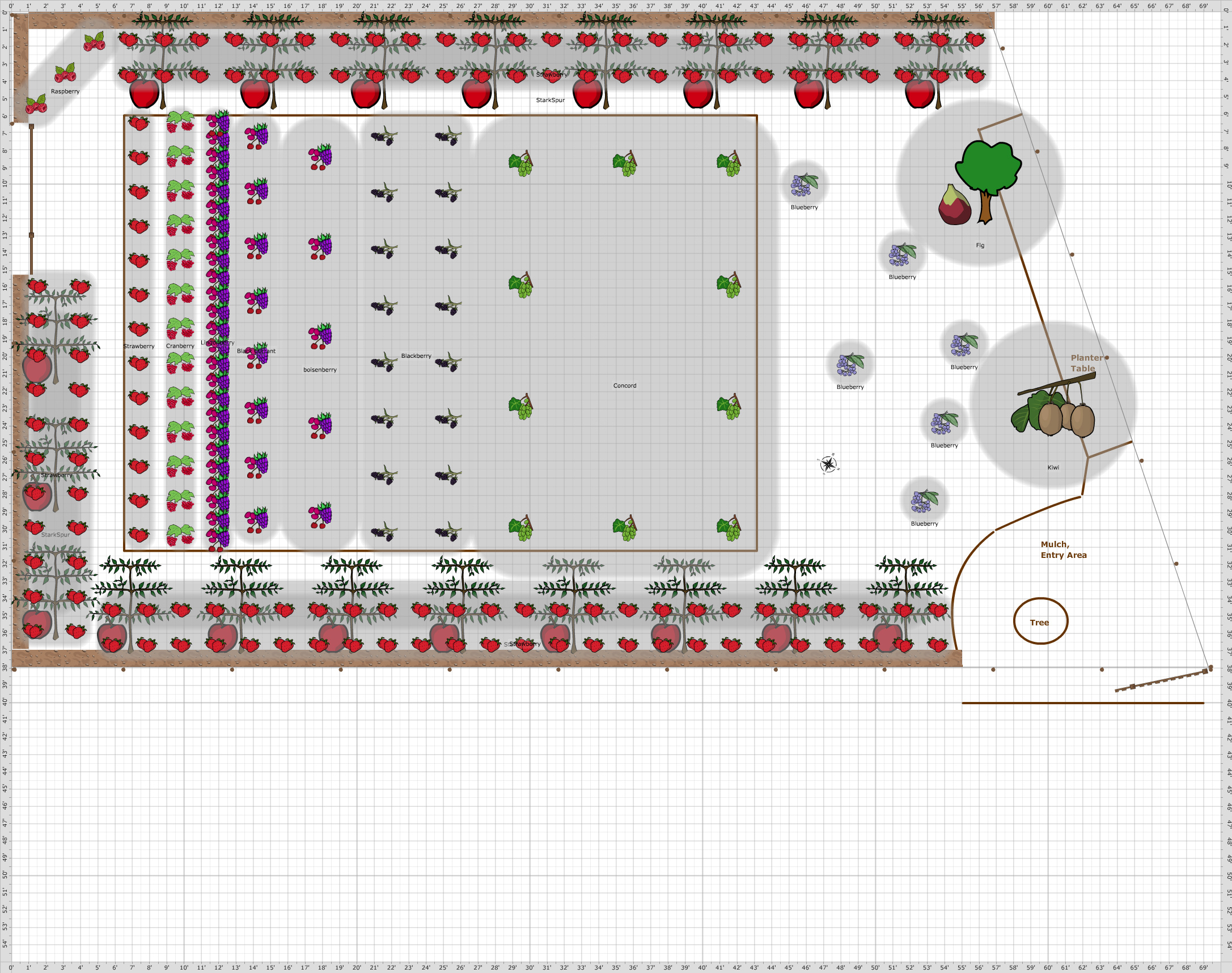
The Art of Fruit Garden Planning
A well-designed fruit garden layout is crucial for maximizing space, optimizing sunlight, and promoting plant health. By carefully planning your fruit garden, you can create an efficient and productive outdoor space that caters to your needs and preferences. This section will explore the benefits of a thoughtfully designed fruit garden layout and provide insights into creating an effective plan for your fruit garden.
A fruit garden layout should prioritize the efficient use of space, ensuring that each plant has enough room to grow and thrive. Proper spacing allows for adequate air circulation, reducing the risk of fungal diseases. Additionally, planning for mature tree sizes helps prevent overcrowding, which can lead to reduced fruit production and increased maintenance requirements.
