Preparing the Perfect Soil for Your Vegetable Garden
When it comes to growing a thriving vegetable garden, the foundation of success lies in the soil. Preparing the perfect soil is crucial for optimal vegetable growth, and it’s essential to understand the importance of soil preparation for a successful harvest. The key to achieving a nutrient-rich soil mix is to test the soil pH and amend it with organic matter.
Soil pH is a critical factor in determining the availability of essential nutrients for your vegetables. Most vegetables prefer a slightly acidic to neutral soil pH, ranging from 6.0 to 7.0. To test your soil pH, you can purchase a soil testing kit or send a sample to a laboratory for analysis. Based on the results, you can adjust the soil pH by adding lime to raise it or sulfur to lower it.
Amending the soil with organic matter is another vital step in creating a nutrient-rich soil mix. Organic matter such as compost, well-rotted manure, or peat moss can help improve soil structure, increase the water-holding capacity, and provide essential nutrients for your vegetables. To incorporate organic matter into your soil, mix 2-4 inches of the material into the top 6-8 inches of soil.
By preparing the perfect soil for your vegetable garden, you’ll be able to provide your plants with the necessary nutrients for optimal growth. This, in turn, will help you achieve a bountiful harvest and make the process of learning how to plant vegetables a rewarding experience. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just starting out, taking the time to prepare your soil will pay off in the long run.
Choosing the Right Vegetables for Your Climate and Space
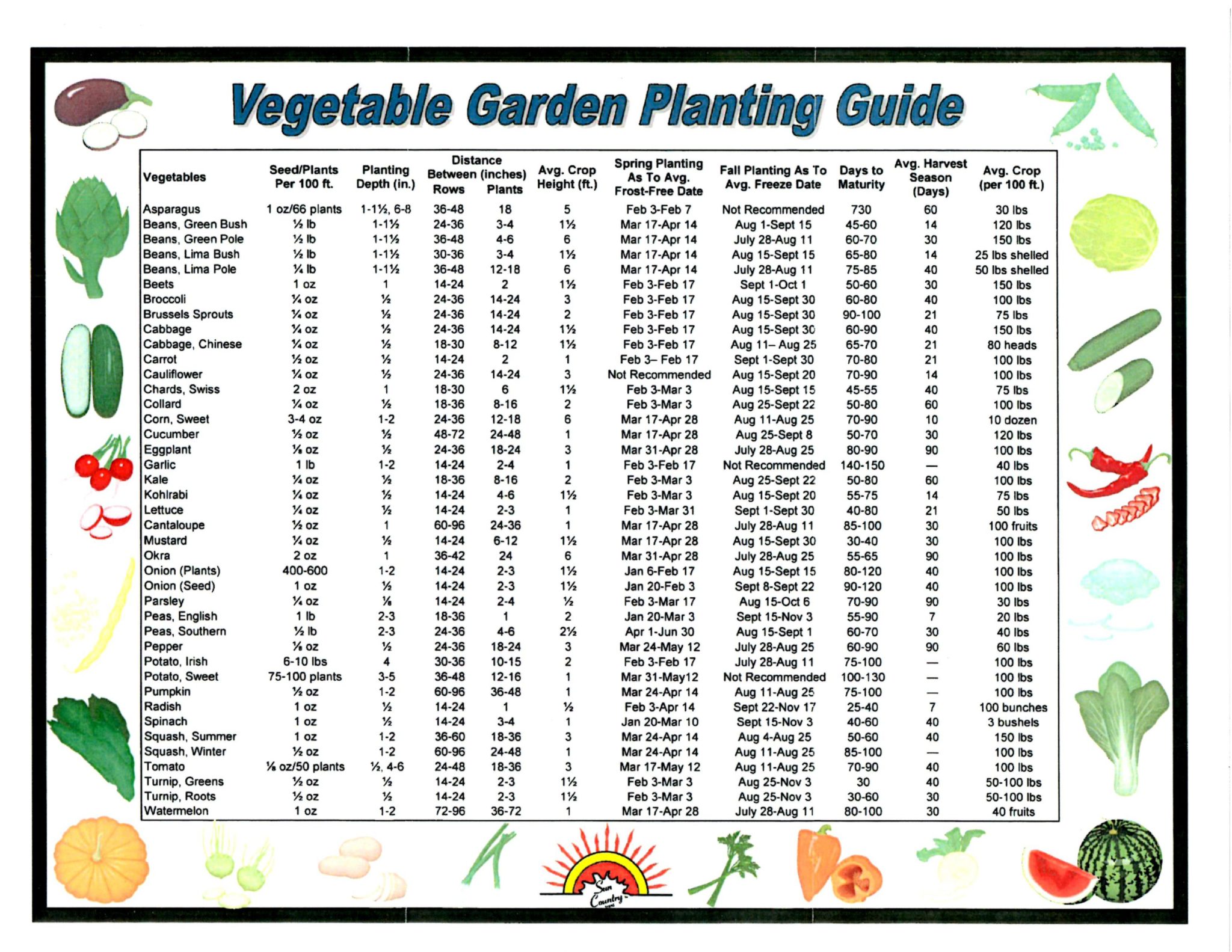
When it comes to planting vegetables, selecting the right varieties for your climate and available space is crucial for a successful harvest. Different vegetables have unique requirements for sunlight, temperature, and moisture, so it’s essential to choose varieties that are well-suited to your region’s conditions.
