Understanding the Onion Growth Cycle
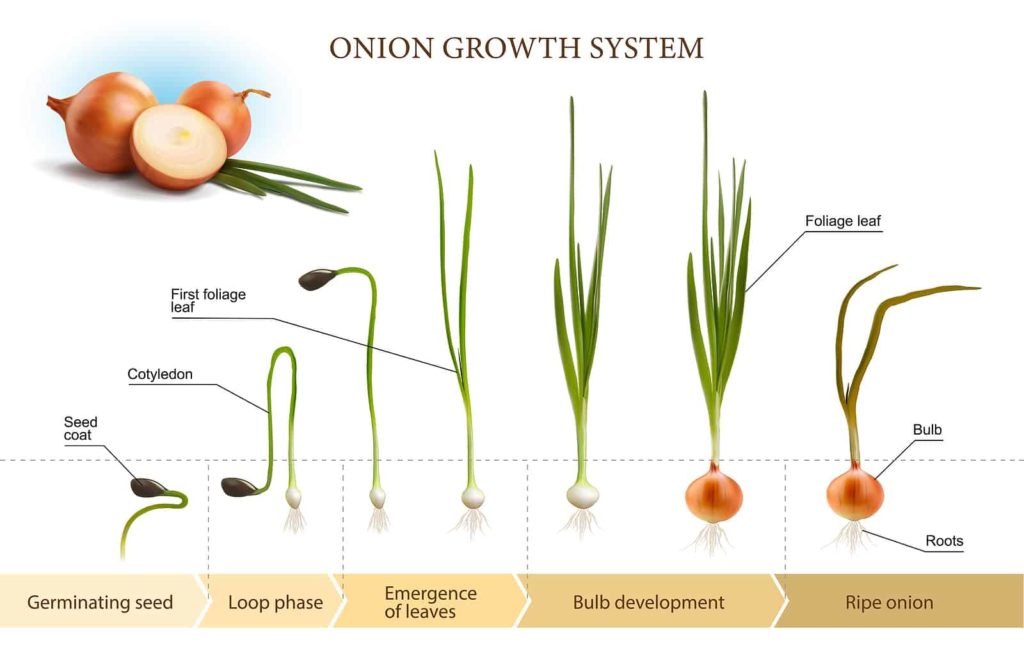
Onions are a fundamental ingredient in many cuisines, and their growth cycle is crucial for determining the time it takes for them to mature. The onion growth cycle consists of several stages, from seed germination to bulb formation. Understanding these stages is essential for gardeners and farmers to optimize growing conditions and ensure a successful harvest.
The onion growth cycle begins with seed germination, which typically occurs within 1-2 weeks after sowing. During this stage, the seedling develops its root system and the first set of leaves. As the plant grows, it enters the vegetative stage, where it produces more leaves and develops a robust root system. This stage usually lasts around 4-6 weeks.
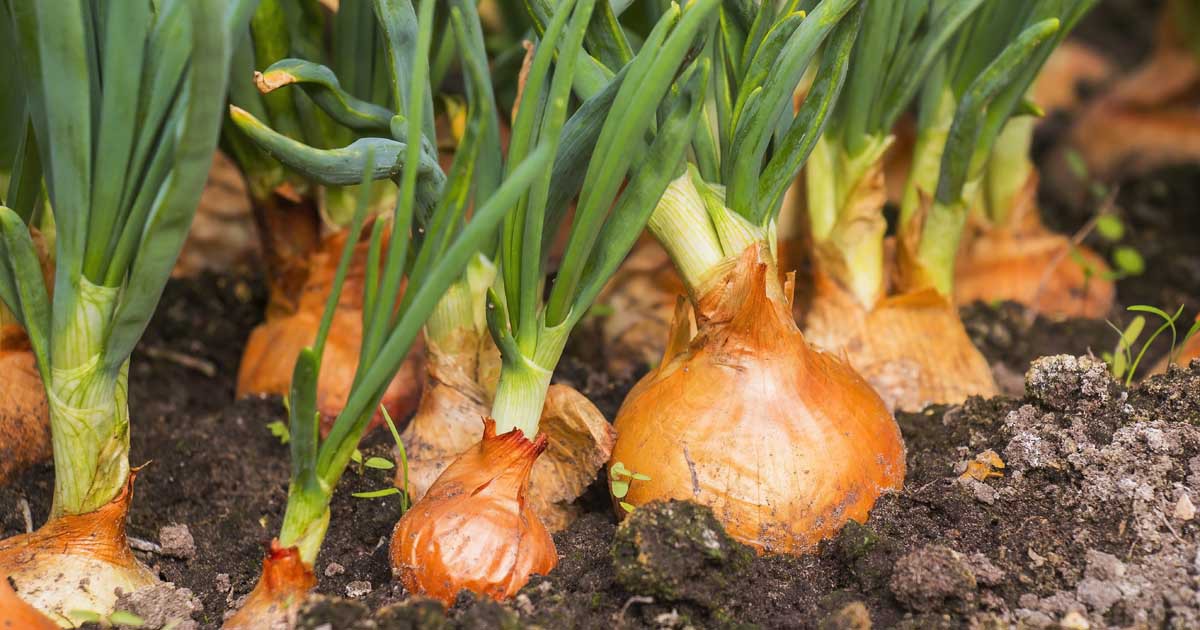
After the vegetative stage, the onion plant enters the reproductive stage, where it begins to form a bulb. This stage is triggered by the lengthening of daylight hours and warmer temperatures. The bulb formation stage typically lasts around 6-8 weeks, during which the onion plant focuses its energy on developing a large, flavorful bulb.