Sunlight is another critical factor to consider when designing a fruit garden layout. Most fruit trees and shrubs require full sun, meaning at least six hours of direct sunlight daily. By strategically placing your plants, you can ensure that they receive the necessary sunlight for optimal growth and fruit production. Additionally, proper orientation of the garden can help maximize sunlight exposure throughout the day.
Promoting plant health is another essential aspect of fruit garden layout design. By incorporating companion plants, you can improve soil health, attract beneficial insects, and deter pests. For example, planting marigolds alongside fruit trees can help repel nematodes and other soil-dwelling pests. Moreover, using organic mulch and compost can improve soil structure, fertility, and water retention, contributing to the overall health of your fruit garden.
Understanding Your Garden Space: Factors to Consider
When planning a fruit garden layout, several essential factors must be taken into account to ensure a successful and productive garden. These factors include garden size, sunlight exposure, soil quality, and local climate. By carefully considering these elements, you can create a fruit garden layout that maximizes the potential for healthy growth and fruit production.
Garden Size
The size of your garden will significantly influence the number and variety of fruit trees and shrubs you can accommodate. When determining the optimal layout for your fruit garden, consider the mature sizes of the plants you intend to grow and ensure that there is enough space for each plant to reach its full potential without overcrowding. A well-planned fruit garden layout can help you make the most of the space you have available, whether it’s a small backyard or a large rural property.
Sunlight Exposure
Sunlight is a critical factor for the growth and development of fruit trees and shrubs. Most fruit plants require full sun, which means at least six hours of direct sunlight daily. When designing your fruit garden layout, consider the path of the sun throughout the day and position your plants accordingly to ensure they receive the necessary sunlight for optimal growth and fruit production.
Soil Quality
Soil quality plays a significant role in the health and productivity of fruit trees and shrubs. Before planting, assess the soil in your garden for factors such as pH, nutrient content, and drainage. Based on your findings, you may need to amend the soil with organic matter, such as compost or aged manure, to create an ideal growing medium for your fruit plants. Maintaining healthy soil is crucial for the long-term success of your fruit garden layout.
Local Climate
Local climate conditions, such as temperature, precipitation, and humidity, can significantly impact the growth and fruiting of fruit trees and shrubs. When planning your fruit garden layout, consider the specific microclimate of your garden and choose plant varieties that are well-suited to your local conditions. By selecting climate-appropriate fruit plants, you can increase the chances of a successful and productive garden.
Selecting Fruit Trees and Shrubs: Types and Varieties
Choosing the right fruit trees and shrubs for your garden is an essential step in creating a successful and productive fruit garden layout. By considering factors such as growth habits, fruiting seasons, and site requirements, you can select plants that will thrive in your specific garden conditions and provide you with an abundant harvest. Here is an overview of popular fruit trees and shrubs for home gardens:
Apples (Malus domestica)
Apples are a popular choice for home gardens due to their versatility and wide range of varieties available. They typically require full sun and well-drained soil. Many apple varieties are suitable for temperate climates, while some are better suited to cooler regions. Dwarf and semi-dwarf rootstocks are available for smaller gardens.
Pears (Pyrus communis)
Pears are another versatile fruit tree, offering various flavors, textures, and ripening times. They generally prefer full sun and well-drained soil. Some pear varieties are more cold-hardy than others, making them a suitable choice for colder climates. Dwarf and semi-dwarf rootstocks are also available for pear trees.
Stone Fruits (Prunus spp.)
Stone fruits, such as peaches, nectarines, plums, and cherries, are known for their juicy and flavorful fruits. They typically require full sun and well-drained soil. Some stone fruit varieties are self-fertile, while others require cross-pollination. Climate and chill hour requirements vary by species and variety.
Berries (Rubus spp., Vaccinium spp., and others)
Berries, including raspberries, blackberries, blueberries, and strawberries, are popular shrubs for home gardens due to their compact growth habits and high yields. They generally prefer full sun to partial shade and well-drained soil. Many berry varieties are suitable for various climates, making them a versatile choice for fruit garden layouts.
Citrus Fruits (Citrus spp.)
Citrus fruits, such as oranges, lemons, limes, and grapefruits, are a delightful addition to any fruit garden layout. They typically require full sun and well-drained soil. While many citrus fruits are tropical or subtropical, some cold-hardy varieties are available for gardeners in colder climates.
