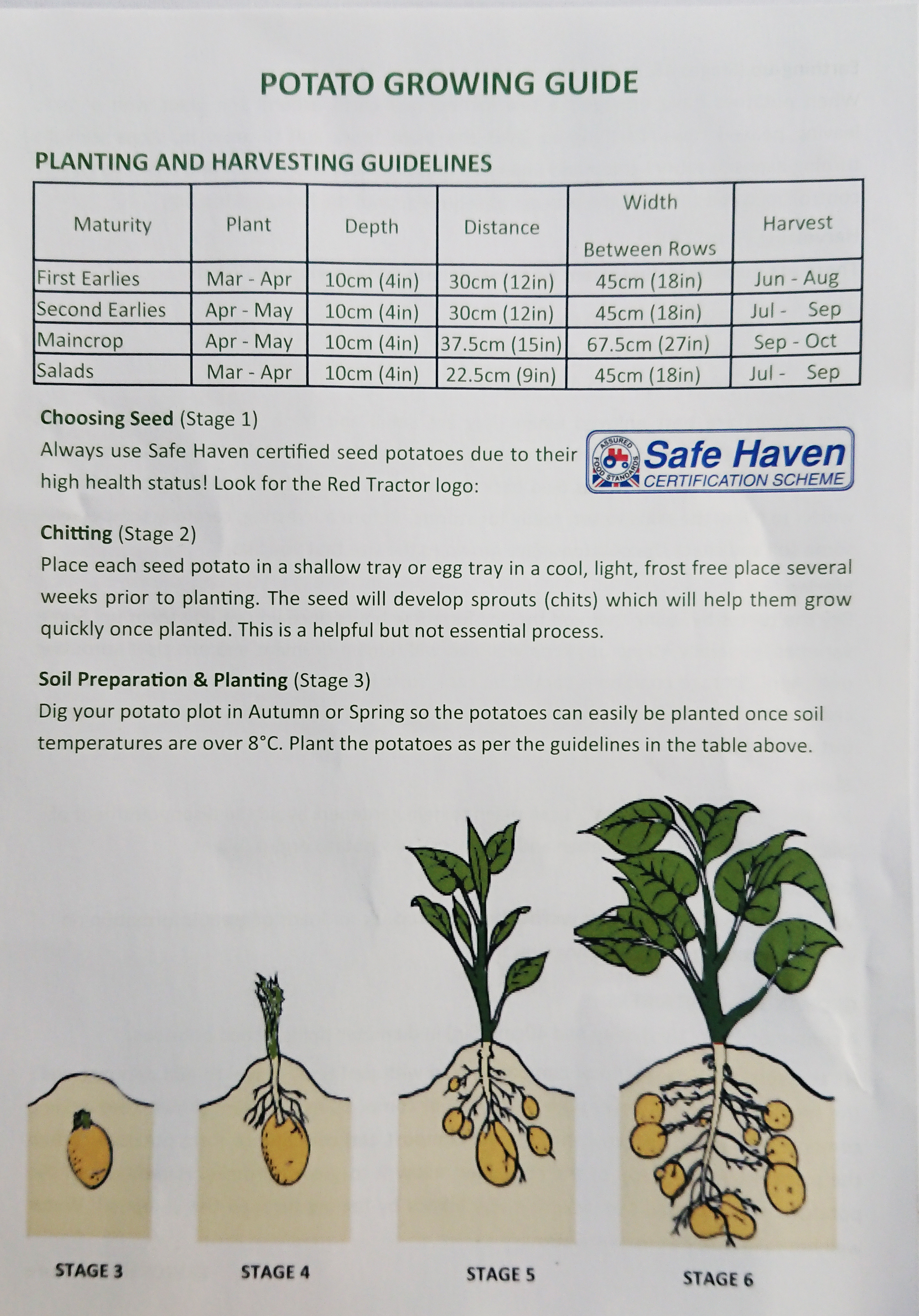
Understanding the Anatomy of a Potato Plant
Potato plants are fascinating organisms that have been a staple crop for centuries. To understand how deep potatoes grow, it’s essential to comprehend the basic structure of a potato plant. The plant consists of a stem, leaves, roots, and tubers. The stem, also known as the haulm, is the above-ground part of the plant that produces leaves and flowers. The leaves are responsible for photosynthesis, while the roots absorb water and nutrients from the soil. The tubers, which are the edible part of the plant, grow underground and can vary in depth depending on factors such as soil type, climate, and variety.
The growth and development of a potato plant are closely tied to the depth of the tubers. As the plant grows, the stem and leaves above ground produce energy through photosynthesis, which is then transferred to the roots and tubers below ground. The roots grow downward, anchoring the plant and absorbing water and nutrients, while the tubers grow outward and upward, producing new tubers and increasing the yield. Understanding the anatomy of a potato plant is crucial for optimizing growing conditions and maximizing yield.
