree Pollination: A Key to Abundant Harvests
Pollination plays a vital role in the fruiting success of pomegranate trees. Without proper pollination, pomegranate trees may fail to produce fruit or yield poorly, resulting in significant losses for farmers and gardeners. The question of whether pomegranate trees are self-pollinating is a common one, and understanding the answer is crucial for optimizing fruit production. While some pomegranate varieties are capable of self-pollination, many others require cross-pollination to produce fruit. In fact, research suggests that cross-pollination can increase fruit set and improve fruit quality in pomegranate trees. By grasping the intricacies of pomegranate tree pollination, growers can take steps to ensure a bountiful harvest.
Are Pomegranate Trees Self-Pollinating? Debunking the Myth
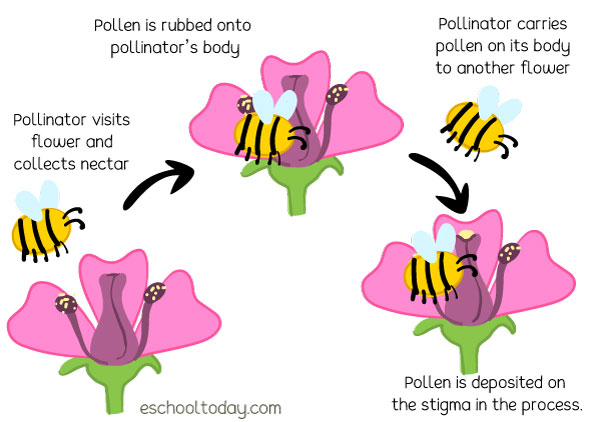
The question of whether pomegranate trees are self-pollinating is a common one, and the answer is not a simple yes or no. While some pomegranate varieties are capable of self-pollination, many others require cross-pollination to produce fruit. In fact, research suggests that only about 20% of pomegranate varieties are truly self-pollinating, with the remaining 80% requiring cross-pollination. This is because pomegranate trees have a complex reproductive system, with both male and female flowers present on the same tree. However, the male flowers often do not produce enough pollen to effectively pollinate the female flowers, making cross-pollination necessary. Bees and other pollinators play a crucial role in pomegranate pollination, transferring pollen from the male flowers to the female flowers. Without these pollinators, pomegranate trees would be unable to produce fruit. So, while some pomegranate trees may be self-pollinating, the majority require cross-pollination to thrive.
How to Ensure Proper Pollination for Your Pomegranate Tree
To ensure proper pollination for your pomegranate tree, it’s essential to create an environment that fosters healthy pollinator activity and optimal tree health. One of the most effective ways to promote pollination is by attracting pollinators, such as bees, butterflies, and hummingbirds, to your tree. This can be achieved by planting a diverse range of flowers that provide nectar and pollen, such as lavender, sunflowers, and coneflowers, around the base of your pomegranate tree. Additionally, consider incorporating a pollinator-friendly herb garden, featuring herbs like mint, oregano, and thyme, which are known to attract beneficial insects. Pruning your pomegranate tree regularly can also help improve air circulation and sunlight penetration, making it easier for pollinators to access the flowers. Furthermore, maintaining healthy soil with adequate nutrients, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, is crucial for supporting the overall health and fertility of your pomegranate tree. By implementing these strategies, you can create an ideal environment for pollination to occur, leading to a bountiful harvest of juicy, flavorful pomegranates.
The Benefits of Cross-Pollination in Pomegranate Trees
Cross-pollination is a crucial aspect of pomegranate tree cultivation, offering numerous benefits that can significantly impact fruit production and tree health. One of the primary advantages of cross-pollination is increased fruit set, as it allows for a more diverse range of genetic material to be introduced into the tree. This, in turn, can lead to a greater number of fruiting bodies and a more abundant harvest. Additionally, cross-pollination has been shown to improve fruit quality, with fruits produced through cross-pollination often exhibiting enhanced flavor, texture, and color. Furthermore, cross-pollination can also enhance tree health by promoting genetic diversity, which can help to reduce the risk of disease and pests. By incorporating multiple pomegranate tree varieties into your orchard or garden, you can create an environment that fosters cross-pollination, leading to a more resilient and productive tree. While some pomegranate trees may be self-pollinating, the benefits of cross-pollination make it a valuable strategy for maximizing fruit production and tree health.
