Understanding the Importance of Pruning Your Rose Bushes
Pruning rose bushes is an essential gardening technique that promotes healthy growth, encourages blooming, and maintains shape. By removing dead, diseased, or damaged branches, pruning helps prevent disease and pest issues that can harm the plant. Regular pruning also allows for better air circulation, which can help prevent fungal diseases that thrive in humid environments. Furthermore, pruning stimulates the plant to produce new growth, leading to more vigorous and productive rose bushes.
When pruning rose bushes, it’s essential to consider the type of rose and its growth habits. For example, hybrid tea and grandiflora roses require more extensive pruning to maintain their shape and promote blooming, while floribunda and shrub roses require less pruning to maintain their natural shape. Climbing roses, on the other hand, require pruning to control their growth and encourage blooming.
Pruning rose bushes also helps to control their size and shape, making them more manageable in small gardens or containers. By pruning regularly, gardeners can encourage their rose bushes to grow in a more compact and bushy shape, making them ideal for hedges or borders.
In addition to promoting healthy growth and blooming, pruning rose bushes can also help to increase their lifespan. By removing dead and diseased branches, pruning helps to prevent the spread of disease and encourages the plant to produce new growth, leading to a longer and healthier life.
While pruning rose bushes may seem intimidating, it’s a relatively simple process that requires minimal equipment and expertise. With the right techniques and tools, gardeners can prune their rose bushes with confidence, knowing that they are promoting healthy growth and blooming.
How to Prepare Your Rose Bushes for Pruning
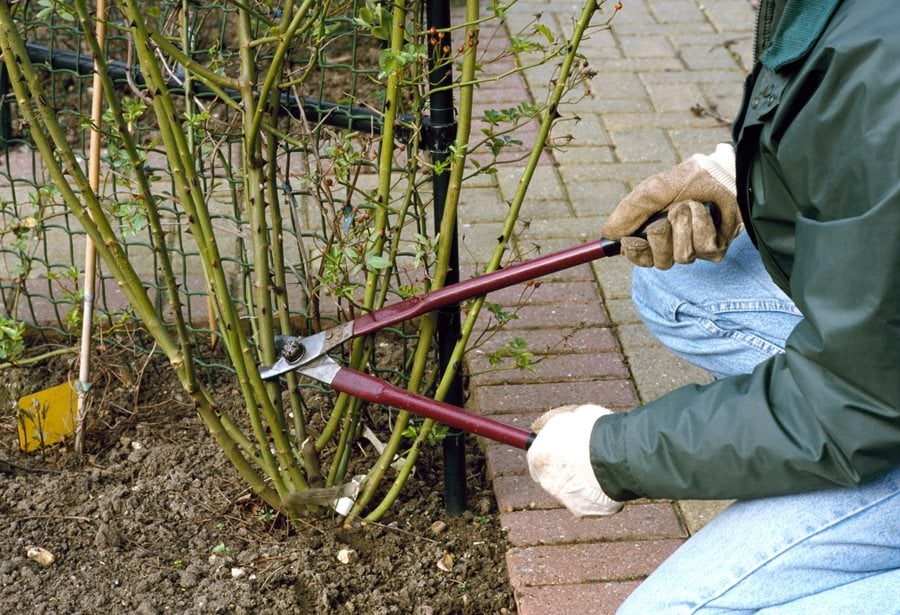
Before pruning your rose bushes, it’s essential to prepare them properly to ensure a safe and effective pruning process. Start by removing any dead, diseased, or damaged branches, as these can be a haven for pests and diseases. Use a pair of sharp, clean pruning shears or loppers to make clean cuts, and remove any weak or spindly growth.
Next, inspect your rose bushes for any signs of disease or pests, such as black spot, powdery mildew, or aphids. If you notice any issues, treat the plant with a fungicide or insecticide before pruning to prevent the spread of disease.
It’s also crucial to clean and disinfect your pruning tools before and after use to prevent the spread of disease. Use a mixture of one part bleach to nine parts water to disinfect your tools, and dry them thoroughly before storing.
Finally, consider the type of rose bush you are pruning and the time of year. Different types of rose bushes have different pruning requirements, and pruning at the wrong time can cause stress to the plant. For example, hybrid tea and grandiflora roses require more extensive pruning in the dormant season, while floribundas and shrub roses require less pruning.
By preparing your rose bushes properly before pruning, you can ensure a safe and effective pruning process that promotes healthy growth and blooming. Remember to always use clean and sharp pruning tools, and to prune at the right time for your specific type of rose bush.
