Discover the Joy of Homegrown Produce: An Overview of Garden Fruits and Vegetables
Growing your own garden fruits and vegetables is a rewarding experience that offers numerous benefits. By cultivating a variety of produce in your backyard or balcony, you can enjoy fresh, flavorful, and cost-effective ingredients that elevate your culinary creations. This article will provide an overview of the different types of fruits and vegetables that can be grown in a home garden, along with the advantages of homegrown produce.
The concept of growing garden fruits and vegetables has been around for centuries, allowing individuals to connect with nature, nurture living organisms, and savor the fruits of their labor. A home garden can include a wide range of produce, such as tomatoes, cucumbers, lettuce, strawberries, and carrots, to name a few. These fruits and vegetables not only add aesthetic appeal to your outdoor space but also contribute to a healthier lifestyle by providing easy access to fresh, nutrient-rich produce.
One of the primary benefits of growing garden fruits and vegetables is their freshness. Unlike store-bought produce, which may have traveled long distances and spent time in storage, homegrown fruits and vegetables are often picked at the peak of ripeness, ensuring optimal flavor and nutritional value. Moreover, homegrown produce is free from preservatives and additives, allowing you to enjoy the natural taste and texture of each fruit and vegetable.
Another advantage of cultivating garden fruits and vegetables is the cost-effectiveness. While the initial setup costs, such as soil, seeds, and gardening tools, may seem substantial, the long-term savings can be significant. By growing your own produce, you can reduce your reliance on store-bought fruits and vegetables, which can be expensive, especially for organic or specialty varieties. Additionally, homegrown produce can be preserved through canning, freezing, or dehydrating, extending its shelf life and providing even more value for your investment.
Lastly, growing garden fruits and vegetables can be a fun and educational experience for individuals of all ages. By engaging in the process of planting, tending, and harvesting, you can develop a deeper appreciation for the natural world and the food that sustains us. Furthermore, home gardening can foster a sense of community, as gardeners often share tips, seeds, and harvests with one another, creating a network of support and collaboration.
Choosing the Right Fruits and Vegetables for Your Garden: Factors to Consider
Selecting the appropriate fruits and vegetables for your garden is crucial to ensure a bountiful harvest and a thriving outdoor space. Various factors, such as climate, space availability, and personal preferences, should be taken into account when choosing plants. By considering these elements, you can create a garden that caters to your unique growing conditions and desired produce.
First and foremost, assess your local climate to determine which fruits and vegetables are most likely to thrive in your garden. Factors such as temperature, humidity, and precipitation can significantly impact the growth and yield of various plants. For instance, warm-season crops, like tomatoes, peppers, and eggplants, require a long, warm growing season and are best suited for regions with mild winters and hot summers. Conversely, cool-season crops, such as lettuce, broccoli, and peas, prefer cooler temperatures and shorter growing seasons, making them ideal for areas with cold winters and mild summers.
Space availability is another essential factor to consider when selecting fruits and vegetables for your garden. Depending on the size of your outdoor space, you may need to choose plants that are suitable for container gardening, vertical gardening, or raised beds. For example, compact varieties of tomatoes, such as cherry or grape tomatoes, are well-suited for small spaces, while sprawling plants, like watermelons or pumpkins, require ample room to grow and are best suited for larger gardens.
Personal preferences also play a significant role in choosing the right fruits and vegetables for your garden. Consider the types of produce you and your family enjoy eating, as well as any unique culinary interests or dietary restrictions. For instance, if you follow a vegetarian or vegan diet, you may want to prioritize growing a variety of fruits and vegetables that can be used as the main ingredients in your meals. Alternatively, if you enjoy canning and preserving, you may want to focus on plants that yield large quantities of produce, such as cucumbers, green beans, or peaches.
Lastly, it is essential to consider the growth requirements and yield of each fruit and vegetable when making your selections. Some plants, like zucchini and kale, are prolific producers and can yield a significant amount of produce from a single plant. In contrast, other plants, like artichokes and asparagus, have a more extended establishment period and lower yields, but they offer unique flavors and textures that can enhance your culinary creations.
