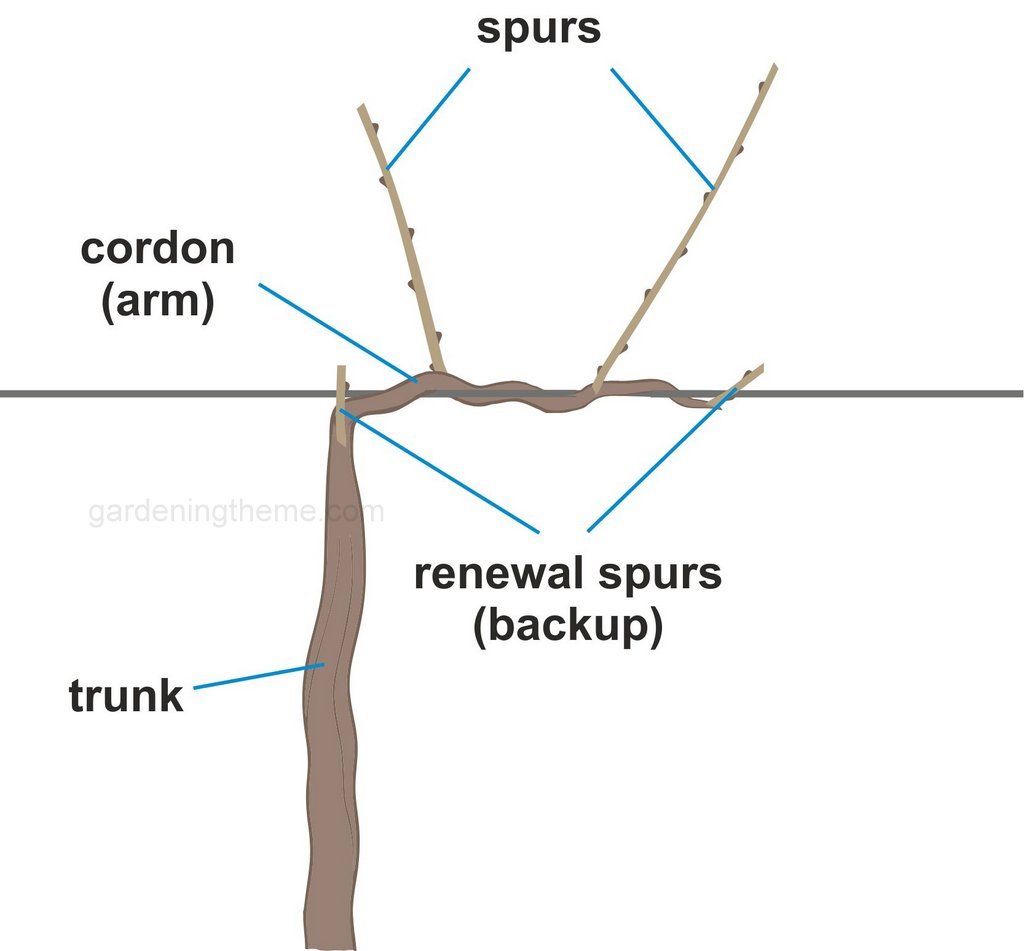
Understanding the Importance of Pruning in Grape Vine Maintenance
Pruning is a crucial aspect of grape vine maintenance, playing a vital role in the overall health and productivity of the vine. By removing select parts of the vine, pruning helps to promote healthy growth, increase fruit production, and prevent disease. In fact, pruning is considered one of the most important practices in grape vine cultivation, with the potential to significantly impact the quality and quantity of the grape harvest.
The best time to prune a grape vine is a topic of much debate among viticulturists and grape growers. While some argue that pruning should be done during the dormant season, others claim that pruning during the growing season is more beneficial. However, regardless of the timing, pruning is essential for maintaining the overall health and productivity of the vine.
One of the primary benefits of pruning is its impact on fruit production. By removing select parts of the vine, pruning helps to promote the growth of fruiting branches, resulting in increased yields and improved fruit quality. Additionally, pruning helps to prevent disease by removing infected or damaged wood, reducing the risk of disease transmission and promoting healthy growth.
