Understanding Tomato Plant Yield: What to Expect
Tomato plant yield is a critical aspect of growing tomatoes, and understanding how many tomatoes grow on one plant is essential for maximizing production. The yield of a tomato plant is influenced by several factors, including the type of tomato variety, climate, soil quality, and care. Different tomato varieties have varying yields, with some producing hundreds of small fruits and others yielding fewer, larger tomatoes. Climate and weather conditions also play a significant role, as temperature, sunlight, and water can impact fruit production. Additionally, the quality of care, including pruning, training, and fertilization, can significantly influence tomato plant yield. By grasping the complexities of these factors, gardeners can optimize their growing conditions and reap a bountiful harvest.
The Role of Tomato Variety in Determining Yield
When it comes to understanding how many tomatoes grow on one plant, the type of tomato variety plays a significant role. Different tomato varieties have unique characteristics that impact their yield, and selecting the right variety can make all the difference in maximizing tomato production. High-yielding varieties, such as cherry tomatoes and patio tomatoes, are bred specifically for their ability to produce large quantities of fruit. These varieties tend to be compact, disease-resistant, and produce fruit continuously throughout the growing season. In contrast, larger, beefsteak-style tomatoes are often bred for their size and flavor, rather than their yield. These varieties may produce fewer, but larger, fruits, and may require more care and support. By understanding the characteristics of different tomato varieties, gardeners can choose the best variety for their specific needs and growing conditions, and optimize their tomato plant yield.
How to Optimize Growing Conditions for Maximum Yield
Creating an ideal growing environment is crucial for maximizing tomato plant yield. Several factors, including soil quality, sunlight, water, and fertilization, can significantly impact tomato production. Soil quality, for instance, plays a critical role in providing essential nutrients to tomato plants. Well-draining, fertile soil with a pH between 6.0 and 6.8 can help promote healthy plant growth and increase yield. Adequate sunlight is also essential, with most tomato varieties requiring at least six hours of direct sunlight per day. Watering is another critical factor, as inconsistent moisture levels can lead to reduced fruit production. Aim to provide about 1-2 inches of water per week, either through rainfall or irrigation. Finally, fertilization can help provide essential nutrients to tomato plants. A balanced fertilizer with a ratio of 10-10-10 (nitrogen-phosphorus-potassium) can help promote healthy plant growth and increase yield. By optimizing these growing conditions, gardeners can create an ideal environment for their tomato plants to thrive and produce a bountiful harvest, answering the question of how many tomatoes grow on one plant.
The Importance of Pruning and Training for Increased Yield
Pruning and training are essential techniques for promoting healthy tomato plant growth and increasing yield. By pruning tomato plants, gardeners can encourage bushy growth, increase fruit production, and improve air circulation, which can help prevent diseases. There are several pruning techniques that can be used, including removing lower leaves, thinning out suckers, and trimming back the plant’s tip. Training tomato plants is also crucial, as it helps to provide support for the plant as it grows. This can be done using tomato cages, trellises, or stakes, which can help to keep the plant upright and encourage fruiting. By pruning and training tomato plants, gardeners can increase their chances of getting a bountiful harvest, answering the question of how many tomatoes grow on one plant. For example, pruning can increase tomato production by up to 20%, while training can help to promote even fruit distribution. By incorporating these techniques into their gardening routine, gardeners can maximize their tomato plant yield and enjoy a more productive harvest.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Growing Tomatoes
When it comes to growing tomatoes, there are several common mistakes that can limit tomato plant yield and prevent gardeners from getting the most out of their plants. One of the most common mistakes is overwatering, which can lead to root rot and reduce fruit production. Underwatering, on the other hand, can cause stress to the plant, leading to reduced yields. Inadequate support is another common mistake, as tomato plants need support as they grow to prevent them from toppling over and reducing fruit production. Other mistakes include failing to provide enough sunlight, using poor quality soil, and not fertilizing regularly. By avoiding these common mistakes, gardeners can create an ideal growing environment for their tomato plants and increase their chances of getting a bountiful harvest, answering the question of how many tomatoes grow on one plant. For example, providing adequate support can increase tomato production by up to 30%, while proper watering can increase yields by up to 25%. By being aware of these common mistakes and taking steps to avoid them, gardeners can maximize their tomato plant yield and enjoy a more productive harvest.
How to Support Your Tomato Plants for Maximum Yield
Providing support for tomato plants is crucial for maximizing yield and promoting healthy growth. As tomato plants grow, they need support to prevent them from toppling over and reducing fruit production. There are several support methods that can be used, including cages, trellises, and stakes. Tomato cages are a popular option, as they provide 360-degree support for the plant and can be easily moved around the garden. Trellises are another option, which can be used to train indeterminate tomato varieties to grow upwards. Stakes are also effective, especially for determinate varieties that grow more compactly. By providing support for tomato plants, gardeners can increase their chances of getting a bountiful harvest, answering the question of how many tomatoes grow on one plant. For example, using tomato cages can increase tomato production by up to 20%, while trellises can increase yields by up to 15%. By choosing the right support method for their tomato plants, gardeners can maximize their yield and enjoy a more productive harvest.