How to Create a Fruitful Garden: Step-by-Step Guide to Planting and Caring for Garden Fruits and Vegetables
Establishing a thriving garden requires careful planning, preparation, and maintenance. By following a step-by-step guide, you can create a fruitful outdoor space that yields a bountiful harvest of delicious and nutritious garden fruits and vegetables. This section outlines the essential steps for creating a successful garden, from site preparation to ongoing care and maintenance.
Step 1: Site Preparation
Selecting the right location for your garden is crucial for ensuring healthy plant growth. Choose a spot that receives at least six to eight hours of sunlight per day and has well-draining soil. Remove any weeds, debris, or rocks from the area, and amend the soil with organic matter, such as compost or aged manure, to improve its structure and fertility.
Step 2: Plant Selection
When choosing fruits and vegetables for your garden, consider factors such as climate, space availability, and personal preferences. Purchase high-quality seeds or seedlings from a reputable supplier, and read the planting instructions carefully to ensure proper spacing and depth.
Step 3: Planting
Plant your seeds or seedlings according to the instructions provided on the seed packet or plant tag. Water the plants thoroughly after planting, and ensure that the soil remains consistently moist but not waterlogged. For container gardens, select pots with adequate drainage holes and use a high-quality potting mix to promote healthy root growth.
Step 4: Watering
Proper watering is essential for the health and productivity of your garden. Water your plants consistently, aiming for a slow, deep watering that reaches the entire root zone. Adjust your watering schedule based on the climate, soil type, and plant species, and avoid overwatering, which can lead to root rot and other diseases.
Step 5: Fertilizing
Feeding your garden fruits and vegetables with the right nutrients can help promote healthy growth and increase yields. Use a balanced, slow-release fertilizer, and follow the manufacturer’s instructions for application rates and timing. Consider conducting a soil test to determine the pH and nutrient levels of your soil, and adjust your fertilization strategy accordingly.
Step 6: Pest Management
Protecting your garden from pests and diseases is crucial for maintaining its health and productivity. Monitor your plants regularly for signs of damage, and take prompt action to address any issues. Use organic or eco-friendly pest control methods whenever possible, such as introducing beneficial insects, applying insecticidal soap, or employing row covers.
Step 7: Maintenance
Ongoing maintenance is essential for keeping your garden in top shape. Remove any dead or dying leaves, stems, or plants, and prune your plants as needed to promote bushy growth and improve air circulation. Keep the soil consistently moist, and mulch around your plants to help retain moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature.
Harvesting Garden Fruits and Vegetables: Tips for Maximizing Yield and Quality
Harvesting your garden fruits and vegetables at the right time is crucial for ensuring optimal yield, quality, and nutritional value. By employing the best practices for harvesting and storage, you can enjoy fresh, delicious, and healthy produce throughout the growing season and beyond. This section provides tips on the right timing, tools, and techniques for harvesting various garden fruits and vegetables, as well as advice on how to store your harvest to maintain its freshness and quality.
Timing is Everything
Harvest your garden fruits and vegetables at the right time to maximize their flavor, texture, and nutritional content. For most vegetables, harvest them when they reach their optimal size and color but before they become overripe or woody. Fruits, on the other hand, usually continue to ripen after they are picked, so harvest them when they are mature but still firm. Consult the seed packet or plant tag for specific harvesting instructions and guidelines for each plant species.
Tools of the Trade
Equip yourself with the right tools for the job to ensure a successful harvest. A sharp pair of pruning shears or scissors is essential for cutting fruits and vegetables cleanly from the plant, reducing damage and promoting faster healing. A small hand trowel or transplanting shovel can help you dig up root crops, such as carrots, beets, and potatoes, without damaging them. A soft-bristled brush or a clean, dry cloth can be used to gently remove dirt and debris from delicate produce, such as tomatoes, peppers, and berries.
Harvesting Techniques
Use proper harvesting techniques to minimize damage and promote healthy plant growth. For above-ground crops, such as tomatoes, peppers, and eggplants, use a sharp knife or scissors to cut the fruit from the plant, leaving a short stem attached. For root crops, such as carrots, beets, and turnips, loosen the soil around the plant with a hand trowel or fork, and gently pull the crop from the ground, taking care not to break or bruise it. For leafy greens, such as lettuce, spinach, and kale, use a sharp knife or scissors to cut the outer leaves from the plant, leaving the inner leaves intact to continue growing.
