Understanding Raspberry Plant Development: From Seed to Harvest
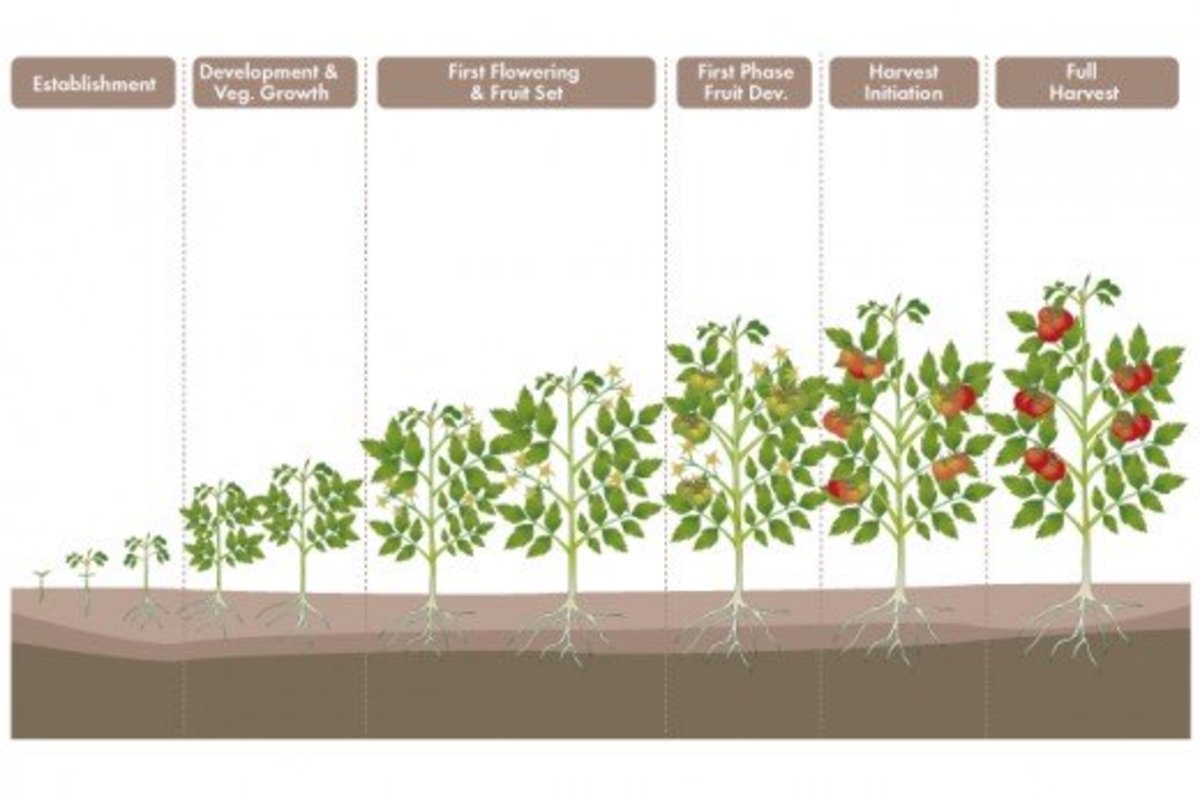
Raspberry plants undergo a series of growth stages, from germination to maturity, which can impact the time it takes to grow raspberries. The life cycle of a raspberry plant typically begins with seed germination, which can occur within 1-3 weeks after sowing. During this period, the seed absorbs water, and the embryo begins to grow. After germination, the seedling develops its first set of leaves, known as cotyledons, which provide essential nutrients for growth.
As the seedling grows, it develops a root system and produces new canes, which can take around 6-8 weeks. These canes will eventually produce leaves, flowers, and fruit. The growth rate of raspberry plants can be influenced by factors such as soil quality, climate, and sunlight exposure. For instance, raspberry plants grown in well-draining soil with a pH between 5.5 and 6.5 tend to grow faster and produce more fruit.