Designing the Fruit Garden Layout: Tips and Techniques
Designing a fruit garden layout that maximizes space, optimizes sunlight, and promotes plant health requires careful planning and consideration. By employing practical tips and techniques, you can create a functional and aesthetically pleasing fruit garden layout that caters to your needs and preferences. Here are some suggestions for designing a successful fruit garden layout:
Consider Mature Tree Sizes
When designing your fruit garden layout, keep in mind the mature sizes of the trees and shrubs you plan to grow. This will help you avoid overcrowding and ensure that each plant has enough space to reach its full potential. Additionally, consider the root systems of your plants and provide adequate space for root growth to prevent competition between plants.
Allow for Accessibility
Design your fruit garden layout with accessibility in mind. Ensure that there is enough space between rows and plants for easy maintenance, such as pruning, watering, and harvesting. Incorporating pathways and seating areas can also create a more inviting and enjoyable outdoor space.
Incorporate Companion Plants
Companion planting can benefit your fruit garden layout by improving soil health, attracting beneficial insects, and deterring pests. For example, planting nitrogen-fixing legumes, such as beans or clover, alongside fruit trees can help improve soil fertility. Additionally, herbs like basil, oregano, and thyme can repel harmful insects and attract pollinators.
Plan for Sunlight Exposure
As mentioned earlier, sunlight is crucial for the growth and development of fruit trees and shrubs. When designing your fruit garden layout, consider the path of the sun throughout the day and position your plants accordingly to ensure they receive the necessary sunlight for optimal growth and fruit production.
Utilize Vertical Space
Maximizing vertical space is an excellent way to make the most of your fruit garden layout, especially in smaller gardens. Espaliering fruit trees, using trellises for berries, and installing raised beds or containers can help you make the most of your available space while promoting healthy growth and fruit production.
Planting and Establishing Fruit Trees and Shrubs
Proper planting techniques are crucial for the successful establishment and growth of fruit trees and shrubs in your garden. By following best practices for soil preparation, planting depth, and watering schedules, you can promote healthy root development and ensure optimal growth and fruit production. Here is a guide to planting and establishing fruit trees and shrubs in your fruit garden layout:
Soil Preparation
Before planting, prepare the soil by removing weeds, rocks, and debris. If necessary, amend the soil with organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, to improve soil structure, fertility, and water retention. This will create an ideal growing medium for your fruit trees and shrubs and promote healthy root development.
Planting Depth
When planting fruit trees and shrubs, ensure that the root collar, the area where the roots meet the trunk, is at or slightly above the soil level. This will help prevent root rot and promote healthy root development. Avoid planting too deeply, as this can lead to poor growth and reduced fruit production.
Watering Schedules
Proper watering is essential for the successful establishment of fruit trees and shrubs. After planting, water your trees and shrubs thoroughly, ensuring that the soil is evenly moist but not waterlogged. During the first growing season, water your plants regularly, providing approximately one inch of water per week. Adjust your watering schedule as needed based on your local climate and weather conditions.
Staking and Support
For young fruit trees, staking and support may be necessary to help establish a strong trunk and prevent damage from wind or heavy fruit loads. Use soft, flexible ties to secure the tree to the stake, and remove the stake once the tree is well-established, typically after one to two years.
Protection from Pests and Damage
Protect your newly planted fruit trees and shrubs from pests, such as rodents and deer, by using tree guards or fencing. Additionally, consider using frost protection measures, such as frost blankets or water-filled containers, to protect your plants from frost damage during the winter months.
Maintaining Your Fruit Garden: Care and Pruning
Proper care and maintenance are essential for ensuring the health, productivity, and longevity of your fruit trees and shrubs. By following best practices for watering, fertilizing, and pruning, you can promote strong growth, improve fruit production, and maintain a thriving fruit garden layout. Here is a guide to maintaining your fruit garden:
Watering
Watering is a critical aspect of fruit garden maintenance. Fruit trees and shrubs require consistent moisture for healthy growth and fruit production. During the growing season, provide approximately one inch of water per week, adjusting your watering schedule based on local climate and weather conditions. Overwatering can lead to root rot and other issues, while underwatering can stress the plants and reduce fruit production.
Fertilizing
Fertilizing your fruit trees and shrubs can help promote healthy growth and improve fruit production. Use a balanced, slow-release fertilizer, following the manufacturer’s instructions for application rates and timing. Avoid over-fertilizing, as this can lead to excessive vegetative growth and reduced fruit production. Regularly test your soil to monitor nutrient levels and adjust your fertilization schedule as needed.
