The Art of Living Off Your Backyard: Embracing Self-Sufficiency
Living off your backyard is an appealing and rewarding lifestyle choice, offering self-sufficiency, sustainability, and cost savings. By cultivating your own food, raising small livestock, and utilizing alternative energy sources, you can significantly decrease your reliance on external resources. This comprehensive guide will explore various aspects of living off your backyard, providing valuable insights and guidance for embarking on a self-sufficient journey.
Assessing Your Backyard’s Potential: Identifying Opportunities
To successfully live off your backyard, it is crucial to evaluate its potential for self-sustainability. Begin by assessing the quality of your soil, as this will significantly impact your gardening efforts. Test the soil for nutrient content, pH levels, and drainage to determine which plants will thrive in your backyard. Additionally, consider sunlight exposure, as most vegetables and fruits require at least six hours of direct sunlight daily. Lastly, take stock of your available space, as you can maximize your growing area through vertical gardening and container gardening.
Growing Your Own Food: A Beginner’s Guide to Backyard Gardening
A fundamental aspect of living off your backyard is growing your own food through backyard gardening. To get started, consider the following factors:
- Selecting Plants: Choose plants that are well-suited to your climate, soil conditions, and sunlight exposure. Opt for a mix of vegetables, fruits, and herbs to ensure a diverse and nutrient-rich harvest.
- Preparing the Soil: Enrich your soil with organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, to improve its structure, fertility, and water-holding capacity. Perform a soil test to determine its pH and nutrient levels, adjusting them as necessary.
- Managing Pests: Employ integrated pest management strategies to control pests and diseases in your garden. This may include introducing beneficial insects, using organic pesticides, and practicing crop rotation.
Additionally, consider implementing crop rotation and companion planting to maintain soil fertility and prevent diseases. Crop rotation involves changing the type of crops grown in a particular area each year, while companion planting involves growing different plants together to enhance their growth and pest resistance.
Raising Small Livestock: Chickens, Rabbits, and Bees
Another crucial aspect of living off your backyard is raising small livestock, such as chickens, rabbits, and bees. These animals offer numerous benefits, including fresh eggs, meat, and honey. However, before getting started, it is essential to understand the legal requirements, necessary infrastructure, and care guidelines.
- Chickens: Check local regulations to ensure that raising chickens is allowed in your area. You will need a coop and a run to house and protect your chickens, as well as a consistent supply of food and water. Regularly collect and clean eggs to prevent contamination and disease.
- Rabbits: Similar to chickens, verify local regulations regarding rabbit rearing. Provide a secure hutch and exercise area for your rabbits, along with a balanced diet and fresh water. Regularly clean the hutch to maintain hygiene and prevent illness.
- Bees: Consult local ordinances regarding beekeeping. Acquire bees from a reputable supplier and house them in a well-ventilated, predator-proof hive. Ensure a consistent supply of nectar-rich flowers for foraging and perform routine hive inspections to monitor health and productivity.
By raising small livestock, you can enjoy the benefits of fresh, homegrown products while contributing to your self-sufficient lifestyle.
Alternative Energy Sources: Harnessing the Power of the Sun and Wind
As part of living off your backyard, consider utilizing alternative energy sources to power your projects and daily needs. By harnessing the sun and wind, you can reduce your reliance on traditional electricity, lower your carbon footprint, and save on energy costs.
- Solar Panels: Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity, providing a clean and renewable energy source. They can be installed on rooftops, ground-mounted, or integrated into portable systems for backyard use. Solar panels require minimal maintenance and can last for 25-30 years.
- Wind Turbines: Wind turbines generate electricity by harnessing the power of the wind. Backyard-scale turbines are typically designed for off-grid or supplemental power applications. They are relatively low maintenance and can provide a significant portion of your energy needs, depending on your local wind resources.
- Battery Systems: Battery systems store excess energy produced by solar panels and wind turbines, ensuring a consistent power supply even during periods of low sunlight or wind. Modern battery systems are compact, safe, and long-lasting, making them an ideal complement to alternative energy sources.
By incorporating alternative energy sources into your backyard setup, you can take a significant step towards self-sufficiency and sustainability.
Preserving Your Harvest: Canning, Freezing, and Dehydrating
Preserving your backyard harvest is a crucial aspect of living off your backyard, allowing you to enjoy fresh produce year-round while reducing food waste. Three primary methods of food preservation are canning, freezing, and dehydrating.
- Canning: Canning involves sealing food in airtight containers, such as jars or cans, and processing them in a boiling water bath or pressure canner. This method kills bacteria, yeasts, and molds, ensuring food safety and extending shelf life. Popular canned items include tomatoes, pickles, and fruits.
- Freezing: Freezing is a simple and effective way to preserve fruits, vegetables, and meats. Rapidly freezing food at 0°F (-18°C) or below inhibits bacterial growth, preserving taste, texture, and nutritional value. Blanching vegetables before freezing can further enhance their quality and shelf life.
