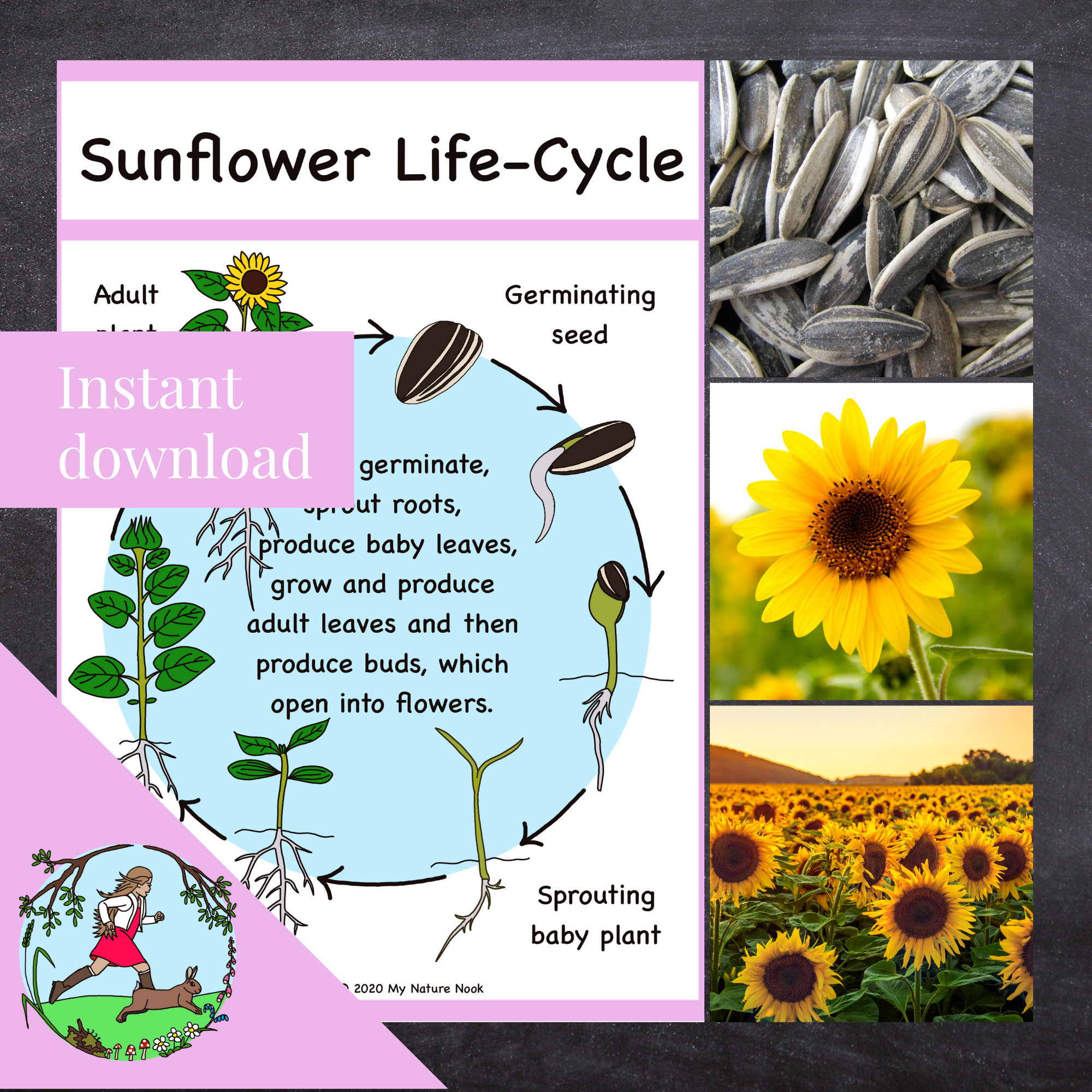
Understanding the Life Cycle of Sunflowers
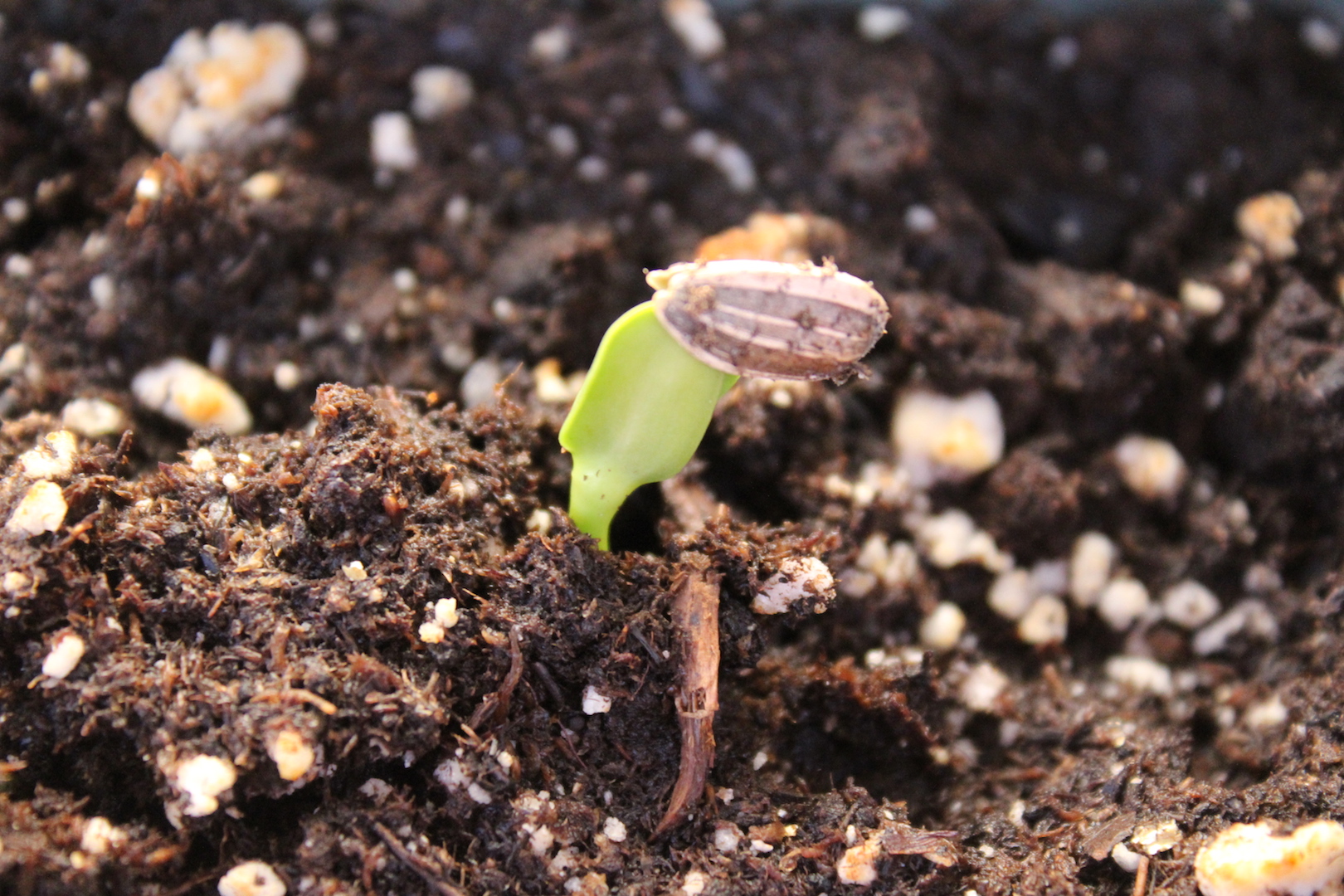
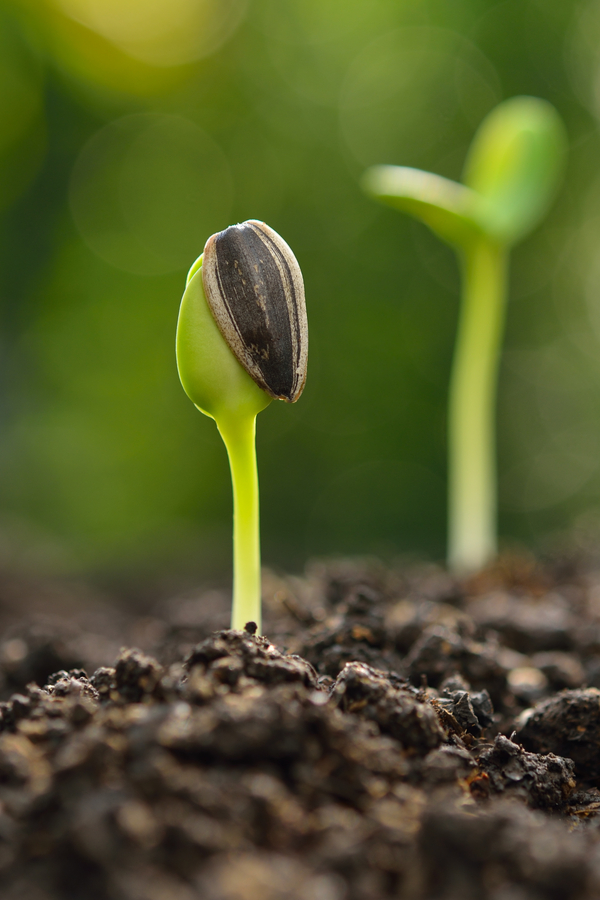
Sunflowers, scientifically known as Helianthus annuus, undergo a unique life cycle that spans several stages. From germination to maturity, understanding these stages is crucial in determining the best time to plant sunflower seeds. The life cycle of sunflowers can be broadly divided into seven stages: seed germination, seedling emergence, vegetative growth, bud formation, flowering, seed production, and maturity. Each stage has its own set of requirements and conditions that need to be met for optimal growth. For instance, during the germination stage, sunflower seeds require adequate moisture and a suitable temperature to break dormancy. Similarly, during the vegetative growth stage, sunflowers need sufficient sunlight, water, and nutrients to develop strong stems and leaves. By grasping the intricacies of the sunflower life cycle, gardeners can better plan and prepare for the best time to plant sunflower seeds, ensuring a successful harvest. This knowledge is essential in determining the ideal time to plant sunflower seeds, as it allows gardeners to synchronize their planting with the optimal growth stages of the sunflower.