On average, it takes around 120 to 180 days for onions to mature from sowing to harvest. However, this timeframe can vary depending on factors such as weather conditions, soil quality, and variety selection. For example, some onion varieties, such as ‘Ebenezer’ and ‘Stuttgarter’, mature in as little as 90 days, while others, like ‘Yellow Granex’ and ‘Texas Grano’, take up to 210 days.
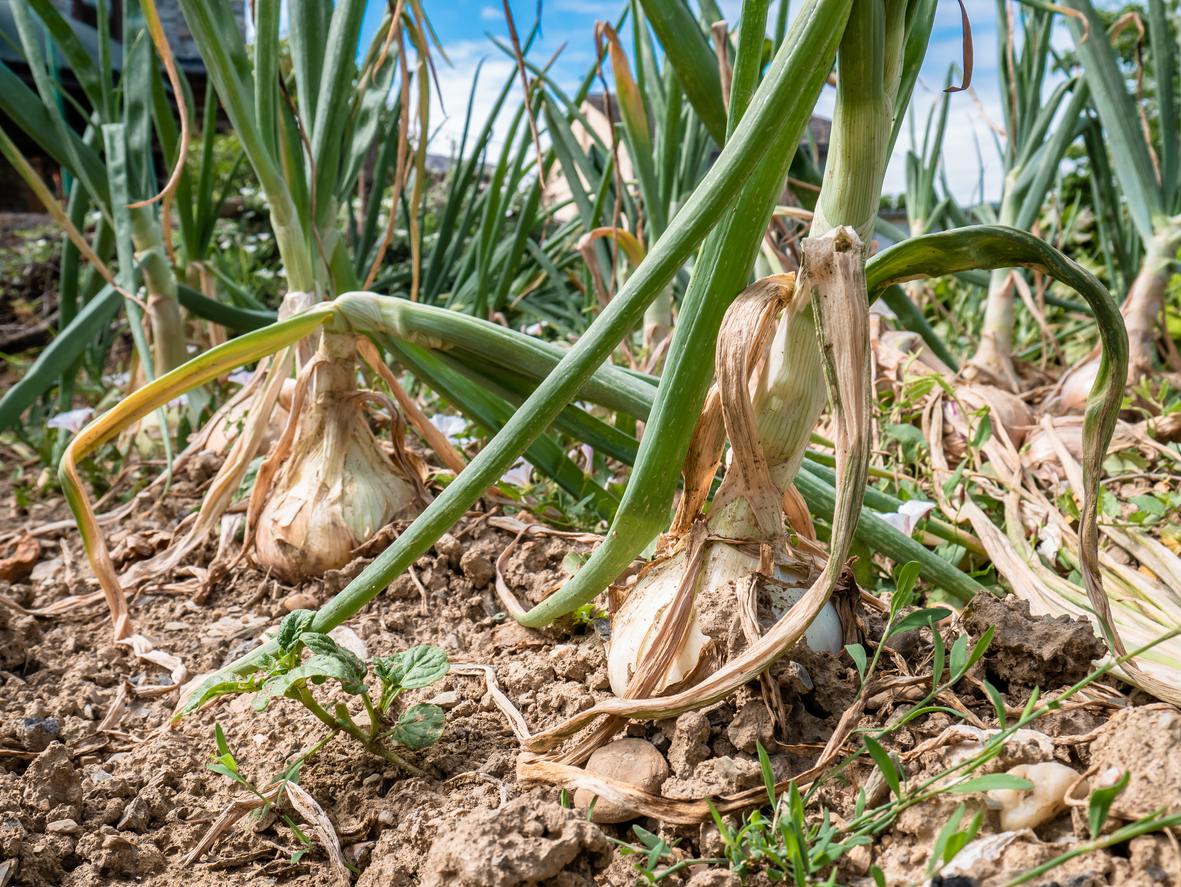
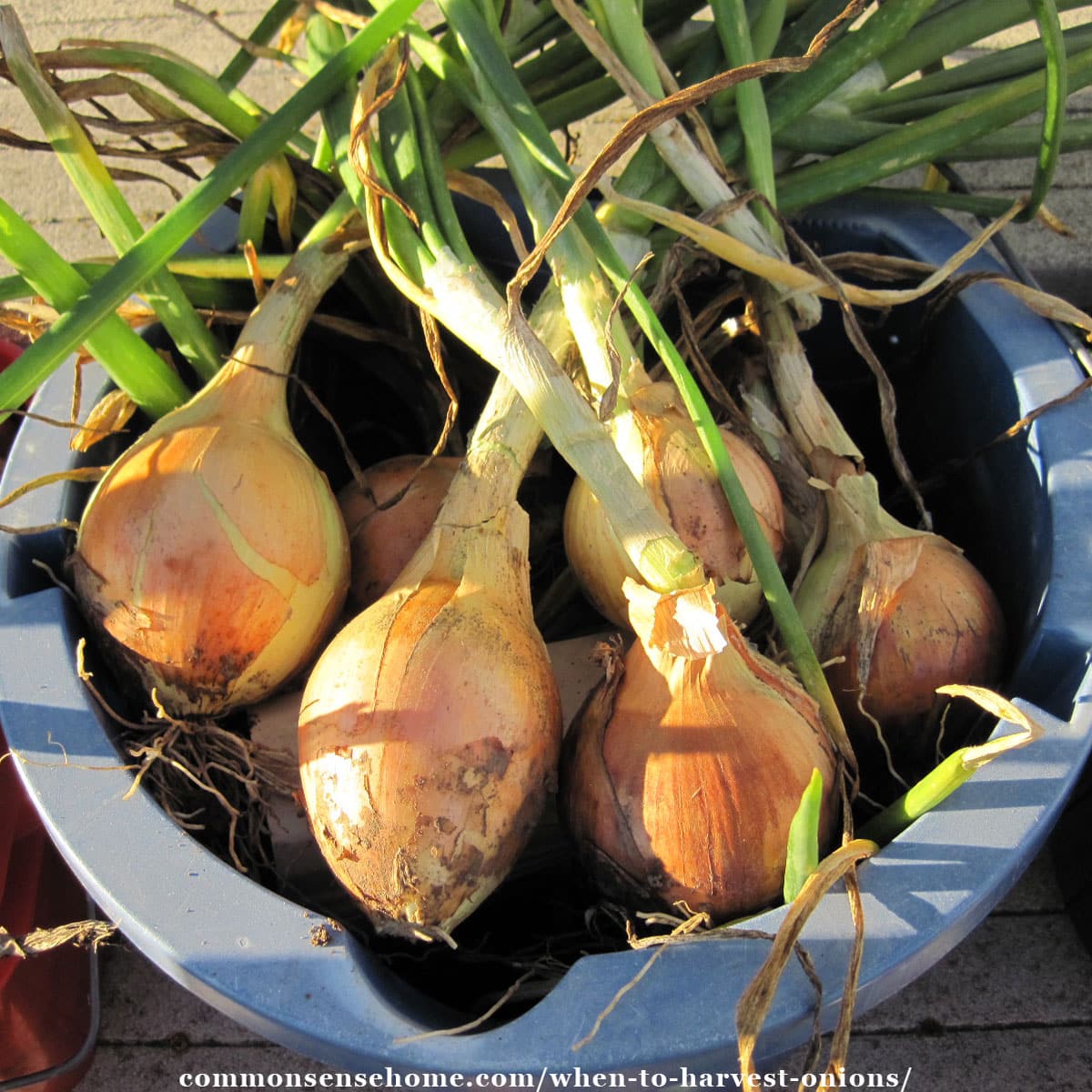
Understanding the onion growth cycle is crucial for determining the optimal time for harvest. Onions are typically ready to harvest when the tops begin to yellow and fall over, and the bulbs are large and firm. Harvesting onions at the right time ensures maximum flavor, texture, and storage quality.
