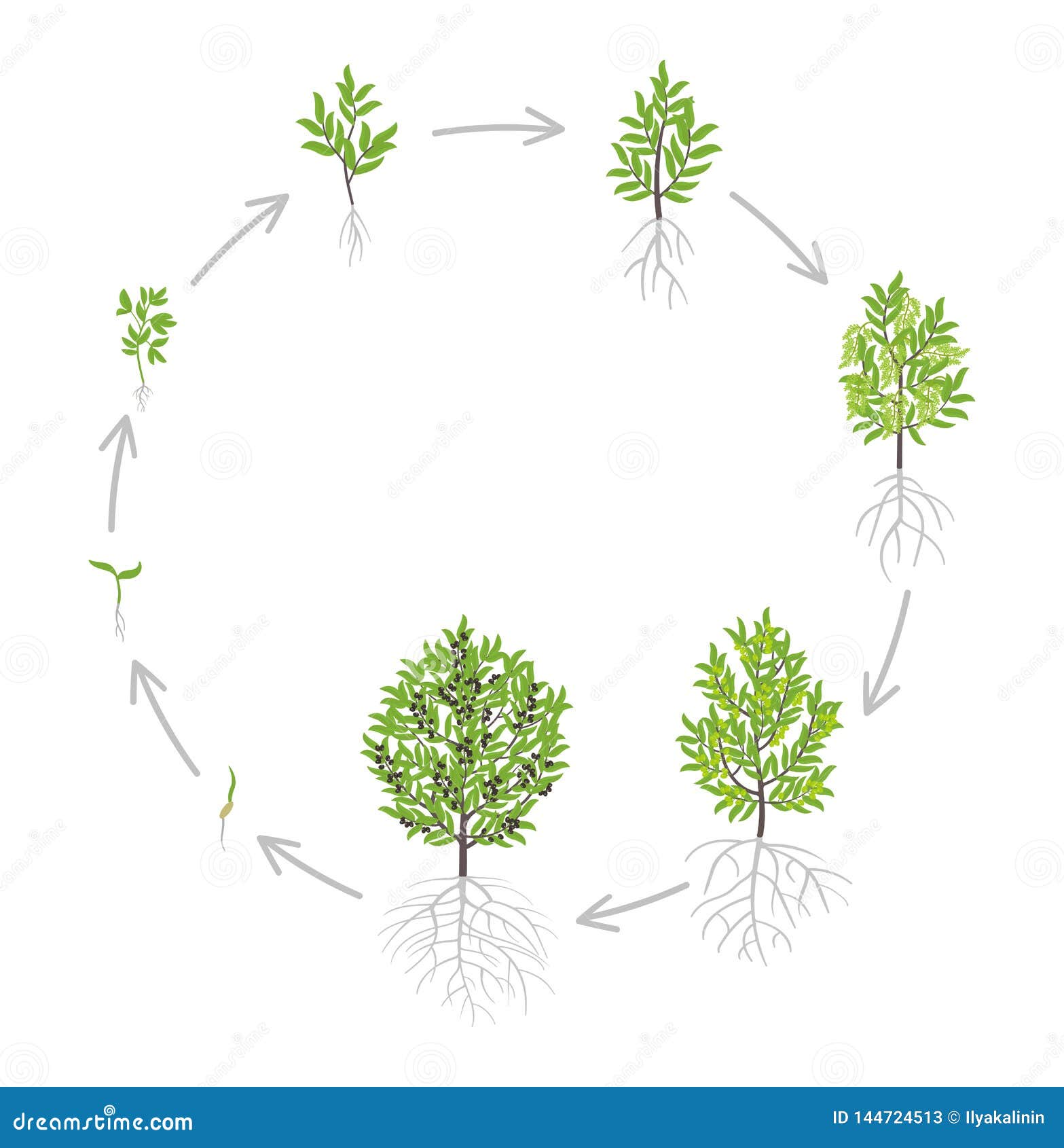
Understanding the Life Cycle of an Olive Tree
The life cycle of an olive tree is a complex and fascinating process that spans several decades. From germination to maturity, an olive tree undergoes significant transformations, influenced by various factors such as climate, soil quality, and genetics. The journey begins with a seedling, which takes root and develops into a sapling. As the tree grows, it reaches a juvenile stage, characterized by rapid growth and development. This stage is critical, as it lays the foundation for the tree’s future growth and productivity. Understanding the different stages of growth is essential in determining how long does a olive tree take to grow, as well as identifying potential challenges and opportunities for optimization. By grasping the olive tree’s life cycle, growers can provide targeted care and attention, ensuring their trees reach their full potential.