Pruning
Pruning is an essential maintenance task for fruit trees and shrubs, helping to promote strong growth, improve fruit production, and maintain plant health. Prune your fruit trees and shrubs annually, removing dead, diseased, or damaged wood, as well as any crossing or rubbing branches. For fruit trees, prune to maintain an open, vase-shaped structure, which allows for better light penetration and improved fruit production.
Monitoring for Pests and Diseases
Regularly inspect your fruit trees and shrubs for signs of pests or diseases, such as discolored leaves, spotted fruit, or weak growth. Address any issues promptly, using organic or chemical treatments as necessary. Encourage beneficial insects and animals, such as ladybugs, spiders, and birds, by incorporating companion plants and providing habitats, such as insect hotels or birdhouses.
Mulching and Weed Control
Mulching your fruit garden can help maintain soil moisture, suppress weeds, and improve soil health. Apply a two- to four-inch layer of organic mulch, such as wood chips or straw, around the base of your fruit trees and shrubs. Regularly remove weeds and invasive plants, as they can compete with your fruit plants for nutrients and water, leading to reduced growth and fruit production.
Harvesting and Storing Fruit: Enjoying the Rewards
After months of careful planning, planting, and maintenance, the moment you’ve been waiting for has arrived: it’s time to harvest and enjoy the fruits of your labor. Knowing when to harvest your fruit and how to store and preserve it can help you maximize the enjoyment of your homegrown produce. Here is a guide to harvesting and storing fruit in your fruit garden layout:
Harvesting Fruit
Harvest your fruit at the right time to ensure optimal flavor, texture, and nutritional value. Familiarize yourself with the typical ripening times and indicators for each fruit variety in your garden. Some fruits, like berries and stone fruits, will change color and become soft when ripe, while others, like apples and pears, may require a taste test to determine ripeness.
Storing Fresh Fruit
Proper storage can help extend the shelf life of your fresh fruit, allowing you to enjoy it over an extended period. Store fruit in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area, away from direct sunlight. Some fruits, like apples and bananas, release ethylene gas, which can cause other fruits to ripen and spoil more quickly. Store these fruits separately to prevent premature spoilage.
Preserving Fruit
Preserving fruit through methods like canning, freezing, and dehydrating can help you enjoy your homegrown produce long after the harvest season has ended. Preserve fruit at its peak of freshness to lock in flavor, texture, and nutritional value. Follow recommended recipes and procedures to ensure food safety and prevent spoilage.
Maximizing the Enjoyment of Your Homegrown Fruit
Harvesting and storing fruit is just the beginning. Get creative in the kitchen by incorporating your homegrown produce into recipes, snacks, and beverages. Share your bounty with friends, family, and neighbors, or consider preserving fruit for gifts or donations to local food banks or community organizations.
Troubleshooting and Problem-Solving in Fruit Gardens
Even with careful planning and maintenance, fruit gardens can sometimes face challenges that may impact the health and productivity of your trees and shrubs. Common issues in fruit gardens include pests, diseases, and poor fruit set. Addressing these challenges promptly and effectively can help maintain a thriving fruit garden layout. Here are some practical solutions to common problems in fruit gardens:
Pests
Pests, such as insects and mites, can damage fruit trees and shrubs, reducing growth and fruit production. Monitor your fruit garden regularly for signs of pests, and take action as needed. Use organic or chemical treatments, such as insecticidal soap or horticultural oil, to control pests while minimizing environmental impact. Encourage beneficial insects and animals, such as ladybugs, spiders, and birds, by incorporating companion plants and providing habitats, such as insect hotels or birdhouses.
Diseases
Diseases, such as fungal infections and bacterial blights, can impact the health and productivity of fruit trees and shrubs. Prevent diseases by practicing good garden hygiene, such as removing dead or diseased plant material, and using disease-resistant plant varieties. Treat diseases with organic or chemical fungicides or bactericides, following the manufacturer’s instructions for application rates and timing. Ensure proper air circulation and sunlight penetration to help prevent the spread of diseases.
Poor Fruit Set
Poor fruit set, or the failure of fruit trees and shrubs to produce fruit, can be caused by various factors, including poor pollination, nutrient deficiencies, and environmental stress. Encourage pollination by planting pollinator-friendly plants, such as flowers and herbs, and providing habitats for bees and other pollinators. Address nutrient deficiencies by testing your soil and amending it with appropriate fertilizers or soil amendments. Minimize environmental stress by providing adequate water, protecting plants from extreme temperatures, and using mulch to maintain soil moisture and temperature.