So, how deep do potatoes grow? The answer depends on various factors, including the variety of potato, soil type, and climate. On average, potato tubers can grow anywhere from 6 to 12 inches deep, with some varieties growing even deeper. However, the depth of the tubers is not the only factor that determines the yield and quality of the potatoes. Other factors, such as soil moisture, temperature, and nutrient availability, also play a critical role in determining the success of the crop.
Factors Affecting Potato Depth: Soil, Climate, and Variety
When it comes to understanding how deep potatoes grow, it’s essential to consider the various factors that influence tuber depth. Soil type, climate, and potato variety are three critical factors that interact and impact the growth of potatoes. Soil type, for instance, plays a significant role in determining tuber depth. Well-draining, loose soils tend to promote deeper root growth, while heavy, compacted soils can limit root depth. Climate also affects tuber depth, with cooler temperatures and adequate moisture promoting deeper root growth.
Potato variety is another crucial factor that influences tuber depth. Different varieties have varying growth habits, and some are bred specifically for deeper or shallower root growth. For example, some varieties like ‘Russet’ and ‘Shepody’ tend to produce deeper tubers, while others like ‘Red Pontiac’ and ‘Yukon Gold’ produce shallower tubers. Understanding the specific growth habits of your chosen variety is essential for optimizing growing conditions and maximizing yield.
Soil pH, nutrient availability, and moisture levels also impact tuber depth. Potatoes prefer a slightly acidic to neutral soil pH, ranging from 4.5 to 7.0. Adequate nutrient availability, particularly potassium and phosphorus, is also essential for promoting healthy root growth. Moisture levels also play a critical role, with consistent moisture promoting deeper root growth.
By understanding the complex interactions between soil type, climate, and potato variety, growers can optimize growing conditions to promote healthy root growth and maximize yield. Whether you’re a seasoned grower or just starting out, recognizing the factors that influence tuber depth is crucial for unlocking the secrets of potato growth and achieving success in the garden.
How to Determine the Optimal Depth for Your Potatoes
Determining the optimal depth for planting potatoes is crucial for maximizing yield and promoting healthy growth. To determine the optimal depth, it’s essential to assess soil conditions and choose the right variety for your specific climate and soil type. Start by evaluating the soil structure and texture. Well-draining, loose soils tend to promote deeper root growth, while heavy, compacted soils can limit root depth.
Next, consider the climate and weather patterns in your area. Cooler temperatures and adequate moisture promote deeper root growth, while hot and dry conditions can lead to shallower root growth. Choose a variety that is specifically bred for your climate and soil type. For example, if you have heavy clay soil, choose a variety that is tolerant of wet conditions, such as ‘Russet’ or ‘Shepody’.
When planting potatoes, it’s also essential to consider the depth of the seed piece. Seed pieces that are planted too deeply can lead to poor emergence and reduced yields, while those planted too shallowly can lead to greening and reduced quality. Aim to plant seed pieces 2-4 inches deep, depending on the variety and soil type.
In addition to soil conditions and variety selection, it’s also important to consider the use of mulch and other soil amendments to promote healthy growth. Mulch can help to retain moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature, all of which can promote deeper root growth and maximize yield.
By following these guidelines and considering the specific needs of your potatoes, you can determine the optimal depth for planting and promote healthy growth and maximum yield. Remember, understanding how deep potatoes grow is just the first step in unlocking the secrets of potato growth and achieving success in the garden.
The Role of Root Depth in Potato Yield and Quality
Root depth plays a crucial role in determining potato yield and quality. Deeper roots can lead to better water and nutrient uptake, resulting in healthier and more productive plants. When roots grow deeper, they are able to access more nutrients and water, which can lead to increased yields and improved tuber quality.
Research has shown that potatoes with deeper roots tend to have higher yields and better tuber quality compared to those with shallower roots. This is because deeper roots are able to access more nutrients and water, which can lead to increased cell division and expansion, resulting in larger and more numerous tubers.
In addition to increased yields, deeper roots can also lead to improved tuber quality. When roots grow deeper, they are able to access more nutrients and water, which can lead to improved tuber texture and flavor. This is because the increased nutrient and water uptake can lead to increased starch production, resulting in a more desirable tuber texture and flavor.
So, how deep do potatoes grow? The depth of potato roots can vary depending on factors such as soil type, climate, and variety. However, in general, potato roots can grow anywhere from 6 to 12 inches deep, with some varieties growing even deeper. By understanding the role of root depth in potato yield and quality, growers can optimize growing conditions to promote healthy root growth and maximize yields.
Optimizing root depth can be achieved through a variety of techniques, including the use of mulch and other soil amendments to promote healthy growth. By creating a favorable soil environment, growers can encourage deeper root growth, leading to increased yields and improved tuber quality.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Planting Potatoes
When planting potatoes, it’s essential to avoid common mistakes that can impact tuber growth and yield. One of the most common mistakes is planting potatoes too deeply or too shallowly. Planting too deeply can lead to poor emergence and reduced yields, while planting too shallowly can lead to greening and reduced quality.