The Ideal Conditions for Olive Tree Growth
Olive trees thrive in specific conditions that mimic their natural Mediterranean habitat. To promote healthy growth and development, it’s essential to provide an olive tree with the right climate, soil, and watering conditions. A warm and sunny climate with mild winters and hot summers is ideal, as olive trees require a certain amount of chill hours to produce fruit. Soil quality is also crucial, with well-draining soil and a pH between 6.0 and 8.0 being optimal. Watering is critical, as olive trees require consistent moisture, especially during the first year after planting. Understanding these ideal conditions is vital in determining how long does a olive tree take to grow, as well as ensuring a strong and healthy tree. By replicating Mediterranean-like environments, growers can create an ideal setting for their olive trees to flourish.
How to Plant and Care for a Young Olive Tree
Planting and caring for a young olive tree requires attention to detail and a commitment to regular maintenance. To ensure a strong and healthy start, choose a location with full sun and well-draining soil. Dig a hole twice as wide and just as deep as the root ball, and gently remove the tree from its container. Place the tree in the hole, backfill with soil, and water thoroughly. Water regularly, especially during the first year, to establish a strong root system. Pruning is also essential, as it promotes healthy growth and encourages fruiting. Prune the tree annually to maintain a central leader, remove any dead or damaged branches, and shape the tree to allow for air circulation and sunlight penetration. Regular maintenance, including protection from pests and diseases, is crucial in determining how long does a olive tree take to grow and thrive. By following these steps, growers can set their young olive trees up for success and enjoy a bountiful harvest for years to come.
The Role of Pruning in Shaping Olive Tree Growth
Pruning is a crucial aspect of olive tree care, playing a vital role in shaping the tree’s growth, promoting healthy development, and increasing fruit production. By pruning an olive tree, growers can control its shape and size, encouraging a strong central leader and a well-balanced canopy. This, in turn, allows for better air circulation, sunlight penetration, and fruiting. Pruning also helps to remove any dead, diseased, or damaged branches, reducing the risk of pest and disease issues. Furthermore, pruning can influence how long does a olive tree take to grow, as it can stimulate or slow down growth depending on the technique and timing. For example, pruning during the dormant season can promote vigorous growth, while pruning during the active growing season can slow down growth. By understanding the importance of pruning and implementing a regular pruning schedule, growers can optimize their olive tree’s growth and productivity.
Factors Affecting Olive Tree Growth Rate
Several factors influence an olive tree’s growth rate, ultimately determining how long does a olive tree take to grow and thrive. Genetics play a significant role, with some olive tree varieties naturally growing faster than others. Climate is also a crucial factor, with olive trees growing more rapidly in regions with mild winters and warm summers. Soil quality is another essential factor, as olive trees require well-draining soil with a pH between 6.0 and 8.0 to grow optimally. Pest management is also critical, as pests like olive fruit fly and olive psyllid can significantly slow down growth. Additionally, factors like watering, fertilization, and pruning practices can impact an olive tree’s growth rate. For example, consistent and adequate watering can promote healthy growth, while over-fertilization can lead to weak and leggy growth. By understanding these factors and optimizing growing conditions, growers can encourage healthy and rapid growth, ultimately reducing the time it takes for an olive tree to mature.