Understanding the growth stages of raspberry plants is crucial for determining how long it takes to grow raspberries. By recognizing the different stages of development, gardeners can provide optimal care and conditions for their plants, ultimately leading to a successful harvest. The entire growth cycle, from seed to harvest, can take around 12-18 months, depending on the variety and growing conditions.
It’s essential to note that some raspberry varieties are bred for specific characteristics, such as earliness or disease resistance, which can impact the growth rate. For example, summer-bearing varieties tend to produce fruit within 12-14 months, while fall-bearing varieties can take around 18-20 months to mature.
By grasping the fundamentals of raspberry plant development, gardeners can better understand the time it takes to grow raspberries and make informed decisions about their gardening practices. This knowledge can help optimize growing conditions, leading to healthier plants and a more bountiful harvest.
Preparing the Perfect Environment: Soil, Climate, and Sunlight Requirements
Raspberry plants require a specific set of environmental conditions to thrive. One of the most critical factors is soil quality. Raspberries prefer well-draining, rich soil with a pH between 5.5 and 6.5. To achieve this, gardeners can add organic matter such as compost or manure to improve soil structure and fertility.
Climate is another essential factor in growing raspberries. Raspberries are typically hardy in USDA zones 3-9, meaning they can tolerate temperatures as low as -40°F (-40°C) and as high as 90°F (32°C). However, extreme temperatures, such as those above 100°F (38°C), can damage the plants. Gardeners should choose a location that provides some protection from wind and extreme weather conditions.
Sunlight is also crucial for raspberry growth. Raspberries require full sun to produce well, so gardeners should choose a location that receives at least 6 hours of direct sunlight per day. However, in warmer climates, some afternoon shade can help prevent heat stress.
In addition to these environmental factors, gardeners should also consider the specific needs of their raspberry variety. Some varieties, such as summer-bearing raspberries, require more chill hours (hours below 45°F/7°C) to produce fruit, while others, such as fall-bearing raspberries, require fewer chill hours.
By understanding the environmental requirements of raspberry plants, gardeners can create an optimal growing environment that promotes healthy growth and fruit production. This, in turn, can help answer the question of how long it takes to grow raspberries, as a well-cared-for plant will produce fruit more quickly and abundantly.
Some tips for optimizing environmental conditions include:
- Using mulch to retain moisture and suppress weeds
- Providing support for the plants, such as a trellis or stake
- Watering regularly, but avoiding overwatering
- Monitoring temperature and adjusting the growing location as needed
By following these tips and creating an optimal growing environment, gardeners can help their raspberry plants thrive and produce delicious fruit.
How to Plant Raspberries: A Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
Planting raspberries can be a straightforward process, but it requires some planning and attention to detail. To ensure a successful harvest, it’s essential to choose the right variety, prepare the soil, and space the plants correctly.
Choosing the Right Variety:
Raspberries come in two main types: summer-bearing and fall-bearing. Summer-bearing varieties produce fruit in the summer, while fall-bearing varieties produce fruit in the fall. Consider the climate and desired harvest period when selecting a variety.
Preparing the Soil:
Raspberries prefer well-draining, rich soil with a pH between 5.5 and 6.5. Test the soil to determine its pH level and nutrient content. Add organic matter such as compost or manure to improve soil structure and fertility.
Planting the Raspberries:
Plant raspberries in the early spring or fall, when the weather is cooler. Dig a hole that is twice as wide and just as deep as the root ball. Gently remove the plant from its container and place it in the hole. Fill the hole with soil, making sure to firm it around the roots. Water thoroughly.
Spacing the Plants:
Raspberries need adequate space to grow and produce fruit. Plant summer-bearing varieties 2-3 feet apart, while fall-bearing varieties can be planted 3-4 feet apart. Consider planting multiple rows, with each row spaced 6-8 feet apart.
Supporting the Plants:
Raspberries need support as they grow. Install a trellis or stake near the planting site to provide structure for the canes. This will help keep the plants upright and promote healthy growth.
Watering and Mulching:
Water the raspberries regularly, providing about 1 inch of water per week. Mulch around the plants to retain moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature.
