Why Propagate Russian Sage?
Russian Sage, a perennial herb native to Central Asia, has become a popular choice for gardeners and landscapers alike. Its hardiness, drought tolerance, and attractive foliage make it an ideal addition to any garden or landscape design. By learning how to propagate Russian Sage, gardeners can preserve the plant’s unique characteristics and ensure a steady supply of new plants. This method of plant reproduction allows for the creation of multiple plants with the same desirable traits, making it an essential skill for any gardener or horticulturist. In this article, we will delve into the world of Russian Sage propagation, providing a comprehensive guide on how to propagate Russian Sage and unlock its full potential.
Understanding Russian Sage’s Growth Habits
Russian Sage, a perennial herb, exhibits unique growth habits that are essential to understand when learning how to propagate Russian Sage. As a perennial, Russian Sage grows back year after year, producing woody stems that can become quite dense. Additionally, Russian Sage has a tendency to spread, making it an ideal choice for gardeners looking to create a lush, full landscape. Understanding these growth habits is crucial in informing propagation strategies, as it allows gardeners to identify the best methods for capturing the plant’s desirable traits. By recognizing the plant’s perennial nature, woody stems, and spreading tendency, gardeners can develop a propagation plan that takes advantage of these characteristics, ultimately leading to successful plant reproduction.
How to Take Cuttings from Russian Sage
When learning how to propagate Russian Sage, taking cuttings is a crucial step in the process. To increase the chances of successful propagation, it’s essential to take cuttings at the right time and with the right tools. The best time to take cuttings from Russian Sage is in the spring or early summer, when the plant is actively growing. Gather the following tools: a sharp, clean knife or pruning shears, a pot or tray filled with a well-draining rooting medium, and a clear plastic bag or cloche. To prepare the cuttings, select healthy, vigorous stems with plenty of foliage. Cut sections of stem around 3-4 inches long, making the cut just above a node (where a leaf meets the stem). Remove lower leaves, leaving only a few at the top, and gently trim the cut end to promote rooting. Dip the cut end in rooting hormone powder or liquid to stimulate root growth. Plant the cuttings in the rooting medium, firming the soil around the stem to secure it in place. Water gently and provide adequate moisture, light, and temperature control to promote healthy root development.
The Art of Rooting Russian Sage Cuttings
Once cuttings are taken, the next crucial step in how to propagate Russian Sage is to root them successfully. Rooting Russian Sage cuttings requires attention to detail and a controlled environment. To promote healthy root development, provide adequate moisture, light, and temperature control. Water the cuttings gently but thoroughly, making sure the rooting medium is consistently moist but not waterlogged. Place the cuttings in a location with bright, indirect light, and maintain a temperature between 65-75°F (18-24°C). Avoid direct sunlight, which can cause the cuttings to dry out. To further encourage root growth, maintain high humidity by covering the cuttings with a clear plastic bag or cloche. Check the cuttings regularly to ensure they are not too wet or dry, and make adjustments as needed. With proper care and attention, Russian Sage cuttings should develop a robust root system within 2-3 weeks, setting the stage for successful propagation.