The Art of Cutting Back Rose Bushes: A Step-by-Step Guide
Cutting back rose bushes is an art that requires patience, skill, and attention to detail. To ensure a successful pruning process, follow these step-by-step guidelines:
Step 1: Identify the Right Branches to Cut
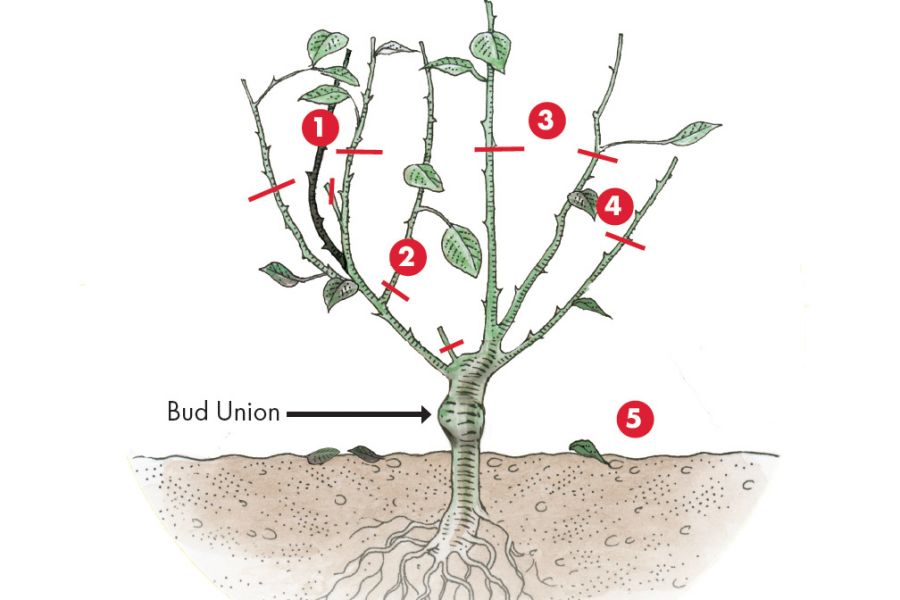
Begin by inspecting your rose bush and identifying the branches that need to be cut. Look for dead, diseased, or damaged branches, as well as any weak or spindly growth. Remove these branches first, as they can be a haven for pests and diseases.
Step 2: Make Clean Cuts
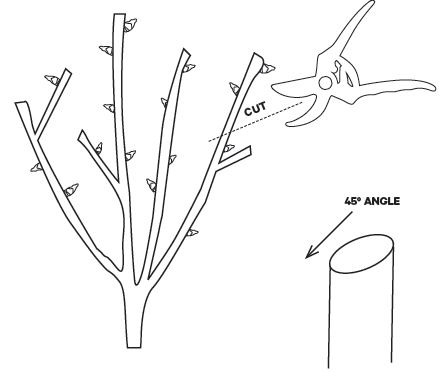
Use a pair of sharp, clean pruning shears or loppers to make clean cuts. Cut the branches at a 45-degree angle, about 1/4 inch above a bud eye. This will help the plant heal quickly and reduce the risk of disease.
Step 3: Shape the Plant
Once you have removed the dead, diseased, or damaged branches, shape the plant to maintain its natural shape and promote healthy growth. Cut back the tips of the branches to encourage branching and promote blooming.
Step 4: Check for Suckers
Check the base of the plant for suckers, which are shoots that grow from the base of the plant. Remove these suckers, as they can take energy away from the rest of the plant.
Step 5: Inspect and Repeat
Inspect your rose bush regularly to ensure that it is healthy and thriving. Repeat the pruning process as necessary to maintain the plant’s shape and promote healthy growth.
By following these step-by-step guidelines, you can master the art of cutting back rose bushes and enjoy beautiful, blooming roses all season long. Remember to always use clean and sharp pruning tools, and to prune at the right time for your specific type of rose bush.
How Far to Cut Back Rose Bushes: A General Guide
When it comes to cutting back rose bushes, one of the most common questions is how far to cut back. The answer depends on the type of rose bush, its age, and its growth habits. Here are some general guidelines to help you determine how far to cut back your rose bushes:
For hybrid tea and grandiflora roses, cut back the canes to about 12-18 inches from the ground. This will help promote new growth and encourage blooming.
For floribunda and shrub roses, cut back the canes to about 6-12 inches from the ground. This will help maintain the plant’s shape and promote healthy growth.
For climbing roses, cut back the canes to about 3-6 feet from the ground. This will help control the plant’s growth and encourage blooming.
It’s also important to consider the age of the plant when determining how far to cut back. For young plants, it’s best to cut back the canes to about 6-12 inches from the ground to promote new growth and establishment.
For older plants, you can cut back the canes to about 12-18 inches from the ground to maintain the plant’s shape and promote healthy growth.
Remember to always make clean cuts, and to cut just above a bud eye. This will help the plant heal quickly and reduce the risk of disease.
By following these general guidelines, you can determine how far to cut back your rose bushes and promote healthy growth and blooming. Remember to always consider the specific needs of your plant, and to prune at the right time for optimal results.
Pruning Different Types of Rose Bushes: What You Need to Know
When it comes to pruning rose bushes, different types of roses have different pruning needs. Understanding these needs is crucial to promote healthy growth, encourage blooming, and maintain the shape of your rose bushes.
Hybrid Tea Roses: These roses are known for their large, repeat-flowering blooms. To prune hybrid tea roses, cut back the canes to about 12-18 inches from the ground. Remove any dead, diseased, or damaged branches, and shape the plant to maintain its natural shape.
