Understanding Oranges: An Overview of Citrus Sinensis
Oranges, scientifically known as Citrus Sinensis, are a popular and beloved fruit enjoyed by people all over the world. These citrus fruits are native to Southeast Asia, specifically in regions such as China, India, and Vietnam. Oranges have a rich history, with evidence suggesting that they were cultivated in China as early as 2500 BC. Today, oranges are grown in many countries, including Spain, the United States, and Brazil, making them one of the most widely consumed fruits globally.
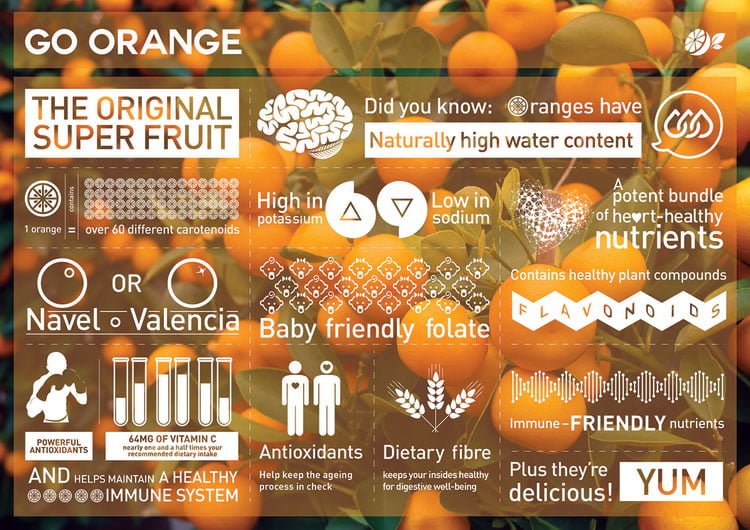
Oranges are known for their bright orange color, round shape, and juicy flesh. They are a great source of vitamin C, fiber, and antioxidants, making them a healthy and nutritious snack. Additionally, oranges have a refreshing and tangy taste that makes them a popular ingredient in various dishes and beverages. In this article, we will delve into the different types of oranges, highlighting their unique features, flavors, and appearances. We will also discuss the growing conditions and seasons for each variety, as well as tips on how to select and store oranges to ensure their freshness and flavor.
Different Kinds of Oranges: A Diverse Range of Varieties
Oranges come in a wide variety of types, each with its own unique features, flavors, and appearances. Here are some of the most popular kinds of oranges:
- Navel Oranges: Navel oranges are characterized by their sweet and juicy flesh, as well as their distinctive “navel” shape, which is actually a second, smaller orange that forms at the end of the fruit. Navel oranges are typically available from November to May and are often used in salads, desserts, and juices.
- Blood Oranges: Blood oranges have a deep red flesh that is both sweet and tart. They are named for their distinctive color, which is due to the presence of anthocyanins, a type of antioxidant. Blood oranges are typically available from December to April and are often used in salads, cocktails, and desserts.
- Valencia Oranges: Valencia oranges are known for their juiciness and high vitamin C content. They are typically available from March to September and are often used in juices, smoothies, and sauces.
- Mandarin Oranges: Mandarin oranges are small, sweet, and easy to peel. They are often used in salads, desserts, and as a snack. Mandarin oranges are typically available from November to January and are often marketed as “tangerines” or “clementines” in the United States.
Each type of orange has its own unique growing conditions and seasons. For example, Navel oranges are typically grown in warm, dry climates, such as California or Florida, while Blood oranges are often grown in cooler, more temperate regions, such as Italy or Spain. Valencia oranges, on the other hand, are typically grown in tropical or subtropical regions, such as Brazil or South Africa. Mandarin oranges are grown in a variety of climates, including China, Spain, and the United States.
How to Select and Store Oranges: Ensuring Freshness and Flavor
When selecting oranges at the grocery store or market, look for fruit that is heavy for its size and has a smooth, firm skin. Avoid oranges that have soft spots, blemishes, or are starting to mold. Additionally, choose oranges that have a bright orange color, as this is often an indicator of freshness and ripeness. If possible, try to buy oranges that are in season, as they will be at their freshest and most flavorful.
To store oranges, keep them in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight. If you plan to eat the oranges within a few days, you can store them at room temperature. However, if you want to keep them fresh for a longer period of time, store them in the refrigerator. Oranges can last for up to two weeks in the refrigerator if stored properly.