Storing Your Harvest
Proper storage is essential for maintaining the freshness and quality of your harvest. Store your garden fruits and vegetables in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area, away from direct sunlight and heat sources. For most vegetables, remove any dirt or debris, and store them in a single layer in shallow containers or perforated plastic bags. For fruits, such as apples, pears, and bananas, store them in a cool, dark place, and separate them from other produce to prevent premature ripening and spoilage. For leafy greens, wrap them in damp paper towels or cloth, and store them in a plastic bag in the refrigerator.
Top 5 Garden Fruits and Vegetables to Grow for Beginners
Growing your own garden fruits and vegetables can be a rewarding and fulfilling experience, but it can also be overwhelming for beginners. With so many options to choose from, it can be challenging to know where to start. In this section, we recommend the top five fruits and vegetables for beginners, based on their ease of cultivation, growth requirements, and yield. We also provide detailed instructions on how to grow and care for each plant, along with their expected harvest time.
1. Lettuce
Lettuce is an excellent choice for beginners due to its quick growth, ease of cultivation, and versatility in the kitchen. It prefers cooler temperatures and partial shade, making it an ideal crop for early spring and fall planting. To grow lettuce, direct sow the seeds in well-draining soil, and keep the soil consistently moist. Harvest the outer leaves when they reach the desired size, leaving the inner leaves to continue growing. Expect to harvest your lettuce in 30-45 days after planting.
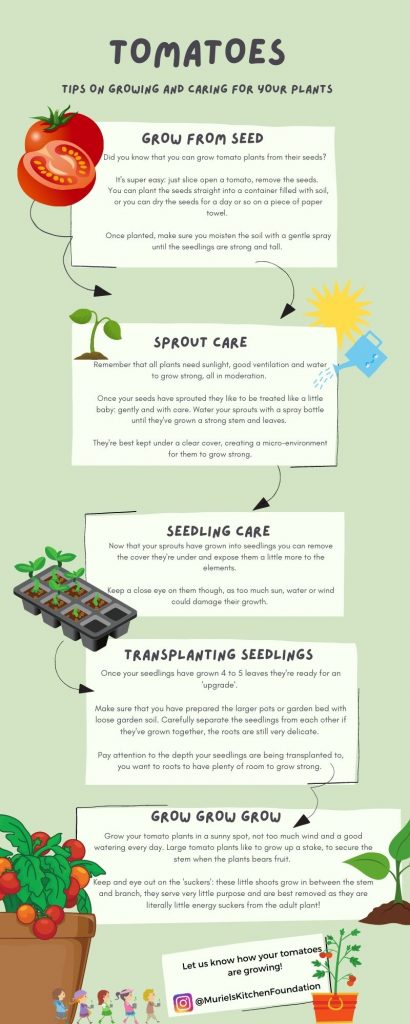
2. Tomatoes
Tomatoes are a popular choice for home gardeners, and for good reason. They are relatively easy to grow, and nothing compares to the taste of a fresh, sun-ripened tomato. Choose a disease-resistant variety, such as Celebrity or Early Girl, and plant them in well-draining soil with full sun. Water consistently, and provide support, such as a tomato cage or stake, to keep the plants upright. Expect to harvest your tomatoes in 60-90 days after planting.
3. Zucchini
Zucchini is a prolific producer, yielding a bountiful harvest with minimal effort. It prefers warm temperatures and well-draining soil with full sun. Direct sow the seeds in the soil, and keep the soil consistently moist. Harvest the zucchini when they are 4-6 inches long, before they become too large and seedy. Expect to harvest your zucchini in 40-50 days after planting.
4. Cucumbers
Cucumbers are another prolific producer, yielding a steady supply of crisp, refreshing produce. They prefer warm temperatures and well-draining soil with full sun. Direct sow the seeds in the soil, and keep the soil consistently moist. Provide support, such as a trellis or cage, to keep the plants upright and promote air circulation. Harvest the cucumbers when they are 4-6 inches long, before they become too large and bitter. Expect to harvest your cucumbers in 50-70 days after planting.