Pruning also plays a critical role in maintaining the overall structure and architecture of the vine. By removing select parts of the vine, pruning helps to promote a balanced and organized structure, making it easier to manage and maintain the vine. This, in turn, can help to reduce the risk of disease and pests, while also improving the overall appearance of the vine.
In order to get the most out of pruning, it’s essential to understand the different types of pruning and how they impact the vine. There are several types of pruning, including dormant season pruning, growing season pruning, and harvest pruning, each with its own unique benefits and drawbacks. By understanding the different types of pruning and how they impact the vine, grape growers can make informed decisions about the best time to prune their grape vines.
When to Prune: A Guide to the Best Time of Year
Determining the best time to prune a grape vine can be a daunting task, as it depends on various factors such as climate, region, and vine variety. However, understanding the different pruning seasons and how they impact the vine can help grape growers make informed decisions about when to prune.
There are three main pruning seasons: dormant, growing, and harvest. Each season has its own unique benefits and drawbacks, and the best time to prune will depend on the specific needs of the vine.
Dormant season pruning, which typically takes place during the winter months, is considered the best time to prune for many grape growers. During this season, the vine is in a state of dormancy, and pruning can help to promote healthy growth and reduce the risk of disease. Additionally, dormant season pruning can help to improve the overall structure and architecture of the vine, making it easier to manage and maintain.
Growing season pruning, which takes place during the spring and summer months, is also an effective time to prune. During this season, the vine is actively growing, and pruning can help to promote fruiting branches and increase yields. However, growing season pruning can also stimulate new growth, which can make the vine more susceptible to disease and pests.
Harvest pruning, which takes place during the fall months, is typically used to prepare the vine for the upcoming harvest. During this season, pruning can help to promote fruit ripening and improve the overall quality of the grapes.
Climate and region also play a significant role in determining the best time to prune a grape vine. In cooler climates, pruning may need to be done earlier in the season to allow for sufficient time for the vine to recover before the onset of winter. In warmer climates, pruning may be done later in the season to avoid stimulating new growth during the hottest months.
Ultimately, the best time to prune a grape vine will depend on the specific needs of the vine and the goals of the grape grower. By understanding the different pruning seasons and how they impact the vine, grape growers can make informed decisions about when to prune and optimize their pruning practices for maximum yield.
Dormant Season Pruning: The Benefits and How-To
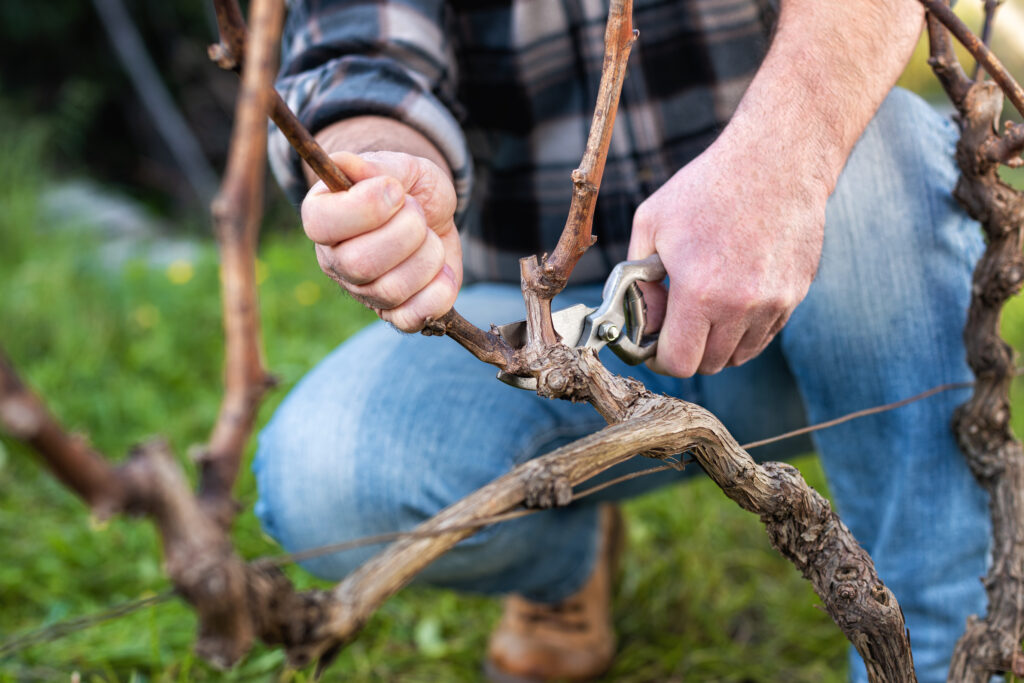
Dormant season pruning is considered one of the best times to prune a grape vine, as it offers several benefits for the vine’s health and productivity. During this season, the vine is in a state of dormancy, making it easier to prune without causing stress to the plant. Additionally, dormant season pruning can help to reduce the risk of disease and promote healthy growth.