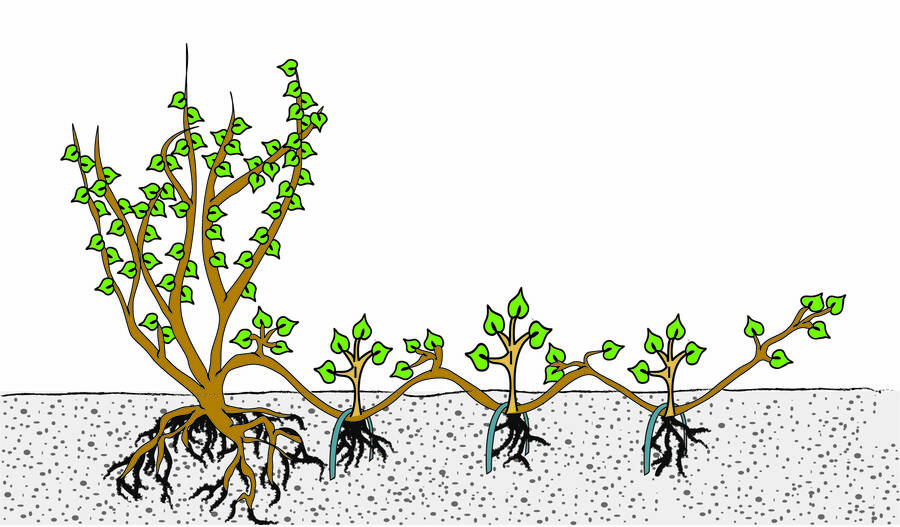
Division and Layering: Alternative Propagation Methods
In addition to taking cuttings, Russian Sage can be propagated through division and layering. These alternative methods offer a unique approach to how to propagate Russian Sage and can be particularly useful for gardeners looking to expand their Russian Sage collection. Division involves separating established Russian Sage plants into smaller sections, making sure each section has a sufficient amount of roots and stems. This method is best done in the spring or fall when the plant is dormant, and can be an effective way to rejuvenate older plants. Layering, on the other hand, involves bending a long stem of Russian Sage to the ground and securing it with a rock or U-pin. Roots will develop at the point of contact, and once established, the new plant can be cut from the parent plant. Both division and layering require careful handling and attention to detail, but can be rewarding ways to propagate Russian Sage. When using these methods, it’s essential to ensure the new plants are provided with adequate moisture, light, and nutrients to promote healthy growth.
Troubleshooting Common Propagation Issues
When learning how to propagate Russian Sage, it’s essential to be aware of common issues that may arise during the process. Root rot, pests, and disease can all hinder successful propagation, but with the right knowledge and preventative measures, these issues can be overcome. Root rot, often caused by overwatering, can be prevented by ensuring the rooting medium is well-draining and not too moist. Regularly inspecting cuttings for signs of rot, such as soft or mushy stems, can also help identify the issue early on. Pests, like aphids and whiteflies, can be controlled with insecticidal soap or neem oil, while diseases, like powdery mildew, can be treated with fungicides. To minimize the risk of these issues, maintain good sanitation practices, such as sterilizing tools and equipment, and provide adequate air circulation around the cuttings. By being proactive and taking preventative measures, gardeners can increase their chances of successful Russian Sage propagation and enjoy the many benefits this beautiful plant has to offer.
Caring for Newly Propagated Russian Sage Plants
Once Russian Sage cuttings have successfully rooted, it’s essential to provide the right care to ensure they establish themselves quickly and healthily. Watering is crucial during this period, as the plants need consistent moisture to develop a strong root system. However, it’s equally important not to overwater, as this can lead to root rot and other problems. A balanced fertilizer applied at half strength can provide the necessary nutrients for growth. Pruning is also vital, as it helps to promote bushy growth and encourages the plant to focus its energy on developing a strong root system. When learning how to propagate Russian Sage, it’s essential to remember that patience is key. Newly propagated plants require gentle handling and careful attention to their needs. By providing the right care, gardeners can help their Russian Sage plants thrive and enjoy the many benefits this beautiful plant has to offer.
Maximizing Success: Tips and Tricks for Russian Sage Propagation
To maximize success when learning how to propagate Russian Sage, it’s essential to pay attention to a few key details. Using fresh cuttings, taken from the current season’s growth, can significantly improve rooting success. Providing adequate air circulation around the cuttings can also help prevent fungal diseases and promote healthy root development. Monitoring for pests and diseases, such as aphids, whiteflies, and powdery mildew, is crucial to prevent infestations and infections. Regularly inspecting the cuttings and plants can help identify issues early on, allowing for prompt treatment and minimizing the risk of propagation failure. Additionally, maintaining a clean and organized propagation area can help prevent the spread of disease and pests. By following these tips and tricks, gardeners can increase their chances of successful Russian Sage propagation and enjoy the many benefits this beautiful plant has to offer.






:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/how-to-propogation-10-c241017e7e9c440a9aef2f58c66a3e4b.jpg)