By following these steps, you’ll be well on your way to growing delicious raspberries. Remember to provide the right environment, care, and attention to your plants, and you’ll be enjoying a bountiful harvest in no time.
Raspberry Growth Stages: What to Expect and When
Raspberry plants go through several growth stages, from emergence to fruiting. Understanding these stages can help gardeners anticipate and prepare for the different phases of growth.
Emergence (1-2 weeks):
This is the initial stage of growth, where the new canes emerge from the ground. During this stage, the canes are vulnerable to damage from wind, frost, and pests.
Leaf Development (2-4 weeks):
As the canes grow, they develop leaves that are essential for photosynthesis and growth. The leaves are typically a bright green color and have a distinctive shape.
Flowering (4-6 weeks):
As the plants mature, they produce flowers that are self-pollinating. The flowers are typically white or pink and have a sweet fragrance.
Fruiting (6-8 weeks):
After the flowers have been pollinated, the plants produce fruit. The fruit is typically red, yellow, or purple, depending on the variety.
Maturation (8-12 weeks):
As the fruit ripens, it becomes sweeter and more flavorful. The exact timing of maturation depends on the variety, weather conditions, and growing practices.
By understanding the different growth stages of raspberry plants, gardeners can better anticipate and prepare for the different phases of growth. This knowledge can help optimize growing conditions, leading to healthier plants and a more bountiful harvest.
It’s also important to note that the growth stages of raspberry plants can vary depending on factors such as climate, soil quality, and pest management. By providing optimal growing conditions and care, gardeners can help their raspberry plants thrive and produce delicious fruit.
In terms of how long it takes to grow raspberries, the entire growth cycle from emergence to harvest can take around 12-18 months, depending on the variety and growing conditions. However, with proper care and attention, gardeners can enjoy a bountiful harvest of delicious raspberries.
Factors Affecting Raspberry Growth Rate: Tips for Optimizing Production
Raspberry growth rate can be influenced by various factors, including weather conditions, pests, and diseases. Understanding these factors and taking steps to mitigate their impact can help optimize production and ensure a successful harvest.
Weather Conditions:
Weather conditions such as temperature, rainfall, and sunlight exposure can significantly impact raspberry growth rate. Extreme temperatures, drought, and excessive rainfall can all negatively impact plant growth and fruit production.
Pests:
Pests such as aphids, spider mites, and Japanese beetles can damage raspberry plants and reduce fruit production. Regular monitoring and integrated pest management strategies can help minimize the impact of pests.
Diseases:
Diseases such as powdery mildew, botrytis, and root rot can also impact raspberry growth rate and fruit production. Practicing good sanitation, using resistant varieties, and applying fungicides can help prevent and manage diseases.
Soil Quality:
Soil quality can also impact raspberry growth rate. Poor soil quality can lead to reduced plant growth, lower fruit production, and increased susceptibility to pests and diseases. Adding organic matter, using cover crops, and practicing crop rotation can help improve soil quality.
Pruning and Training:
Pruning and training raspberry plants can also impact growth rate and fruit production. Proper pruning and training techniques can help promote healthy plant growth, increase fruit production, and reduce the risk of disease.
By understanding the factors that can impact raspberry growth rate and taking steps to mitigate their impact, gardeners can optimize production and ensure a successful harvest. This knowledge can help answer the question of how long it takes to grow raspberries, as a well-cared-for plant will produce fruit more quickly and abundantly.
Some tips for optimizing raspberry growth rate include:
- Providing optimal growing conditions, including temperature, rainfall, and sunlight exposure
- Practicing integrated pest management strategies to minimize the impact of pests
- Using resistant varieties and practicing good sanitation to prevent and manage diseases
- Improving soil quality through the addition of organic matter and cover crops
- Pruning and training plants to promote healthy growth and increase fruit production
How Long Does it Take to Grow Raspberries: A Realistic Timeline
Now that we’ve discussed the life cycle of raspberry plants, the essential environmental factors that impact growth, and the factors that can affect growth rate, it’s time to provide a realistic timeline for growing raspberries.
