The Fascination with Homegrown Produce: An Introduction
Cultivating vegetables at home has gained popularity due to the numerous advantages it offers. Fresh produce, cost savings, and a closer connection with nature are just a few reasons why many individuals are turning to homegrown vegetables. By understanding the growing timeline of vegetables, gardeners can plan and manage their gardens more effectively, ultimately leading to a more successful and rewarding gardening experience.
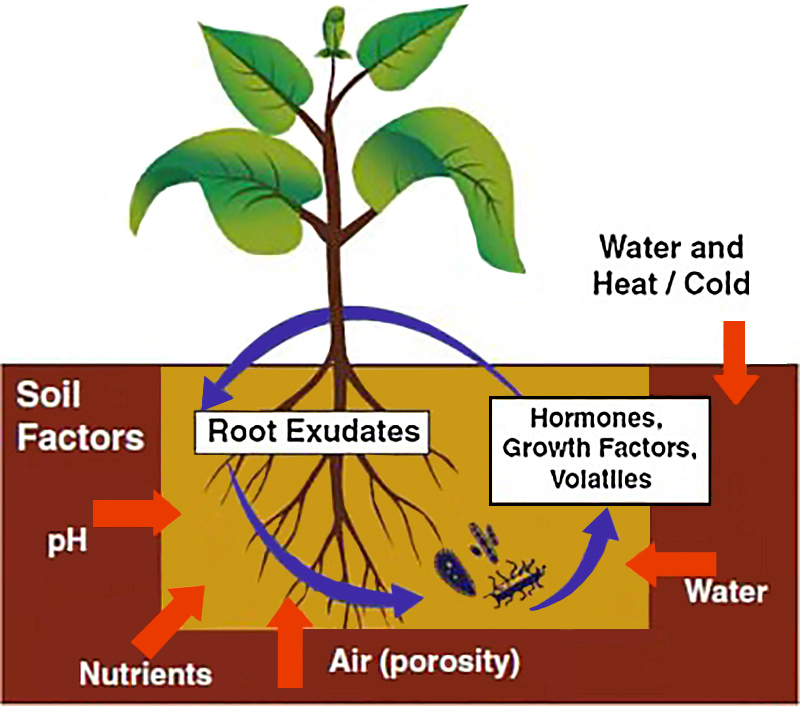
Factors Influencing Vegetable Growth: Soil, Sunlight, and Water
When determining how long it takes to grow vegetables, it’s essential to consider various factors that can impact their growth rate. Soil quality, sunlight exposure, and water availability are three critical elements that significantly influence the growth of vegetables. By understanding these factors, gardeners can create optimal conditions for their plants, ensuring a healthier and more bountiful harvest.
Soil Quality
Soil is the foundation of any garden, and its quality plays a crucial role in vegetable growth. Rich, well-draining soil with a balanced pH level provides the ideal environment for vegetables to thrive. High-quality soil ensures that plants receive the necessary nutrients for growth, which can lead to faster maturation times and improved yields. To enhance soil quality, consider incorporating organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, before planting.
Sunlight Exposure
Sunlight exposure is another vital factor in the growth of vegetables. Most vegetables require at least six hours of direct sunlight daily to grow and produce optimally. Insufficient sunlight can lead to slower growth rates, reduced yields, and weakened plants. When planning a garden, ensure that vegetables are placed in areas with adequate sunlight exposure, taking into account the changing sun patterns throughout the year.
Water Availability
Water is essential for photosynthesis and the overall growth and development of vegetables. Proper watering practices help maintain consistent moisture levels in the soil, promoting healthy root growth and faster vegetable maturation. However, overwatering can lead to various issues, such as root rot and fungal diseases, which can hinder growth. Adequate water availability, combined with good drainage, ensures that vegetables receive the necessary hydration for optimal growth.
Quick-Growing Vegetables: Harvest in 30-60 Days
For those eager to enjoy the fruits of their labor in a relatively short period, quick-growing vegetables are an excellent choice. These plants typically mature within 30-60 days, providing gardeners with a rapid turnaround and the opportunity to grow multiple crops in a single season. Some popular fast-growing vegetables include radishes, lettuce, and arugula.
Radishes (Raphanus sativus)
Radishes are root vegetables that come in various shapes, sizes, and colors. They are known for their crisp texture and mildly spicy flavor. Radishes are incredibly fast-growing, often ready to harvest in as little as 25-35 days from planting. To ensure optimal growth, plant radishes in well-draining soil with ample sunlight and consistent moisture. Thin seedlings to about 1 inch apart to allow for proper root development.