Start by researching the average temperature and precipitation patterns in your area. This will help you determine which vegetables are most likely to thrive in your climate. For example, cool-season crops like broccoli and kale do well in temperate climates with moderate temperatures, while warm-season crops like tomatoes and peppers require warmer temperatures and more sunlight.
In addition to climate, consider the amount of space you have available for your vegetable garden. Some vegetables, like leafy greens and herbs, can be grown in small spaces and can even be cultivated in containers. Others, like vining peas and cucumbers, require more space to spread out and may need to be trellised or staked.
When selecting vegetables for your garden, also consider factors like days to maturity, growth habits, and disease resistance. Days to maturity refers to the number of days it takes for a vegetable to mature from sowing the seeds. Growth habits refer to the way a vegetable grows, such as upright, sprawling, or vining. Disease resistance is also an important consideration, as some vegetables are more prone to certain diseases than others.
By choosing the right vegetables for your climate and space, you’ll be well on your way to growing a thriving and productive vegetable garden. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced gardener, selecting the right varieties will help you achieve a bountiful harvest and make the process of learning how to plant vegetables a rewarding experience.
How to Plant Vegetable Seeds for Optimal Growth
Planting vegetable seeds is a crucial step in starting a successful garden. To ensure optimal growth, it’s essential to follow proper planting techniques. When learning how to plant vegetables, it’s essential to understand the importance of sowing seeds at the correct depth, spacing, and watering techniques.
The first step in planting vegetable seeds is to prepare the soil. Make sure the soil is loose and well-draining, and that the area is clear of debris. Next, read the seed package or consult a gardening guide to determine the correct sowing depth for the specific variety of vegetable you are planting. Generally, seeds should be sown at a depth of 2-3 times their diameter.
Once you have determined the correct sowing depth, use a garden tool or your fingers to create a small hole in the soil. Place the seed in the hole and cover it with soil. Firm the soil gently to ensure good contact between the seed and the soil.
Spacing is also critical when planting vegetable seeds. Different varieties of vegetables have different spacing requirements, so make sure to check the seed package or consult a gardening guide. Generally, seeds should be spaced 1-3 inches apart, depending on the variety.
After planting the seeds, water the soil gently but thoroughly. Make sure the soil is consistently moist during the first few weeks after planting. As the seeds germinate and grow, you can gradually reduce the frequency of watering.
Proper seed placement and soil coverage are also essential for optimal growth. Make sure the seeds are planted at the correct depth and that the soil is covering the seeds evenly. This will help to prevent washing away of the seeds and ensure that they receive adequate moisture and nutrients.
By following these simple steps and techniques, you can ensure that your vegetable seeds are planted correctly and have the best chance of optimal growth. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced gardener, learning how to plant vegetables is a crucial step in starting a successful garden.
Transplanting Seedlings: Tips for a Smooth Transition
Transplanting seedlings is a critical step in the process of growing vegetables. When done correctly, it can help seedlings thrive and increase their chances of survival. However, when done incorrectly, it can lead to transplant shock, which can be detrimental to the health of the seedlings.
To minimize transplant shock, it’s essential to harden off seedlings before transplanting them into larger containers or directly into the garden. Hardening off involves gradually exposing seedlings to outdoor conditions, such as sunlight, wind, and temperature fluctuations, over the course of 7-10 days. This helps seedlings develop a stronger root system and increases their tolerance to stress.
When transplanting seedlings, it’s also crucial to handle the roots with care. Gently remove the seedlings from their containers, taking care not to disturb the roots. If the roots are wrapped in a soilless mix, gently loosen the mix to prevent damaging the roots.
When placing the seedlings in their new containers or in the garden, make sure the soil is moist but not waterlogged. Water the seedlings gently but thoroughly after transplanting, and keep the soil consistently moist during the first few weeks after transplanting.
Minimizing transplant shock is also essential for the health and well-being of the seedlings. To do this, transplant seedlings in the early morning or late evening when the sun is not intense. Avoid transplanting seedlings during periods of extreme weather, such as intense heat or cold.
By following these tips and techniques, you can ensure a smooth transition for your seedlings and help them thrive in their new environment. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced gardener, learning how to transplant seedlings is an essential skill for growing healthy and productive vegetables.
Watering and Mulching: Essential Techniques for Healthy Vegetable Growth
Watering and mulching are two essential techniques for promoting healthy vegetable growth. Proper watering techniques can help prevent overwatering, which can lead to root rot and other problems. Mulching, on the other hand, can help retain moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature.