- Dehydrating: Dehydrating removes moisture from food, preventing bacterial growth and enzymatic reactions that cause spoilage. Dehydrated foods are lightweight, compact, and long-lasting, making them ideal for snacks and camping trips. Commonly dehydrated items include herbs, fruits, and jerky.
By incorporating these preservation techniques into your backyard gardening routine, you can maximize the benefits of your harvest and minimize waste.
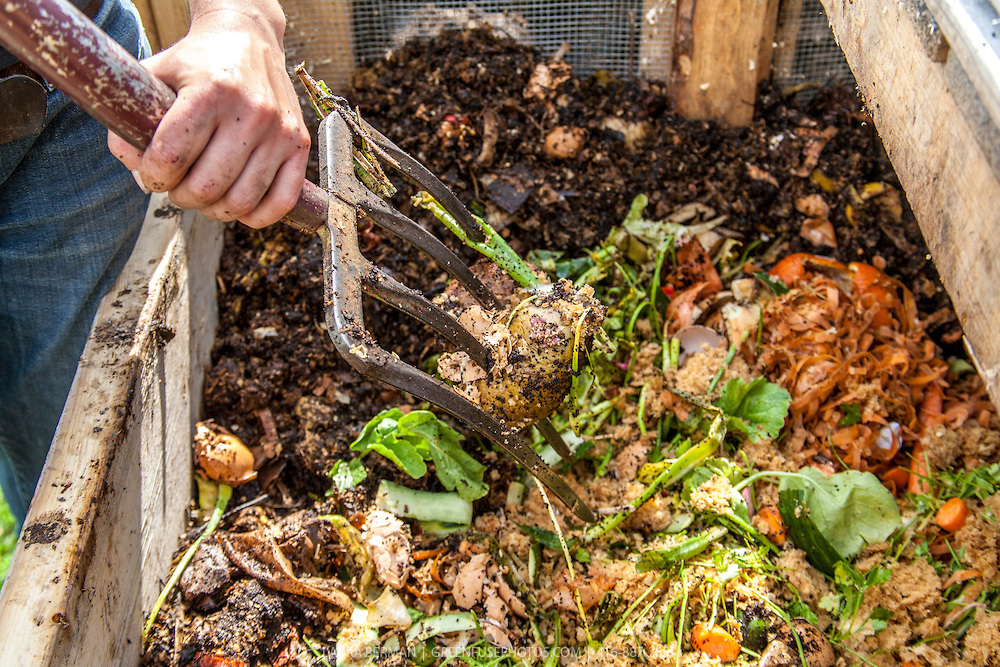
Composting and Vermicomposting: Turning Waste into Wealth
Composting and vermicomposting are essential practices for living off your backyard, as they reduce waste, enrich the soil, and promote sustainability. By transforming organic materials into nutrient-rich compost, you can improve your garden’s productivity and resilience.
- Composting: Composting involves breaking down organic waste, such as fruit and vegetable scraps, yard trimmings, and coffee grounds, into a valuable soil amendment. This process can be accomplished through various methods, including cold composting, hot composting, and tumbling. Composting not only reduces landfill waste but also helps retain moisture in the soil, suppress plant diseases, and promote healthy root development.
- Vermicomposting: Vermicomposting is a form of composting that utilizes worms to break down organic waste. This method is ideal for small spaces, as it can be performed indoors in a compact bin. Worm castings, the end product of vermicomposting, are rich in nutrients and beneficial microorganisms, making them an excellent addition to your garden soil.
By incorporating composting or vermicomposting into your backyard routine, you can enhance your self-sufficiency and contribute to a more sustainable lifestyle.
Living Off Your Backyard: A Journey Towards Self-Sufficiency
Leveraging your backyard for self-sustainability offers numerous rewards, including reduced reliance on external resources, lower costs, and a more environmentally friendly lifestyle. By incorporating various aspects of backyard gardening, raising small livestock, and utilizing alternative energy sources, you can embark on a fulfilling journey towards self-sufficiency.
To begin living off your backyard, consider the following steps:
- Assess your backyard’s potential for self-sustainability, taking into account soil quality, sunlight exposure, and available space.
- Experiment with backyard gardening, starting small and gradually expanding your efforts as you gain confidence and experience.
- Investigate local regulations regarding raising small livestock, and if permitted, explore the possibility of incorporating chickens, rabbits, or bees into your backyard setup.
- Research alternative energy sources, such as solar panels or wind turbines, to determine which options best suit your needs and budget.
- Embrace food preservation techniques, such as canning, freezing, and dehydrating, to extend the life of your garden produce and minimize waste.
- Implement composting or vermicomposting systems to enrich your soil and reduce landfill waste.
By taking these steps, you can begin living off your backyard and enjoy the many benefits of self-sufficiency, sustainability, and cost savings. Remember, the journey towards self-sufficiency is a continuous process, so be patient, persistent, and open to learning from your experiences and those of others.