5. Strawberries
Strawberries are a delightful addition to any home garden, offering sweet, juicy fruit and attractive foliage. They prefer well-draining soil with full sun and partial shade. Plant the strawberry plants in the soil, and keep the soil consistently moist. Provide support, such as a raised bed or container, to keep the plants off the ground and prevent rot. Harvest the strawberries when they are fully red and ripe. Expect to harvest your strawberries in 30-60 days after planting, depending on the variety.
How to Incorporate Garden Fruits and Vegetables into Your Daily Diet: Creative Recipes and Ideas
Growing your own garden fruits and vegetables is a rewarding experience, but it can also be challenging to find creative ways to incorporate them into your daily diet. In this section, we provide inspiration and ideas for using your homegrown produce, highlighting the nutritional benefits of each fruit and vegetable and offering suggestions on how to use them in meals and snacks. By incorporating more garden fruits and vegetables into your diet, you can enjoy a healthier, more flavorful, and cost-effective way of eating.
1. Salads
Salads are an excellent way to enjoy fresh, crisp garden vegetables. Toss together a mix of lettuce, spinach, arugula, and other leafy greens, and add in sliced tomatoes, cucumbers, bell peppers, and radishes. Top with a homemade vinaigrette and enjoy as a light and refreshing meal or side dish.
2. Smoothies
Smoothies are a convenient and delicious way to consume garden fruits and vegetables. Blend together a mix of berries, bananas, spinach, kale, and other leafy greens, and add in a scoop of protein powder, chia seeds, or flaxseeds for added nutrition. Enjoy as a breakfast, snack, or post-workout treat.
3. Roasted Vegetables
Roasting vegetables brings out their natural sweetness and flavor. Toss together sliced carrots, beets, parsnips, and other root vegetables, and roast in the oven until tender and caramelized. Serve as a side dish, add to a grain bowl, or blend into a soup for added depth and richness.
4. Grilled Fruits and Vegetables
Grilling fruits and vegetables adds a smoky, charred flavor that is perfect for summer barbecues. Slice up peaches, nectarines, pineapple, zucchini, and bell peppers, and grill until tender and caramelized. Serve as a side dish, add to a salad, or blend into a salsa or chutney.
5. Soups and Stews
Soups and stews are a comforting and warming way to enjoy garden fruits and vegetables. Simmer together a mix of vegetables, such as tomatoes, carrots, celery, and onions, and add in broth, herbs, and spices for a hearty and nutritious meal. Serve with a side of crusty bread or over rice or pasta for added texture and flavor.
6. Pickles and Preserves
Pickling and preserving garden fruits and vegetables is a great way to enjoy them year-round. Preserve cucumbers, peppers, onions, and other vegetables in vinegar, brine, or oil, and enjoy as a snack, condiment, or side dish. Preserve fruits, such as berries, peaches, and plums, in syrup or honey, and enjoy as a topping for yogurt, oatmeal, or ice cream.
Sustainable Gardening Practices: How to Grow Garden Fruits and Vegetables with Minimal Environmental Impact
Sustainable gardening practices are essential for reducing the environmental impact of growing garden fruits and vegetables. By implementing these practices, you can conserve natural resources, protect the soil and water, and promote biodiversity. In this section, we discuss the importance of sustainable gardening practices and provide tips on how to implement them in a home garden. By following these practices, you can enjoy fresh, healthy, and environmentally friendly produce.
1. Reducing Water Usage
Water is a precious resource, and reducing water usage in the garden is essential for sustainability. To conserve water, use drip irrigation or soaker hoses to deliver water directly to the plant roots, reducing evaporation and runoff. Also, consider using mulch to retain moisture in the soil and plant in the morning or evening to reduce evaporation.
2. Composting
Composting is a natural way to enrich the soil and reduce waste. By composting kitchen scraps, yard waste, and other organic materials, you can create a nutrient-rich soil amendment that promotes healthy plant growth. Composting also reduces the need for chemical fertilizers, which can harm the environment and the produce.