When it comes to watering, it’s essential to understand the specific needs of your vegetables. Different vegetables have different watering requirements, so make sure to research the specific needs of your plants. Generally, vegetables need about 1-2 inches of water per week, either from rainfall or irrigation.
To conserve water, consider using drip irrigation or soaker hoses, which deliver water directly to the roots of the plants. Avoid overhead watering, which can lead to evaporation and runoff. Also, water your vegetables in the morning or early afternoon to allow the plants to absorb the water throughout the day.
Mulching is another essential technique for promoting healthy vegetable growth. Organic mulch, such as straw, bark chips, or grass clippings, can help retain moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature. Apply a 2-3 inch layer of mulch around your vegetables, keeping it a few inches away from the plant stems.
Some of the benefits of mulching include reduced soil temperature, improved soil structure, and increased water retention. Mulching can also help suppress weeds, which can compete with your vegetables for water and nutrients.
By incorporating proper watering and mulching techniques into your vegetable gardening routine, you can promote healthy growth and maximize your harvest. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced gardener, learning how to plant vegetables and care for them properly is essential for success.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Planting Vegetables
When it comes to planting vegetables, there are several common mistakes that can lead to poor growth, reduced yields, and even plant death. By understanding these mistakes and taking steps to avoid them, you can ensure a successful and productive vegetable garden.
One of the most common mistakes is inadequate soil preparation. This can include failing to test the soil pH, not adding organic matter, and not removing debris and rocks. To avoid this mistake, make sure to test your soil pH and amend it if necessary, add organic matter such as compost or manure, and remove any debris and rocks from the soil.
Another common mistake is insufficient sunlight. Most vegetables require at least 6 hours of direct sunlight per day, so make sure to choose a location that receives sufficient sunlight. If you’re planting in a location with partial shade, choose varieties that are tolerant of shade.
Poor spacing is another common mistake. Planting vegetables too close together can lead to reduced air circulation, increased disease risk, and reduced yields. Make sure to follow the recommended spacing guidelines for each variety of vegetable you’re planting.
Overwatering is another common mistake that can lead to root rot, nutrient deficiencies, and other problems. Make sure to water your vegetables deeply but infrequently, and avoid getting water on the leaves to prevent fungal diseases.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can ensure a successful and productive vegetable garden. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced gardener, learning how to plant vegetables and avoid common mistakes is essential for success.
Vegetable Garden Maintenance: Keeping Your Plants Healthy and Thriving
Once your vegetable garden is established, it’s essential to maintain it regularly to ensure healthy and thriving plants. Regular maintenance includes fertilization, pruning, and pest management.
Fertilization is an essential part of vegetable garden maintenance. Vegetables require a balanced diet of nutrients to grow and thrive. Use a balanced fertilizer that contains nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. Follow the instructions on the fertilizer package for application rates and timing.
Pruning is another important aspect of vegetable garden maintenance. Pruning helps to promote healthy growth, increase yields, and prevent disease. Remove any dead or diseased leaves or stems, and trim back overgrown plants to encourage bushy growth.
Pest management is also crucial for maintaining a healthy vegetable garden. Keep an eye out for common pests like aphids, whiteflies, and spider mites. Use organic or integrated pest management methods to control infestations, such as introducing beneficial insects or using neem oil.
Regular monitoring is also essential for maintaining a healthy vegetable garden. Keep an eye out for signs of disease, pests, or nutrient deficiencies. Take prompt action to address any issues that arise, and make adjustments to your maintenance routine as needed.
By following these maintenance tips, you can keep your vegetable garden healthy and thriving. Remember to stay vigilant and take prompt action to address any issues that arise. With regular maintenance, you can enjoy a bountiful harvest of delicious and nutritious homegrown vegetables.
Enjoying the Fruits of Your Labor: Harvesting Your Homegrown Vegetables
After weeks of careful planning, planting, and tending, the moment of truth has finally arrived: it’s time to harvest your homegrown vegetables Harvesting is a crucial step in the gardening process, and it’s essential to do it correctly to ensure the best flavor, texture, and nutritional value.
Before you start harvesting, make sure to check the specific instructions for each variety of vegetable you’re growing. Some vegetables, like tomatoes and peppers, are ready to pick when they’re fully ripe, while others, like broccoli and cauliflower, are best harvested when they’re still slightly immature.
When harvesting, handle the produce gently to avoid bruising or damaging it. Use scissors or a sharp knife to cut the vegetables from the plant, leaving a small piece of stem attached to the plant. This will help the plant to continue producing new growth.
Once you’ve harvested your vegetables, enjoy them fresh, or store them in a cool, dry place to keep them fresh for longer. Consider sharing your bounty with friends and family, or preserving some of your harvest through canning, freezing, or dehydrating.
Harvesting your homegrown vegetables is a rewarding experience that’s sure to bring a sense of pride and accomplishment. By following these tips and techniques, you can enjoy the fruits of your labor and savor the delicious flavors of your homegrown produce.




/Containergarden-GettyImages-155360996-5a0917a1ec2f640036a63a1b.jpg)