One of the main advantages of dormant season pruning is that it allows for a more thorough pruning of the vine. Without the leaves and fruit to obscure the view, it’s easier to see the vine’s structure and identify areas that need attention. This makes it an ideal time to remove any dead, diseased, or damaged wood, which can help to prevent the spread of disease and promote healthy growth.
To prune a grape vine during the dormant season, follow these steps:
1. Gather your pruning tools, including pruning shears, loppers, and gloves.
2. Inspect the vine for any dead, diseased, or damaged wood, and remove it using your pruning shears or loppers.
3. Identify any crossing or rubbing branches, and remove them to improve air circulation and reduce the risk of disease.
4. Cut back any vigorous growth to encourage a more balanced structure and promote fruiting branches.
5. Remove any suckers or water sprouts that are growing from the base of the vine.
By following these steps, you can help to promote healthy growth and maximize fruit yield during the dormant season. Remember to always prune your grape vine at the best time for your specific climate and region, and to use the right tools and techniques to avoid damaging the vine.
In addition to the benefits mentioned above, dormant season pruning can also help to improve the overall structure and architecture of the vine. By removing select branches and promoting a more balanced structure, you can help to increase the vine’s productivity and make it easier to manage and maintain.
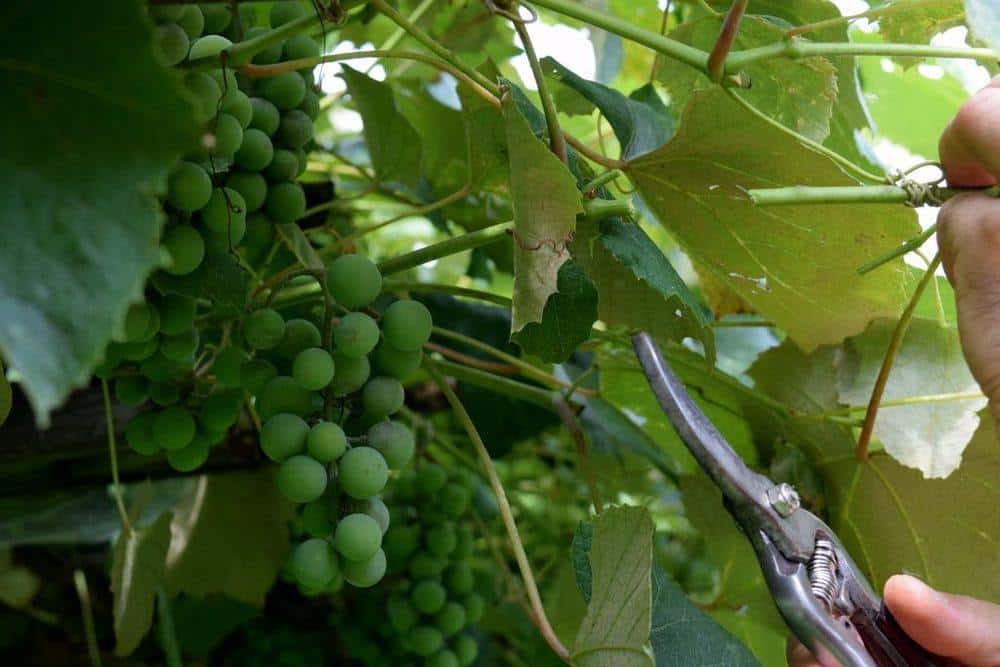
Pruning for Productivity: Tips for Maximizing Fruit Yield
Pruning is a crucial step in maximizing fruit yield in grape vines. By removing unproductive wood and promoting fruiting branches, grape growers can increase the overall productivity of their vines. Here are some tips for pruning to maximize fruit yield:
1. Identify and remove unproductive wood: Unproductive wood is any branch or stem that is not producing fruit or is not contributing to the overall structure of the vine. Removing this wood can help to redirect the vine’s energy towards producing fruit.