3. Avoiding Chemical Pesticides
Chemical pesticides can harm the environment, beneficial insects, and the produce. To avoid chemical pesticides, use organic or natural pest control methods, such as introducing beneficial insects, using insecticidal soap, or planting pest-repelling plants. Also, practice crop rotation and companion planting to disrupt pest cycles and promote healthy plant growth.
4. Choosing Native Plants
Native plants are adapted to the local climate and soil conditions, requiring less water, fertilizer, and maintenance than non-native plants. By choosing native plants, you can reduce the environmental impact of your garden and promote biodiversity. Native plants also attract pollinators and other beneficial insects, promoting healthy ecosystems.
5. Conserving Soil
Soil conservation is essential for sustainability. To conserve soil, use cover crops, such as clover or rye, to prevent erosion and add organic matter to the soil. Also, practice crop rotation and avoid over-tilling, which can damage the soil structure and reduce its fertility.
6. Supporting Local Agriculture
Supporting local agriculture is an essential part of sustainable gardening. By buying locally grown produce, you can reduce the carbon footprint of your food and support the local economy. Also, consider joining a community-supported agriculture (CSA) program or visiting a farmers market to connect with local farmers and learn more about sustainable agriculture practices.
Overcoming Common Challenges in Growing Garden Fruits and Vegetables: Expert Advice and Solutions
Growing garden fruits and vegetables can be a rewarding experience, but it also comes with its fair share of challenges. From pests and diseases to unpredictable weather conditions, various obstacles can hinder your garden’s success. However, with the right knowledge and strategies, you can overcome these challenges and enjoy a bountiful harvest. This article provides expert advice and solutions to help you tackle common issues in growing garden fruits and vegetables.
Pests and Diseases
Pests and diseases are common challenges in gardening. To combat them, it’s essential to identify the specific issue affecting your plants. Some general strategies include:
- Keeping the garden clean and free of debris, which can harbor pests and diseases.
- Rotating crops each year to prevent the buildup of pests and diseases in the soil.
- Using organic pest control methods, such as introducing beneficial insects or applying insecticidal soap.
- Choosing disease-resistant plant varieties whenever possible.
Unpredictable Weather Conditions
Weather can be unpredictable, and extreme conditions, such as droughts, heavy rains, or frost, can damage your garden. To protect your garden from adverse weather, consider the following:
- Choosing plants that are well-suited to your local climate and microclimate.
- Using mulch or row covers to regulate soil temperature and conserve moisture.
- Installing a rainwater collection system to ensure a consistent water supply during dry spells.
- Constructing windbreaks or shade structures to protect plants from strong winds or intense sunlight.
Limited Space
Space constraints are common in urban or small-scale gardens. To maximize your growing area, consider the following:
- Using vertical gardening techniques, such as trellises or wall-mounted planters, to grow vining plants upward.
- Implementing square-foot gardening, which divides the garden into small, densely planted squares to optimize space usage.
- Growing plants in containers or raised beds, which can be placed on balconies, patios, or rooftops.
Insufficient Sunlight
Most garden fruits and vegetables require at least six hours of direct sunlight each day. If your garden receives limited sunlight, consider the following:
- Planting shade-tolerant crops, such as lettuce, spinach, or herbs, which can thrive in partial shade.
- Trimming or pruning nearby trees or structures to increase sunlight exposure.
- Relocating the garden to a sunnier spot, if possible.
Nutrient Deficiencies
Plant nutrient deficiencies can lead to stunted growth, yellowing leaves, or poor yields. To ensure your garden fruits and vegetables receive adequate nutrients, consider the following:
- Conducting a soil test to determine the nutrient levels and pH of your garden soil.
- Amending the soil with organic matter, such as compost or aged manure, to improve fertility and structure.
- Applying targeted fertilizers, based on your soil test results, to address specific nutrient deficiencies.
By understanding and addressing these common challenges, you can create a thriving garden filled with delicious, nutritious garden fruits and vegetables. Remember that patience, persistence, and continuous learning are essential components of successful gardening. Happy growing!




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/vegetable-gardening-in-small-spaces-1403451-containers-38fba88c8dd1449596b756304cae86cb.jpg)