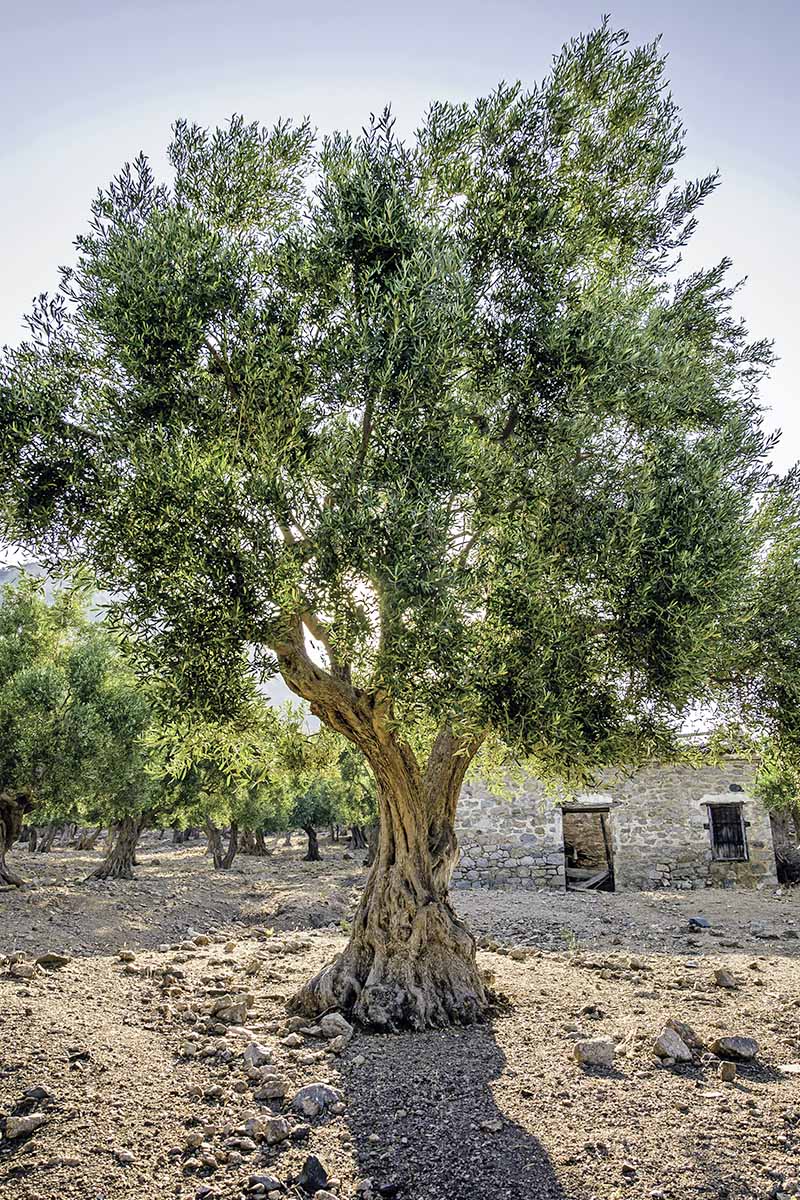
How Long Does it Take for an Olive Tree to Mature?
The time it takes for an olive tree to mature can vary significantly depending on several factors, including the tree’s variety, growing conditions, and care. On average, it can take anywhere from 3 to 10 years for an olive tree to reach maturity, with some trees taking up to 20 years. Factors such as climate, soil quality, and pruning practices can all impact how long does a olive tree take to grow and mature. For example, olive trees growing in ideal Mediterranean-like conditions with mild winters and warm summers may mature faster than those growing in cooler or more temperate climates. Additionally, regular pruning and proper care can help promote healthy growth and accelerate the maturation process. Understanding the factors that influence an olive tree’s growth rate and providing optimal growing conditions can help growers reduce the time it takes for their trees to mature and produce fruit.
Common Challenges and Solutions for Olive Tree Growth
Olive trees, like any other plant, can face various challenges that can hinder their growth and productivity. Pests, diseases, and nutrient deficiencies are some of the most common issues that olive tree growers may encounter. For instance, pests like olive fruit fly and olive psyllid can cause significant damage to the tree’s fruit and leaves, while diseases like olive knot and root rot can weaken the tree’s immune system. Nutrient deficiencies, particularly a lack of nitrogen, phosphorus, or potassium, can also impact an olive tree’s growth rate and overall health. To overcome these challenges, growers can implement preventative measures such as regular pruning, proper irrigation, and fertilization. Additionally, using organic pest control methods, like introducing beneficial insects, and applying fungicides can help mitigate the risk of pests and diseases. By being aware of these common challenges and taking proactive steps to address them, growers can promote healthy growth and maximize their olive tree’s productivity, ultimately reducing the time it takes for the tree to mature and produce a bountiful harvest.
Maximizing Olive Tree Productivity and Harvesting
To ensure a bountiful and healthy crop, olive tree growers must focus on optimizing their tree’s productivity. This can be achieved through a combination of proper fertilization, irrigation, and harvesting techniques. Fertilization, for instance, plays a crucial role in providing olive trees with the necessary nutrients for growth and fruit production. A balanced fertilizer with a mix of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium can help promote healthy growth and increase fruit yield. Irrigation is also essential, as olive trees require consistent moisture levels, especially during the fruiting stage. However, over-irrigation can be detrimental, so it’s essential to monitor soil moisture levels and adjust irrigation schedules accordingly. When it comes to harvesting, timing is everything. Olives should be picked at the optimal stage of ripeness to ensure maximum flavor and quality. By implementing these strategies, growers can maximize their olive tree’s productivity, reducing the time it takes for the tree to mature and produce a healthy crop. Additionally, regular pruning and pest management practices can also help promote healthy growth and increase fruit production, ultimately leading to a successful harvest.