2. Promote fruiting branches: Fruiting branches are the branches that produce fruit. By promoting these branches, grape growers can increase the overall fruit yield of their vines. This can be done by pruning the vine to allow more sunlight to reach the fruiting branches.
3. Thin out the canopy: A dense canopy can reduce fruit yield by blocking sunlight and preventing air from circulating around the fruit. By thinning out the canopy, grape growers can improve fruit yield and reduce the risk of disease.
4. Prune for air circulation: Good air circulation is essential for healthy fruit production. By pruning the vine to allow for good air circulation, grape growers can reduce the risk of disease and improve fruit yield.
5. Monitor and adjust: Pruning is an ongoing process, and grape growers should monitor their vines regularly to ensure that they are pruning effectively. By adjusting their pruning techniques as needed, grape growers can maximize fruit yield and improve the overall health of their vines.
By following these tips, grape growers can prune their vines to maximize fruit yield and improve the overall health of their vines. Remember to always prune at the best time for your specific climate and region, and to use the right tools and techniques to avoid damaging the vine.
In addition to these tips, grape growers should also consider the specific needs of their vine variety. Different varieties have different pruning requirements, and grape growers should research the specific needs of their variety to ensure that they are pruning effectively.
Pruning for Pest and Disease Management
Pruning is an essential tool in managing pests and diseases in grape vines. By removing infected or infested wood, grape growers can prevent the spread of disease and reduce the risk of pest infestations. Here are some tips for pruning to manage pests and diseases:
1. Inspect the vine regularly: Regular inspections can help grape growers identify potential problems before they become major issues. Look for signs of disease or pest infestations, such as yellowing leaves, black spots, or white powdery patches.
2. Remove infected or infested wood: If you identify any infected or infested wood, remove it immediately. This will help prevent the spread of disease and reduce the risk of pest infestations.
3. Prune for air circulation: Good air circulation can help prevent disease by reducing the amount of moisture on the leaves and stems. Prune the vine to allow for good air circulation, especially in humid or wet climates.
4. Use clean pruning tools: Make sure to use clean pruning tools to prevent the spread of disease. Disinfect your pruning tools between cuts, and wash your hands regularly.
5. Monitor for pests: Keep an eye out for pests, such as mites, mealybugs, and spider mites. Prune the vine to remove any infested areas, and consider using integrated pest management (IPM) techniques to control pest populations.
By following these tips, grape growers can use pruning as a tool to manage pests and diseases in their vines. Remember to always prune at the best time for your specific climate and region, and to use the right tools and techniques to avoid damaging the vine.
In addition to these tips, grape growers should also consider the specific needs of their vine variety. Different varieties have different pruning requirements, and grape growers should research the specific needs of their variety to ensure that they are pruning effectively.
Pruning for pest and disease management is an ongoing process, and grape growers should regularly inspect their vines to identify potential problems. By staying on top of pruning, grape growers can reduce the risk of pest and disease infestations, and promote healthy growth in their vines.
Regional Variations: Pruning for Different Climates and Regions
Pruning practices can vary significantly depending on the climate, region, and grape variety. Understanding these regional variations is crucial to optimize pruning techniques and achieve maximum yield. Here are some regional variations to consider:
In cooler climates, such as those found in the Pacific Northwest, pruning is typically done later in the dormant season to allow for more time for the vine to recover before the onset of winter. In warmer climates, such as those found in California, pruning is often done earlier in the dormant season to avoid stimulating new growth during the hottest months.