By grasping the basics of onion growth and development, gardeners and farmers can better navigate the challenges of onion cultivation and enjoy a bountiful harvest. Whether you’re a seasoned grower or just starting out, understanding the onion growth cycle is essential for unlocking the secrets of onion maturation and achieving success in the garden.
Factors Influencing Onion Maturation Time
Onion maturation time is influenced by a combination of factors, including weather conditions, soil quality, and variety selection. Understanding these factors is crucial for determining how long it takes onions to mature and optimizing growing conditions for a successful harvest.
Weather conditions, such as temperature, daylight hours, and moisture levels, play a significant role in onion maturation. Onions typically require a cool and dry period to form bulbs, followed by a warm and dry period to mature. Prolonged periods of extreme weather, such as excessive rain or heat, can delay or hasten onion maturation.
Soil quality is another critical factor affecting onion maturation. Onions prefer well-draining, fertile soil with a pH between 6.0 and 7.0. Soil with poor drainage or inadequate nutrients can lead to delayed or stunted growth, resulting in longer maturation times.
Variety selection is also a significant factor in determining onion maturation time. Different onion varieties have distinct maturation times, ranging from early-season to late-season varieties. For example, ‘Ebenezer’ onions mature in as little as 90 days, while ‘Yellow Granex’ onions take up to 210 days.
In addition to these factors, other environmental and cultural practices can impact onion maturation time. For instance, onions grown in regions with shorter daylight hours may take longer to mature than those grown in regions with longer daylight hours. Similarly, onions grown using intensive farming practices, such as irrigation and fertilization, may mature faster than those grown using traditional methods.
By understanding the factors that influence onion maturation time, growers can optimize growing conditions to promote faster maturation and improve yields. This includes selecting suitable varieties, managing weather conditions, and maintaining optimal soil quality.
For example, growers can use techniques such as mulching and irrigation to regulate soil temperature and moisture levels, promoting healthy growth and maturation. Additionally, growers can use row covers or other forms of protection to shield onions from extreme weather conditions, reducing the risk of damage or delay.
By taking a holistic approach to onion cultivation, growers can better navigate the complexities of onion maturation and achieve a successful harvest. Whether you’re a seasoned grower or just starting out, understanding the factors that influence onion maturation time is essential for unlocking the secrets of onion maturation and achieving success in the garden.
How to Determine Onion Maturity
Determining onion maturity is crucial for harvesting onions at the optimal time. Onions that are harvested too early may not have reached their full flavor and texture potential, while those that are harvested too late may become over-mature and prone to spoilage.
So, how can you determine when onions are mature and ready for harvest? Here are some visual cues and tactile checks to help you determine onion maturity:
Visual Cues:
- Bulb size: Check the size of the onion bulb. Most onion varieties are ready to harvest when the bulb is between 1-2 inches in diameter.
- Bulb color: Check the color of the onion bulb. Most onion varieties will turn a yellow or golden color when they are mature.
- Top growth: Check the top growth of the onion plant. When the tops begin to yellow and fall over, it’s a sign that the onion is mature.
Tactile Checks:
- Gently dig around the plants: Carefully dig around the onion plants to check the size and shape of the bulb.
- Check for firmness: Gently squeeze the onion bulb to check for firmness. A mature onion will be firm and compact.
It’s also important to note that different onion varieties have different maturity dates. Some onion varieties, such as ‘Ebenezer’ and ‘Stuttgarter’, mature in as little as 90 days, while others, like ‘Yellow Granex’ and ‘Texas Grano’, take up to 210 days.
By checking for these visual cues and tactile checks, you can determine when your onions are mature and ready for harvest. Remember, the key is to harvest onions at the optimal time to ensure maximum flavor, texture, and storage quality.
Harvesting onions at the right time requires patience and attention to detail. However, with a little practice and experience, you’ll be able to determine onion maturity like a pro. Whether you’re a seasoned grower or just starting out, understanding how to determine onion maturity is essential for unlocking the secrets of onion maturation and achieving success in the garden.
Onion Variety and Maturation Time
Onion varieties play a significant role in determining the time it takes for onions to mature. Different onion varieties have distinct maturation times, ranging from early-season to late-season varieties. Understanding the maturation time of your onion variety is crucial for determining when to harvest and how to optimize growing conditions.