Lettuce (Lactuca sativa)
Lettuce is a cool-season vegetable that thrives in mild temperatures and partial shade. With a maturation time of 30-45 days, lettuce is an excellent option for gardeners looking for quick results. There are many lettuce varieties to choose from, including loose-leaf, romaine, and butterhead. Plant lettuce seeds in rich, well-draining soil, and keep the soil consistently moist for best results. Thin seedlings to about 8 inches apart to promote healthy leaf growth.
Arugula (Eruca sativa)
Arugula is a leafy green vegetable with a peppery, tangy flavor. It is an ideal choice for gardeners seeking fast-growing vegetables, as it typically matures in just 30-45 days. Arugula prefers cooler temperatures and partial shade, making it a perfect candidate for spring and fall gardens. Plant arugula seeds in well-draining soil and maintain consistent moisture. Thin seedlings to about 4 inches apart to encourage leaf growth and prevent overcrowding.
Moderately Paced Vegetables: Harvest in 60-90 Days
For gardeners looking for a balance between quick turnaround and more extended growth periods, moderately paced vegetables are an excellent choice. These plants typically take around 60-90 days to mature, offering a variety of flavors, textures, and growing requirements. Some popular vegetables in this category include broccoli, peppers, and cucumbers.
Broccoli (Brassica oleracea var. italica)
Broccoli is a cool-season vegetable that thrives in temperatures between 60-70°F (15-21°C). It typically takes 60-90 days to mature, depending on the variety. Broccoli requires rich, well-draining soil and consistent moisture. Plant broccoli seeds or seedlings in full sun, and provide adequate spacing to encourage healthy growth. Regular fertilization and consistent watering contribute to faster, more robust growth.
Peppers (Capsicum annuum)
Peppers are warm-season vegetables that require a longer growing period, usually 60-90 days. They thrive in warm temperatures, ideally between 70-85°F (21-29°C), and full sun exposure. Peppers require well-draining soil and consistent moisture. To encourage faster growth, use a balanced fertilizer and maintain even soil moisture. Pinch back the first few blossoms to promote bushier plants and a larger overall yield.
Cucumbers (Cucumis sativus)
Cucumbers are warm-season vegetables that typically take 60-90 days to mature. They prefer full sun exposure and well-draining soil. Cucumbers require consistent moisture, so water regularly and mulch around the base of the plants to retain soil moisture. Provide a trellis or support structure for the vines to grow on, as this can help improve air circulation and reduce the risk of fungal diseases.
Slow-Growing Vegetables: Patience Pays Off
While some vegetables offer a quick turnaround, others require more time and patience. Slow-growing vegetables typically take between 90-150 days to mature, but their extended growth period often results in a bountiful harvest. Popular vegetables in this category include tomatoes, eggplants, and artichokes.
Tomatoes (Solanum lycopersicum)
Tomatoes are warm-season vegetables that usually take 90-150 days to mature, depending on the variety. They require full sun exposure and well-draining soil. To encourage faster growth, use a balanced fertilizer and maintain even soil moisture. Prune suckers to promote better air circulation and reduce the risk of fungal diseases. Tomatoes can be grown in cages, trellises, or containers for optimal support and growth.
Eggplants (Solanum melongena)
Eggplants are warm-season vegetables that typically take 90-150 days to mature. They thrive in warm temperatures, ideally between 70-85°F (21-29°C), and full sun exposure. Eggplants require well-draining soil and consistent moisture. To promote faster growth, use a balanced fertilizer and stake the plants for added support. Regularly pinch off the lower leaves to encourage fruit production and improve air circulation.
Artichokes (Cynara cardunculus var. scolymus)
Artichokes are perennial vegetables that take approximately 120-150 days to mature. They prefer full sun exposure and well-draining soil. Artichokes require consistent moisture and regular fertilization to encourage healthy growth. While they have a longer growth period, artichokes can produce multiple harvests over several years, making them a worthwhile investment for the dedicated gardener.
Seasonal Considerations: Timing Your Garden
Timing is crucial when it comes to growing vegetables, as local climate and temperature significantly impact the growth rate and success of various plants. By understanding the importance of planting vegetables according to the season, gardeners can maximize their growing potential throughout the year.
Understanding Your Growing Season
To make the most of your garden, determine your area’s growing season length, which is the number of days between the last spring frost and the first fall frost. This information will help you select vegetables that are best suited for your climate and ensure that you plant them at the optimal time.