Another common mistake is not providing adequate soil conditions. Potatoes require well-draining, loose soil to grow, and compacted or waterlogged soil can lead to poor growth and reduced yields. Additionally, failing to provide adequate nutrients and water can also impact tuber growth and yield.
So, how can you avoid these mistakes and optimize potato growth? First, make sure to plant potatoes at the correct depth. The ideal planting depth will depend on the variety and soil type, but a general rule of thumb is to plant seed pieces 2-4 inches deep. Next, ensure that the soil is well-draining and loose, and provide adequate nutrients and water throughout the growing season.
It’s also essential to choose the right variety for your specific climate and soil type. Some varieties are more tolerant of wet or dry conditions, while others are more susceptible to disease. By choosing the right variety, you can optimize tuber growth and yield, and reduce the risk of common mistakes.
Finally, make sure to monitor soil conditions and adjust as necessary. Keep an eye on soil moisture and temperature, and adjust irrigation and fertilization accordingly. By taking these steps, you can avoid common mistakes and optimize potato growth, leading to a bountiful harvest and delicious, nutritious tubers.
Maximizing Potato Yield: Tips for Deep Planting
Deep planting is a technique that can help maximize potato yield by creating a favorable soil environment for tuber growth. When potatoes are planted deeply, the soil above the tubers acts as a blanket, regulating soil temperature and moisture levels. This can lead to improved tuber growth and increased yields.
So, how can you use deep planting to maximize potato yield? First, make sure to plant seed pieces at the correct depth. The ideal planting depth will depend on the variety and soil type, but a general rule of thumb is to plant seed pieces 4-6 inches deep. Next, use mulch and other soil amendments to promote healthy growth. Mulch can help retain moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature, all of which can lead to improved tuber growth.
Another key factor in maximizing potato yield through deep planting is soil preparation. Make sure the soil is well-draining and loose, and add organic matter such as compost or manure to improve soil fertility. This will help create a favorable environment for tuber growth and increase yields.
In addition to soil preparation and mulching, there are several other techniques you can use to maximize potato yield through deep planting. One technique is to use a technique called “hilling,” where soil is mounded up around the base of the plants as they grow. This can help create a favorable environment for tuber growth and increase yields.
Finally, make sure to monitor soil conditions and adjust as necessary. Keep an eye on soil moisture and temperature, and adjust irrigation and fertilization accordingly. By following these tips and techniques, you can maximize potato yield through deep planting and enjoy a bountiful harvest of delicious, nutritious tubers.
Exploring the Science Behind Potato Growth and Development
Potato growth and development are complex processes that involve the interaction of multiple factors, including hormones, nutrients, and environmental conditions. Understanding the science behind potato growth can help growers optimize growing conditions and improve yields.
One of the key factors that affects potato growth is the hormone auxin. Auxin is a plant hormone that plays a crucial role in cell elongation and cell division. It is produced in the apical meristem, the growing tip of the plant, and is transported down the stem to the roots, where it promotes cell elongation and cell division.
Nutrients also play a critical role in potato growth and development. Potatoes require a range of nutrients, including nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, to grow and develop. These nutrients are absorbed by the roots and transported to the rest of the plant, where they are used to support growth and development.
Environmental conditions, such as temperature and light, also affect potato growth and development. Potatoes grow best in cool, moist conditions, and are sensitive to extreme temperatures and light levels. Understanding how these environmental conditions affect potato growth can help growers optimize growing conditions and improve yields.
In addition to these factors, the depth at which potatoes grow also affects their growth and development. Potatoes that are grown at a depth of 6-8 inches tend to produce more tubers and have a higher yield than those grown at a shallower depth. This is because the deeper soil provides a more stable and favorable environment for tuber growth.
By understanding the science behind potato growth and development, growers can optimize growing conditions and improve yields. This includes providing the right nutrients, environmental conditions, and depth for potato growth, as well as using techniques such as deep planting and mulching to promote healthy growth.
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Growing Potatoes
Growing potatoes can be a rewarding and delicious experience, but it requires a deep understanding of the factors that affect tuber depth and yield. By understanding the anatomy of a potato plant, the factors that influence potato depth, and the role of root depth in potato yield and quality, growers can optimize growing conditions and improve yields.
Additionally, by avoiding common mistakes and using techniques such as deep planting and mulching, growers can promote healthy growth and maximize potato yield. By exploring the science behind potato growth and development, growers can gain a deeper understanding of the complex processes that affect tuber depth and yield.
In conclusion, growing potatoes is an art that requires patience, knowledge, and practice. By following the tips and guidelines outlined in this article, growers can master the art of growing potatoes and enjoy a bountiful harvest of delicious, nutritious tubers. Whether you’re a seasoned grower or just starting out, understanding how deep potatoes grow and how to optimize growing conditions is key to success.
So, how deep do potatoes grow? The answer depends on a variety of factors, including soil type, climate, and potato variety. By understanding these factors and using the techniques outlined in this article, growers can optimize growing conditions and improve yields. Happy growing!