Early-season onion varieties, such as ‘Ebenezer’ and ‘Stuttgarter’, mature in as little as 90 days. These varieties are ideal for growers who want to harvest onions quickly and have a shorter growing season. Early-season onions are typically smaller in size and have a milder flavor.
Mid-season onion varieties, such as ‘Yellow Granex’ and ‘Texas Grano’, mature in around 120-150 days. These varieties are popular among growers who want to harvest onions in the summer months. Mid-season onions are typically larger in size and have a sweeter flavor.
Late-season onion varieties, such as ‘Walla Walla’ and ‘Vidalia’, mature in around 180-210 days. These varieties are ideal for growers who want to harvest onions in the fall months. Late-season onions are typically larger in size and have a stronger flavor.
Some popular onion varieties and their corresponding maturation times include:
- ‘Ebenezer’: 90 days
- ‘Stuttgarter’: 90 days
- ‘Yellow Granex’: 120 days
- ‘Texas Grano’: 120 days
- ‘Walla Walla’: 180 days
- ‘Vidalia’: 180 days
By understanding the maturation time of your onion variety, you can optimize growing conditions and determine the best time to harvest. This will ensure that your onions are harvested at the optimal time, resulting in maximum flavor, texture, and storage quality.
It’s also important to note that onion varieties can be influenced by factors such as weather conditions, soil quality, and pest management. By understanding these factors and how they impact onion maturation, you can make informed decisions to optimize growing conditions and ensure a successful harvest.
Whether you’re a seasoned grower or just starting out, understanding onion variety and maturation time is essential for unlocking the secrets of onion maturation and achieving success in the garden.
Optimizing Growing Conditions for Faster Maturation
Optimizing growing conditions is crucial for promoting faster onion maturation. By providing onions with the right environment, growers can encourage healthy growth and development, leading to a faster maturation time.
Soil Fertility:
Onions require a well-balanced diet of nutrients to grow and mature. Soil fertility plays a critical role in determining the growth rate and maturity of onions. To optimize soil fertility, growers can use a combination of organic and inorganic fertilizers. Organic fertilizers, such as compost and manure, provide a slow release of nutrients, while inorganic fertilizers, such as ammonium sulfate and potassium nitrate, provide a quick burst of nutrients.
Moisture Levels:
Onions require consistent moisture levels to grow and mature. Growers can optimize moisture levels by using irrigation systems and mulching. Irrigation systems provide a controlled release of water, while mulching helps to retain moisture in the soil.
Pest and Disease Management:
Pests and diseases can significantly impact onion growth and maturity. Growers can optimize pest and disease management by using integrated pest management (IPM) techniques. IPM involves using a combination of cultural, biological, and chemical controls to manage pests and diseases.
Some strategies for optimizing growing conditions include:
- Using raised beds to improve soil drainage and aeration
- Implementing crop rotation to reduce soil-borne diseases
- Using row covers to protect onions from pests and diseases
- Providing supplemental lighting to extend the growing season
By optimizing growing conditions, growers can promote faster onion maturation and improve yields. This can be especially beneficial for growers who want to harvest onions quickly and have a shorter growing season.
It’s also important to note that optimizing growing conditions can vary depending on the specific onion variety and growing location. Growers should research the specific needs of their onion variety and adjust their growing conditions accordingly.
By providing onions with the right environment, growers can encourage healthy growth and development, leading to a faster maturation time and improved yields.
Whether you’re a seasoned grower or just starting out, optimizing growing conditions is essential for unlocking the secrets of onion maturation and achieving success in the garden.
Common Challenges and Solutions for Onion Growers
Onion growers often face a range of challenges that can impact the success of their crop. Some of the most common challenges include bolting, rot, and pests. In this section, we will discuss these challenges and provide solutions for overcoming them to ensure successful onion maturation.
Bolting:
Bolting is a common problem in onion crops, where the plants produce a flower stalk and seeds instead of a bulb. This can be caused by a range of factors, including temperature fluctuations, moisture stress, and genetic predisposition. To prevent bolting, growers can use a range of strategies, including:
- Planting high-quality seeds that are resistant to bolting
- Providing consistent moisture levels and avoiding drought stress
- Using row covers to regulate temperature and prevent extreme temperature fluctuations
Rot:
Rot is a fungal disease that can cause onions to rot and become unusable. This can be caused by a range of factors, including excess moisture, poor air circulation, and fungal spores. To prevent rot, growers can use a range of strategies, including:
- Providing good air circulation and avoiding excess moisture
- Using fungicides to control fungal spores
- Removing any infected plants to prevent the spread of the disease
Pests:
Pests, such as aphids, thrips, and mites, can cause significant damage to onion crops. To control pests, growers can use a range of strategies, including:
- Using insecticides to control pest populations
- Introducing beneficial insects, such as ladybugs and lacewings, to control pest populations
- Using physical barriers, such as fine mesh, to prevent pests from reaching the plants
By understanding the common challenges faced by onion growers and using the strategies outlined above, growers can overcome these issues and ensure successful onion maturation. Whether you’re a seasoned grower or just starting out, being aware of these challenges and having a plan in place to overcome them is essential for achieving success in the garden.