Spring Planting
Spring is an ideal time to plant cool-season vegetables, such as peas, lettuce, radishes, and broccoli. These plants thrive in cooler temperatures and can be sown directly into the garden soil when the soil temperature reaches 40-50°F (4-10°C). Providing adequate protection, such as row covers or cold frames, can help extend the growing season and protect young plants from unexpected frosts.
Summer Planting
Summer is the perfect time to plant warm-season vegetables, like tomatoes, peppers, eggplants, and cucumbers. These plants require higher temperatures and full sun exposure to thrive. To ensure successful growth, wait until the soil temperature reaches at least 60-70°F (15-21°C) before planting. Additionally, consider using mulch to retain soil moisture and maintain even temperatures during the hot summer months.
Fall and Winter Planting
Fall and winter are excellent times to plant cool-season vegetables for a late-season harvest. Root vegetables, such as carrots, beets, and turnips, can be sown directly into the garden soil in late summer or early fall, depending on your local climate. In milder regions, hardy greens like kale, spinach, and collards can be grown throughout the winter, providing fresh produce even during the colder months.
Extending the Growing Season: Techniques for Year-Round Harvest
By employing various techniques, such as using cold frames, greenhouses, or row covers, gardeners can extend their growing season and cultivate vegetables faster and for a more extended period. These methods create a microclimate that protects plants from harsh weather conditions, allowing for earlier spring plantings and later fall harvests.
Cold Frames
Cold frames are simple structures made of a bottomless box with a transparent lid, typically made of glass or plastic. They are placed directly on the ground and can be used to protect young plants from frost, maintain soil warmth, and create a favorable environment for early spring or late fall plantings. Cold frames can also be used to harden off seedlings before transplanting them into the garden.
Greenhouses
Greenhouses are larger, enclosed structures that provide a controlled environment for plants to grow year-round. They trap heat from the sun, maintaining a warm temperature that allows for the cultivation of warm-season vegetables, even during the colder months. Greenhouses can be equipped with heating and cooling systems, ventilation, and artificial lighting to ensure optimal growing conditions.
Row Covers
Row covers are lightweight, transparent materials that can be draped over plants or hoops to create a protective barrier. They help retain heat, reduce wind damage, and protect plants from frost. Row covers can be used to extend the growing season by allowing for earlier plantings and later harvests, as well as providing additional protection from pests and diseases.
Benefits of Extending the Growing Season
Extending the growing season has several benefits, including the ability to grow a wider variety of vegetables, increased yields, and a longer harvest period. By employing techniques such as cold frames, greenhouses, or row covers, gardeners can enjoy fresh produce for a more extended period, even in regions with harsh climates or short growing seasons.
Monitoring Plant Growth: Essential Gardening Practices
Regular monitoring and maintenance are crucial elements of successful vegetable gardening. By staying attentive to your plants’ needs, you can ensure optimal growth, minimize potential issues, and ultimately harvest healthier, more abundant produce. Key tasks to focus on include watering, fertilizing, and pest control.
Watering
Proper watering is essential for healthy vegetable growth. Aim to provide vegetables with a consistent water supply, ideally delivering water directly to the root zone. Overhead watering can lead to evaporation and fungal diseases, while insufficient watering can stunt growth and reduce yields. Consider using drip irrigation or soaker hoses to maintain consistent soil moisture and promote even growth.
Fertilizing
Fertilizers provide essential nutrients that support vegetable growth and development. Choose a balanced, slow-release fertilizer to ensure a steady supply of nutrients throughout the growing season. Additionally, consider incorporating organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, into the soil to improve fertility and structure. Regularly test your soil to monitor nutrient levels and adjust your fertilization strategy accordingly.
Pest Control
Pests can significantly impact vegetable growth and yield. Regularly inspect your plants for signs of infestation, such as discolored leaves, holes, or sticky residue. If you identify pests, consider using integrated pest management (IPM) strategies, which involve a combination of cultural, mechanical, and biological methods to control pest populations. In some cases, you may need to use organic or synthetic pesticides, but always follow label instructions and exercise caution to minimize harm to beneficial insects and the environment.
Additional Maintenance Tasks
In addition to watering, fertilizing, and pest control, consider incorporating other maintenance tasks to promote healthy vegetable growth. These may include mulching to retain soil moisture and suppress weeds, staking or trellising to support climbing plants, and pruning or pinching to encourage bushier growth and improve air circulation.