In regions with high humidity, such as the Southeastern United States, pruning is often done to promote air circulation and reduce the risk of disease. In regions with low humidity, such as the Southwest, pruning is often done to conserve water and reduce the risk of drought stress.
Soil type is also an important factor to consider when pruning grape vines. In regions with heavy clay soils, pruning is often done to improve drainage and reduce the risk of waterlogged soil. In regions with sandy soils, pruning is often done to conserve water and reduce the risk of drought stress.
Grape variety is also an important factor to consider when pruning grape vines. Some varieties, such as Chardonnay and Pinot Noir, require more frequent pruning to promote fruiting and reduce the risk of disease. Other varieties, such as Cabernet Sauvignon and Merlot, require less frequent pruning to promote vigor and reduce the risk of over-production.
By understanding these regional variations, grape growers can adapt their pruning techniques to optimize yield and reduce the risk of disease and pests. Remember to always prune at the best time for your specific climate and region, and to use the right tools and techniques to avoid damaging the vine.
In addition to these regional variations, grape growers should also consider the specific needs of their vineyard. Factors such as vine age, vine density, and trellis system can all impact pruning practices and should be taken into account when developing a pruning strategy.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Pruning Grape Vines
Pruning grape vines can be a complex process, and making mistakes can have serious consequences for the health and productivity of the vine. Here are some common mistakes to avoid when pruning grape vines:
Over-pruning: Over-pruning can cause stress to the vine, leading to reduced fruit production and increased susceptibility to disease. To avoid over-pruning, prune only what is necessary to maintain the vine’s structure and promote fruiting.
Under-pruning: Under-pruning can lead to a lack of fruit production and reduced vine health. To avoid under-pruning, make sure to remove all dead, diseased, or damaged wood, and prune the vine to promote fruiting branches.
Pruning at the wrong time: Pruning at the wrong time can cause stress to the vine and reduce fruit production. To avoid pruning at the wrong time, prune during the dormant season, when the vine is less active.
Not using clean pruning tools: Not using clean pruning tools can spread disease and pests from one vine to another. To avoid this, make sure to disinfect your pruning tools between cuts, and wash your hands regularly.
Not pruning for air circulation: Not pruning for air circulation can lead to reduced fruit production and increased susceptibility to disease. To avoid this, prune the vine to allow for good air circulation, especially in humid or wet climates.
By avoiding these common mistakes, grape growers can ensure that their vines are healthy and productive, and that they are getting the most out of their pruning efforts. Remember to always prune at the best time for your specific climate and region, and to use the right tools and techniques to avoid damaging the vine.
In addition to these mistakes, grape growers should also be aware of the potential risks associated with pruning, such as the spread of disease and pests. By taking the necessary precautions and using the right techniques, grape growers can minimize these risks and ensure that their vines are healthy and productive.
Pruning Tools and Equipment: What You Need to Get the Job Done
Pruning grape vines requires the right tools and equipment to ensure a safe and effective pruning process. Here are some of the essential tools and equipment you’ll need to get the job done:
Pruning shears: Pruning shears are the most commonly used tool for pruning grape vines. They are available in different sizes and types, including bypass and anvil-style shears.
Loppers: Loppers are long-handled pruning shears that are used for cutting thicker branches. They are ideal for pruning larger grape vines or for cutting branches that are out of reach.
Gloves: Pruning gloves are essential for protecting your hands from thorns and other sharp objects. They are available in different materials, including leather and synthetic fabrics.
Pruning saw: A pruning saw is a specialized saw that is designed for cutting thicker branches. It is ideal for pruning larger grape vines or for cutting branches that are too thick for pruning shears.
Pruning ladder: A pruning ladder is a specialized ladder that is designed for pruning grape vines. It is ideal for reaching high branches and for providing a safe and stable platform for pruning.
By using the right tools and equipment, grape growers can ensure a safe and effective pruning process. Remember to always use clean and sharp tools to prevent the spread of disease and to promote healthy growth.
In addition to these tools and equipment, grape growers should also consider the importance of proper pruning techniques. By using the right techniques and tools, grape growers can optimize their pruning efforts and achieve maximum yield.