From seed to harvest, the entire growth cycle of raspberries can take around 12-18 months, depending on the variety and growing conditions. Here’s a breakdown of what you can expect:
Month 1-3: Germination and seedling growth
Month 4-6: Plant establishment and cane growth
Month 7-9: Flowering and fruiting
Month 10-12: Harvest and fruit production
Month 13-18: Continued fruit production and plant maturation
Keep in mind that this is just a general timeline, and the actual growth cycle of your raspberries may vary depending on factors such as climate, soil quality, and pest management.
It’s also important to note that some raspberry varieties are bred for specific characteristics, such as earliness or disease resistance, which can impact the growth cycle. Be sure to research the specific needs and growth habits of your variety to ensure optimal growth and production.
By understanding the realistic timeline for growing raspberries, you can better plan and prepare for the different stages of growth, and ultimately enjoy a successful and bountiful harvest.
Some tips for optimizing your raspberry growth timeline include:
- Providing optimal growing conditions, including temperature, rainfall, and sunlight exposure
- Practicing good sanitation and integrated pest management strategies to minimize the impact of pests and diseases
- Using resistant varieties and practicing good pruning and training techniques to promote healthy growth and fruit production
- Monitoring your plants regularly and taking action to address any issues that may arise
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Growing Raspberries
While growing raspberries can be a rewarding experience, there are several common mistakes that can impact growth and production. By being aware of these mistakes and taking steps to avoid them, you can ensure a successful harvest and enjoy your homegrown raspberries for years to come.
Inadequate Pruning:
Pruning is an essential part of raspberry care, as it helps to promote healthy growth, increase fruit production, and reduce the risk of disease. However, inadequate pruning can lead to reduced fruit production, weak canes, and increased susceptibility to pests and diseases.
Poor Soil Quality:
Raspberries require well-draining, rich soil to grow and produce fruit. Poor soil quality can lead to reduced plant growth, lower fruit production, and increased susceptibility to pests and diseases.
Insufficient Watering:
Raspberries require consistent moisture, especially during the fruiting stage. Insufficient watering can lead to reduced fruit production, weak canes, and increased susceptibility to pests and diseases.
Overwatering:
While raspberries require consistent moisture, overwatering can be detrimental to plant growth and fruit production. Overwatering can lead to root rot, reduced fruit production, and increased susceptibility to pests and diseases.
Not Providing Support:
Raspberries require support to grow and produce fruit. Not providing support can lead to weak canes, reduced fruit production, and increased susceptibility to pests and diseases.
Some tips for avoiding these common mistakes include:
- Pruning your raspberry plants regularly to promote healthy growth and increase fruit production
- Providing well-draining, rich soil to support plant growth and fruit production
- Watering your raspberry plants consistently, but avoiding overwatering
- Providing support for your raspberry plants to promote healthy growth and fruit production
Enjoying Your Homegrown Raspberries: Harvesting and Preservation Tips
Congratulations You’ve successfully grown your own raspberries. Now it’s time to enjoy the fruits of your labor. Here are some tips on how to harvest and preserve your homegrown raspberries:
Harvesting:
Raspberries are typically ready to harvest in mid to late summer. Check your plants regularly for ripe fruit, as it can spoil quickly. Gently grasp the fruit and twist it to remove it from the plant.
Preservation:
There are several ways to preserve raspberries, including freezing, canning, and dehydrating. Freezing is a great way to preserve the fruit’s flavor and texture. Simply rinse the fruit, pat it dry, and place it in an airtight container or freezer bag.
Canning is another popular method for preserving raspberries. This involves heating the fruit to a high temperature to kill off any bacteria, then sealing it in a jar or can. Dehydrating is a great way to preserve raspberries for use in recipes or as a healthy snack.
Ways to Enjoy Your Homegrown Raspberries:
There are many ways to enjoy your homegrown raspberries, including:
- Eating them fresh off the plant
- Adding them to salads or desserts
- Using them in jams, jellies, or preserves
- Freezing them for later use
- Dehydrating them for a healthy snack
By following these tips, you can enjoy your homegrown raspberries for months to come. Happy harvesting and preserving!