Floribunda Roses: These roses are known for their clusters of blooms. To prune floribunda roses, cut back the canes to about 6-12 inches from the ground. Remove any dead, diseased, or damaged branches, and shape the plant to maintain its natural shape.
Climbing Roses: These roses are known for their long, trailing canes. To prune climbing roses, cut back the canes to about 3-6 feet from the ground. Remove any dead, diseased, or damaged branches, and shape the plant to maintain its natural shape.
Shrub Roses: These roses are known for their compact, bushy growth. To prune shrub roses, cut back the canes to about 6-12 inches from the ground. Remove any dead, diseased, or damaged branches, and shape the plant to maintain its natural shape.
English Roses: These roses are known for their old-world charm and fragrance. To prune English roses, cut back the canes to about 12-18 inches from the ground. Remove any dead, diseased, or damaged branches, and shape the plant to maintain its natural shape.
By understanding the specific pruning needs of your rose bushes, you can promote healthy growth, encourage blooming, and maintain the shape of your plants. Remember to always prune at the right time, and to use clean and sharp pruning tools to prevent the spread of disease.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Pruning Rose Bushes
When pruning rose bushes, it’s easy to make mistakes that can harm the plant and reduce its blooming potential. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
Over-pruning: Pruning too much of the plant can cause stress and reduce blooming. Only remove what is necessary to maintain the plant’s shape and promote healthy growth.
Under-pruning: Not pruning enough can lead to a leggy, unproductive plant. Make sure to remove any dead, diseased, or damaged branches to promote healthy growth and blooming.
Pruning at the wrong time: Pruning at the wrong time can cause stress to the plant and reduce blooming. Prune in the dormant season or after blooming to minimize stress and promote healthy growth.
Not making clean cuts: Making clean cuts is essential to prevent the spread of disease and promote healthy growth. Use sharp, clean pruning tools and make cuts at a 45-degree angle.
Not removing suckers: Suckers are shoots that grow from the base of the plant and can take energy away from the rest of the plant. Remove suckers to promote healthy growth and blooming.
Not pruning for air circulation: Pruning for air circulation is essential to prevent disease and promote healthy growth. Remove any branches that are rubbing against each other or growing inward to promote air circulation.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can prune your rose bushes effectively and promote healthy growth and blooming. Remember to always prune with clean and sharp tools, and to prune at the right time for your specific type of rose bush.
After Pruning: How to Care for Your Rose Bushes
After pruning your rose bushes, it’s essential to provide them with the right care to promote healthy growth and blooming. Here are some tips on how to care for your rose bushes after pruning:
Watering: Water your rose bushes regularly, but make sure not to overwater. Aim to provide about 1-2 inches of water per week, either from rainfall or irrigation.
Fertilizing: Fertilize your rose bushes with a balanced fertilizer in the spring and again in the summer. This will provide them with the necessary nutrients to promote healthy growth and blooming.
Mulching: Mulch around the base of your rose bushes to retain moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature. Use a layer of 2-3 inches of organic mulch, such as wood chips or bark.
Deadheading: Remove any dead or spent blooms from your rose bushes to promote new blooming and prevent seed production.
Pest and disease control: Keep an eye out for pests and diseases, such as aphids, whiteflies, and black spot. Use organic or chemical controls as needed to prevent infestations and infections.
Pruning maintenance: Check your rose bushes regularly to ensure that they are not becoming too leggy or overgrown. Prune as needed to maintain their shape and promote healthy growth.
By following these tips, you can provide your rose bushes with the right care after pruning and promote healthy growth and blooming. Remember to always monitor your rose bushes for any signs of stress or disease, and take action promptly to prevent any issues.
After Pruning: How to Care for Your Rose Bushes
After pruning your rose bushes, it’s essential to provide them with the right care to promote healthy growth and blooming. Here are some tips on how to care for your rose bushes after pruning:
Watering: Water your rose bushes regularly, but make sure not to overwater. Aim to provide about 1-2 inches of water per week, either from rainfall or irrigation.
Fertilizing: Fertilize your rose bushes with a balanced fertilizer in the spring and again in the summer. This will provide them with the necessary nutrients to promote healthy growth and blooming.
Mulching: Mulch around the base of your rose bushes to retain moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature. Use a layer of 2-3 inches of organic mulch, such as wood chips or bark.
Deadheading: Remove any dead or spent blooms from your rose bushes to promote new blooming and prevent seed production.
Pest and disease control: Keep an eye out for pests and diseases, such as aphids, whiteflies, and black spot. Use organic or chemical controls as needed to prevent infestations and infections.
Pruning maintenance: Check your rose bushes regularly to ensure that they are not becoming too leggy or overgrown. Prune as needed to maintain their shape and promote healthy growth.
By following these tips, you can provide your rose bushes with the right care after pruning and promote healthy growth and blooming. Remember to always monitor your rose bushes for any signs of stress or disease, and take action promptly to prevent any issues.