Climate and Weather Considerations for Sunflower Planting
When it comes to planting sunflowers, climate and weather conditions play a significant role in determining the best time to plant sunflower seeds. Sunflowers are warm-season crops that thrive in temperatures between 65°F and 95°F (18°C and 35°C). They require full sun and well-drained soil to grow optimally. In regions with a short growing season, it’s essential to choose a variety that matures quickly, typically within 60 days. In areas with a longer growing season, gardeners can opt for taller, more robust varieties that take around 90 days to mature. Understanding the local climate and weather patterns is crucial in determining the best time to plant sunflower seeds, as it allows gardeners to synchronize their planting with the optimal growth stages of the sunflower. For instance, in regions with a high risk of frost, it’s best to wait until the last frost date has passed before planting sunflower seeds. In areas with a hot and dry climate, it’s essential to plant sunflowers in the early spring or late summer to avoid the intense heat. By considering the climate and weather conditions, gardeners can increase their chances of success and enjoy a bountiful harvest of sunflowers.
How to Prepare Your Soil for Sunflower Planting
Before planting sunflower seeds, it’s essential to prepare the soil to ensure optimal growth. Sunflowers prefer well-draining, fertile soil with a pH between 6.0 and 7.0. To achieve this, gardeners should test their soil to determine its pH level and nutrient content. Based on the test results, amendments such as compost, manure, or fertilizers can be added to adjust the pH and provide necessary nutrients. Additionally, sunflowers require a soil temperature of at least 60°F (15°C) to germinate, so it’s crucial to wait until the soil has warmed up before planting. To further improve soil quality, gardeners can incorporate organic matter such as straw or grass clippings into the soil. This helps to increase the soil’s water-holding capacity, reduce soil temperature fluctuations, and provide a habitat for beneficial microorganisms. By preparing the soil properly, gardeners can create an ideal environment for their sunflowers to thrive, ultimately leading to a successful harvest. When determining the best time to plant sunflower seeds, soil preparation is a critical factor to consider, as it sets the stage for healthy growth and development.
The Ideal Time to Plant Sunflower Seeds in Different Regions
Determining the best time to plant sunflower seeds varies depending on the region, climate, and growing season. In general, sunflowers thrive in warm weather, making spring and early summer the ideal times to plant. However, the specific planting time depends on the region’s last frost date, growing season, and climate zone. In areas with a short growing season, such as the northern United States and Canada, it’s best to plant sunflower seeds in late spring to early summer, when the soil has warmed up and the risk of frost has passed. In regions with a longer growing season, such as the southern United States, sunflower seeds can be planted in early spring or late summer. In areas with a Mediterranean climate, such as California and the Southwest, sunflowers can be planted in the fall, as the cooler temperatures and increased moisture promote healthy growth. By understanding the specific climate and growing conditions of their region, gardeners can choose the best time to plant sunflower seeds, ensuring a successful harvest. For example, in the Midwest, the best time to plant sunflower seeds is in late May to early June, while in the Northeast, it’s best to plant in early June. By planting at the right time, gardeners can increase their chances of success and enjoy a bountiful harvest of sunflowers.
Spring vs. Fall Planting: Which is Best for Sunflowers?