What to Expect from Your Tomato Plant: Average Yield and Harvest Time
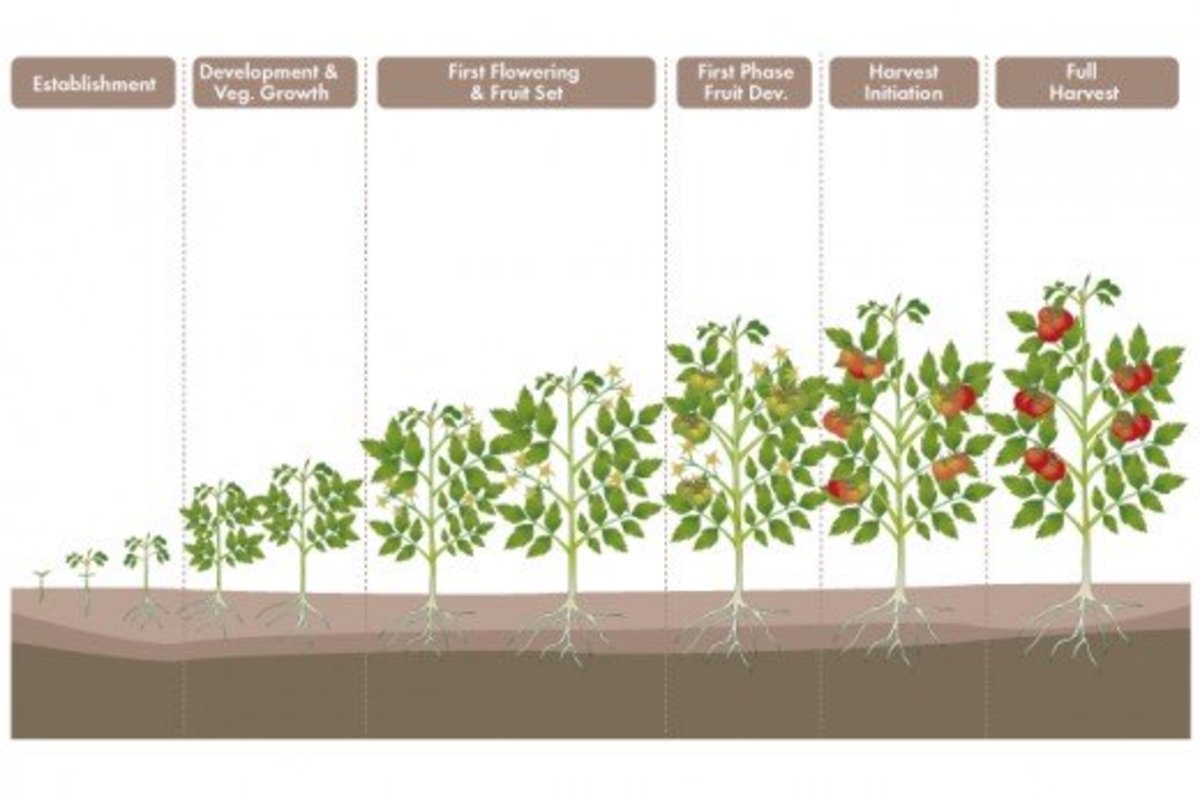
When growing tomatoes, it’s essential to have realistic expectations about what to expect from your plants. Understanding average yield and harvest time can help gardeners plan and prepare for a bountiful harvest. On average, a healthy tomato plant can produce between 10 to 20 pounds of fruit per season, with some varieties producing more than others. For example, cherry tomato varieties can produce hundreds of fruits per season, while larger beefsteak-style tomatoes may only produce 10 to 20 fruits per season. Harvest time typically occurs between 60 to 90 days after planting, depending on the variety and growing conditions. To determine when tomatoes are ripe and ready to harvest, gardeners can look for signs such as a deep red color, a slight softening of the skin, and a sweet, earthy aroma. By understanding what to expect from their tomato plants, gardeners can better plan and prepare for a successful harvest, answering the question of how many tomatoes grow on one plant. With proper care and attention, tomato plants can provide a bountiful harvest, making them a rewarding and productive addition to any garden.
Maximizing Your Tomato Harvest: Tips and Tricks
To maximize tomato plant yield and extend the harvest season, gardeners can employ several strategies. One key approach is to encourage continuous production by providing tomato plants with a steady supply of nutrients and water. This can be achieved by fertilizing tomato plants regularly and ensuring they receive adequate moisture. Another important tip is to handle pests and diseases promptly, as these can significantly reduce tomato plant yield. By monitoring tomato plants regularly and taking action at the first sign of trouble, gardeners can minimize the impact of pests and diseases. Additionally, gardeners can extend the harvest season by using techniques such as succession planting, where new tomato plants are planted every few weeks to ensure a continuous supply of fresh tomatoes. By implementing these strategies, gardeners can maximize their tomato harvest and enjoy a bountiful supply of fresh, delicious tomatoes, answering the question of how many tomatoes grow on one plant. Furthermore, gardeners can also experiment with different tomato varieties, such as determinate and indeterminate varieties, to find the ones that produce the highest yield and best suit their growing conditions. By combining these tips and tricks with proper care and attention, gardeners can unlock the full potential of their tomato plants and enjoy a successful and productive harvest.


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/indeterminate-tomato-variety-1403423-03-2c86cc32f3d74719a90eba7df2f399bc.jpg)