It’s also important to note that prevention is key when it comes to overcoming common challenges in onion growing. By taking steps to prevent bolting, rot, and pests, growers can reduce the risk of these issues occurring and ensure a healthy and productive crop.
By following the tips and strategies outlined in this article, growers can overcome common challenges and ensure successful onion maturation. Remember, with the right knowledge and techniques, you can unlock the secrets of onion maturation and achieve success in the garden.
Harvesting Onions at the Right Time
Harvesting onions at the right time is crucial for ensuring maximum flavor, texture, and storage quality. Onions that are harvested too early may not have reached their full flavor and texture potential, while those that are harvested too late may become over-mature and prone to spoilage.
So, how do you know when to harvest your onions? Here are some tips to help you determine the optimal harvest time:
Check for Visual Cues:
Onions are typically ready to harvest when the tops begin to yellow and fall over. This is a sign that the bulb is mature and ready to be harvested.
Check for Tactile Cues:
Gently dig around the onion plants to check for bulb size and shape. Onions that are ready to harvest will have a firm, compact bulb that is free of soft spots or signs of rot.
Harvesting Techniques:
When harvesting onions, it’s essential to handle them carefully to avoid damaging the bulbs. Here are some tips for harvesting onions:
- Use a garden fork to gently loosen the soil around the onion plants.
- Carefully lift the onions out of the soil, taking care not to damage the bulbs.
- Remove any excess soil or debris from the bulbs.
- Allow the onions to dry in the sun for a few hours before storing them.
Timing is Everything:
The timing of onion harvest is critical for ensuring maximum flavor, texture, and storage quality. Onions that are harvested too early may not have reached their full flavor and texture potential, while those that are harvested too late may become over-mature and prone to spoilage.
By following these tips and techniques, you can ensure that your onions are harvested at the optimal time, resulting in maximum flavor, texture, and storage quality.
Whether you’re a seasoned grower or just starting out, harvesting onions at the right time is essential for unlocking the secrets of onion maturation and achieving success in the garden.
Remember, the key to successful onion harvest is to be patient and observant. By monitoring your onion plants closely and harvesting them at the optimal time, you can enjoy a bountiful harvest of delicious, flavorful onions.
Post-Harvest Care for Onions
After harvesting onions, it’s essential to provide proper care to maintain their quality and longevity. This includes drying, curing, and storing the onions in a way that prevents spoilage and preserves their flavor and texture.
Drying Onions:
Onions should be dried immediately after harvest to remove excess moisture. This can be done by spreading the onions out in a single layer on a wire rack or tray, allowing air to circulate around them. The onions should be dried in a warm, dry place with good ventilation.
Curing Onions:
After drying, onions should be cured to further reduce moisture and prevent spoilage. This can be done by storing the onions in a warm, dry place with good ventilation. The onions should be checked regularly for signs of spoilage, such as mold or rot.
Storing Onions:
Once the onions are cured, they can be stored in a cool, dry place with good ventilation. The onions should be stored in a way that prevents moisture from accumulating, such as in a mesh bag or a ventilated container.
Tips for Storing Onions:
- Store onions in a cool, dry place with good ventilation.
- Keep onions away from direct sunlight and heat sources.
- Don’t store onions near potatoes or apples, as these can cause the onions to spoil.
- Check onions regularly for signs of spoilage, such as mold or rot.
By following these tips, you can help maintain the quality and longevity of your onions and enjoy them for months to come.
Proper post-harvest care is essential for maintaining the quality and longevity of onions. By drying, curing, and storing onions properly, you can help prevent spoilage and preserve their flavor and texture.
Whether you’re a seasoned grower or just starting out, providing proper post-harvest care for onions is essential for unlocking the secrets of onion maturation and achieving success in the garden.
Remember, the key to successful onion storage is to provide a cool, dry environment with good ventilation. By following these tips and techniques, you can enjoy a bountiful harvest of delicious, flavorful onions for months to come.