When it comes to planting sunflowers, gardeners often debate whether to plant in the spring or fall. Both seasons have their advantages and disadvantages, and the best time to plant sunflower seeds depends on various factors, including climate, soil temperature, and pest management. In the spring, the soil is typically cooler, and the air is filled with moisture, making it an ideal time to plant sunflowers. The cooler temperatures and increased moisture help to promote healthy growth and reduce the risk of pests and diseases. Additionally, spring-planted sunflowers tend to grow taller and produce larger blooms. On the other hand, fall planting can be beneficial in regions with hot summers, as the cooler temperatures and reduced humidity help to reduce stress on the plants. Fall-planted sunflowers also tend to mature more quickly, allowing for a faster harvest. However, fall planting can be risky in areas with early frosts, as the plants may not have enough time to mature before the first frost. Ultimately, the best time to plant sunflower seeds depends on the specific climate and growing conditions of the region. By understanding the advantages and disadvantages of spring and fall planting, gardeners can choose the best time to plant sunflower seeds and maximize their chances of success. For example, in regions with a long growing season, spring planting may be the best option, while in areas with hot summers, fall planting may be more suitable. By planting at the right time, gardeners can ensure a successful harvest and enjoy the beauty of sunflowers in their garden.
Getting a Head Start: Sowing Sunflower Seeds Indoors
Starting sunflower seeds indoors can give them a head start on the growing season, allowing them to get a jumpstart on the weather and pests. To sow sunflower seeds indoors, you’ll need a few simple materials, including seed starting mix, small pots or cell trays, and a warm location with indirect light. Begin by filling the pots or cell trays with seed starting mix, and then plant one or two sunflower seeds about 1 inch deep in each pot. Water the soil gently but thoroughly, and then place the pots in a warm location with indirect light. The ideal temperature for germinating sunflower seeds is between 70°F and 80°F (21°C and 27°C). Keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged, and make sure the pots have good drainage. It typically takes 7-10 days for sunflower seeds to germinate indoors. Once the seeds have germinated, move the pots to a sunny location, such as a south-facing window or under grow lights. Continue to care for the seedlings indoors for 2-3 weeks, or until the danger of frost has passed in your area. At this point, you can transplant the seedlings outdoors, hardening them off first by gradually exposing them to outdoor conditions over the course of 7-10 days. By starting sunflower seeds indoors, you can get a head start on the growing season and increase your chances of success. This is especially important in regions with short growing seasons or unpredictable weather patterns. By giving your sunflowers a strong start, you can ensure a healthy and productive harvest.
Avoiding Common Mistakes When Planting Sunflower Seeds
When it comes to planting sunflower seeds, there are several common mistakes that can hinder their growth and reduce yields. One of the most critical mistakes is planting too early or too late. Planting sunflower seeds too early, before the last frost date, can expose them to frost damage or kill them altogether. On the other hand, planting too late can result in reduced growth and lower yields. To avoid this mistake, it’s essential to determine the best time to plant sunflower seeds in your region, taking into account the last frost date, growing season, and climate zone. Another common mistake is not preparing the soil properly before planting. Sunflowers require well-draining, fertile soil with a pH between 6.0 and 7.0. Failure to prepare the soil can lead to poor germination, weak growth, and increased susceptibility to pests and diseases. Additionally, not providing adequate spacing between plants can lead to overcrowding, reducing air circulation and increasing the risk of disease. To overcome these errors, it’s crucial to research the specific needs of sunflowers in your region, prepare the soil accordingly, and plant at the optimal time. By avoiding these common mistakes, you can increase your chances of success and enjoy a bountiful harvest of sunflowers. Remember, the best time to plant sunflower seeds is when the soil has warmed up, and the risk of frost has passed, typically in late spring or early summer. By planting at the right time and providing proper care, you can maximize sunflower growth and enjoy their beautiful blooms.
Maximizing Sunflower Growth with Proper Care and Maintenance
To ensure optimal growth and maximize yields, it’s essential to provide proper care and maintenance to your sunflowers after planting. One of the most critical factors is watering. Sunflowers require consistent moisture, especially during the germination and seedling stages. Water them deeply once or twice a week, depending on weather conditions, to encourage healthy growth. However, avoid overwatering, which can lead to root rot and other diseases. Fertilizing is another crucial aspect of sunflower care. Feed your sunflowers with a balanced fertilizer once a month, taking care not to overfertilize, which can damage the plants. Pruning is also essential to promote healthy growth and encourage blooming. Remove any weak or damaged leaves and stems, and trim back the plant to encourage bushy growth. Additionally, provide support to the plants as they grow taller, using stakes or trellises to prevent them from toppling over in the wind. Pest management is also crucial, as sunflowers are susceptible to pests like aphids, whiteflies, and spider mites. Use organic or chemical pest control methods as needed to protect your plants. By providing proper care and maintenance, you can maximize sunflower growth and enjoy a bountiful harvest of beautiful blooms. Remember, the best time to plant sunflower seeds is when the soil has warmed up, and the risk of frost has passed, typically in late spring or early summer. By planting at the right time and providing proper care, you can enjoy a successful sunflower harvest.