Choosing the Right Pomegranate Tree Variety for Your Climate
Selecting the right pomegranate tree variety is crucial for successful fruit production, as different varieties have unique characteristics, growth habits, and pollination requirements. When choosing a pomegranate tree variety, it’s essential to consider the climate and region you’re in, as well as the specific growing conditions of your orchard or garden. For example, varieties like ‘Wonderful’ and ‘Granada’ are well-suited for warm and dry climates, while ‘Fuyu’ and ‘Karo’ are more tolerant of cooler temperatures and humidity. Additionally, some pomegranate tree varieties, such as ‘Eversweet’ and ‘Sierra’, are self-fertile, but still benefit from cross-pollination, while others, like ‘Wonderful’ and ‘Granada’, require cross-pollination for optimal fruit set. By selecting a pomegranate tree variety that is well-suited to your climate and region, you can ensure optimal growth, fruit production, and pollination. It’s also important to consider factors such as disease resistance, pest tolerance, and fruit quality when making your selection. By doing so, you can create an ideal environment for your pomegranate tree to thrive and produce an abundant harvest.
Pomegranate Tree Care Essentials: Beyond Pollination
While pollination is a critical aspect of pomegranate tree care, it’s essential to remember that it’s just one part of the overall care equation. To ensure optimal fruit production and tree health, it’s necessary to provide your pomegranate tree with the right conditions and care practices. Watering is a critical aspect of pomegranate tree care, and trees should be watered regularly, especially during the first year after planting. Fertilization is also essential, with a balanced fertilizer applied annually to promote healthy growth and fruit production. Pest management is another crucial aspect of pomegranate tree care, with common pests like aphids, whiteflies, and mealybugs requiring regular monitoring and control. Pruning is also vital, with regular pruning helping to maintain tree shape, promote air circulation, and encourage fruiting. Additionally, soil management is critical, with pomegranate trees preferring well-draining soil with a pH between 6.0 and 7.0. By combining these essential care practices with effective pollination strategies, you can create an ideal environment for your pomegranate tree to thrive and produce an abundant harvest.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Pomegranate Tree Pollination
While pomegranate trees are relatively low-maintenance, there are some common mistakes that can hinder pollination and ultimately affect fruit production. One of the most critical mistakes is inadequate pollinator attraction. Pomegranate trees rely heavily on bees and other pollinators to facilitate pollination, so it’s essential to create an environment that attracts these beneficial insects. This can be achieved by planting a diverse range of flowers that provide a source of nectar and pollen, as well as avoiding the use of pesticides that can harm pollinators. Poor tree spacing is another common mistake that can impact pollination. Pomegranate trees should be planted at a distance of around 15-20 feet apart to allow for adequate air circulation and sunlight penetration, which can help promote healthy growth and fruit production. Insufficient soil nutrients are also a common mistake that can affect pollination. Pomegranate trees require a balanced diet of nutrients to produce healthy flowers and fruit, so it’s essential to regularly test soil pH and nutrient levels and adjust accordingly. By avoiding these common mistakes, you can create an ideal environment for your pomegranate tree to thrive and produce an abundant harvest.
Maximizing Pomegranate Fruit Production: A Holistic Approach
When it comes to achieving abundant fruit production in pomegranate trees, a comprehensive approach is essential. While pollination plays a critical role in fruit set, it’s just one piece of the puzzle. To maximize fruit production, it’s necessary to consider the interplay between pollination, tree health, and environmental factors. By understanding the complex relationships between these factors, growers can create an ideal environment for their pomegranate trees to thrive. This includes providing optimal growing conditions, such as adequate sunlight, water, and nutrients, as well as implementing effective pest management and pruning strategies. Additionally, selecting the right pomegranate tree variety for your climate and region can also impact fruit production. By taking a holistic approach to pomegranate tree care, growers can optimize fruit production, improve fruit quality, and enhance overall tree health. Remember, pollination is just the starting point – by considering the bigger picture, you can unlock the full potential of your pomegranate tree and enjoy a bountiful harvest.






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/155351657-56a98c8c3df78cf772a82cd7.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/pomegranate-growing-tips-3269232-hero-f9849529ed6644168d8dc22232e857c2.jpg)