To tell if an orange is no longer good to eat, look for signs of spoilage such as mold, soft spots, or an off smell. If the orange has any of these signs, it is best to discard it. Additionally, if the orange has started to dry out or shrivel, it may not be as juicy or flavorful as a fresher orange.
Unique Uses of Oranges: From Cooking to Crafting
Oranges are a versatile fruit that can be used in a variety of ways beyond simply eating them raw. Here are some unique uses of oranges that you may not have considered:
- Cooking: Oranges can be used in a variety of savory and sweet dishes to add flavor and nutrition. For example, you can use fresh orange juice and zest in marinades, sauces, and dressings. You can also use oranges in baking, such as in muffins, cakes, and cookies. Additionally, oranges can be used in slow cooker recipes, such as stews and soups, to add depth of flavor.
- Beverage-making: Oranges are a popular ingredient in a variety of beverages, such as smoothies, juices, and cocktails. You can make your own fresh orange juice at home using a juicer or blender. Additionally, you can use fresh orange zest and juice in cocktails, such as margaritas or cosmopolitans, to add a refreshing twist. Oranges can also be used in non-alcoholic beverages, such as iced tea or lemonade, to add flavor and nutrition.
- Crafting: Orange peels can be used in a variety of crafting projects, such as potpourri, candles, and decorations. For example, you can dry orange peels and use them in potpourri or as natural air fresheners. You can also use orange peels to make candles, which can be used as a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative to traditional candles. Additionally, you can use orange peels to make decorations, such as wreaths or garlands, which can be used to add a festive touch to your home.
Orange Cultivation: From Seed to Tree
Orange trees are a popular choice for home gardeners and commercial farmers alike. Growing oranges from seeds or seedlings can be a rewarding experience, but it requires careful planning and attention to detail. Here are the steps for cultivating orange trees:
- Choosing the right seeds or seedlings: When selecting seeds or seedlings, look for varieties that are well-suited to your climate and growing conditions. Some popular orange varieties include Navel, Blood, Valencia, and Mandarin oranges. Choose seeds or seedlings that are healthy and free from pests or diseases.
- Preparing the soil: Orange trees prefer well-draining soil that is rich in organic matter. Before planting, prepare the soil by adding compost or well-rotted manure. Avoid using soil that is heavy in clay or sand, as this can lead to poor drainage and nutrient deficiencies.
- Providing adequate sunlight and water: Orange trees require at least six hours of direct sunlight per day. Water the trees regularly, providing enough moisture to keep the soil consistently moist but not waterlogged. Overwatering can lead to root rot and other diseases.
- Protecting against pests and diseases: Common pests that affect orange trees include aphids, scales, and whiteflies. Diseases that can affect orange trees include citrus greening, a devastating disease that can kill the tree. To protect against pests and diseases, use organic pesticides and fungicides, and practice good sanitation by removing dead leaves and debris from around the tree.
Orange Festivals and Celebrations: A Global Perspective
Oranges have been a beloved fruit for centuries, and their cultural significance is evident in the many festivals and celebrations that feature oranges as a central theme. Here are some examples of orange festivals from around the world:
- The annual Orange Festival in Spain: Held in the town of Nerja, Spain, the annual Orange Festival celebrates the region’s abundant citrus crops. The festival features a variety of events, including a parade, live music, and a tasting of local orange-based dishes and drinks.
- The Kumquat Festival in Florida: Held in the town of Dade City, Florida, the Kumquat Festival celebrates the small, tart citrus fruit that is native to the region. The festival features a variety of events, including a kumquat cook-off, a kumquat recipe contest, and a kumquat-themed parade.
- The Citrus Festival in South Africa: Held in the town of Citrusdal, South Africa, the Citrus Festival celebrates the region’s citrus industry. The festival features a variety of events, including a citrus-themed parade, live music, and a tasting of local citrus fruits and juices.
Orange-Derived Products: From Beauty to Health
Oranges are not only delicious and nutritious, but they are also a valuable source of ingredients for a variety of products. Here are some examples of orange-derived products:
- Essential oils: Orange essential oil is extracted from the peel of the fruit and is used in aromatherapy, skincare, and household cleaning products. It has a refreshing, uplifting scent and is believed to have antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Skincare products: Oranges are rich in vitamin C and antioxidants, making them a popular ingredient in skincare products. They are used in creams, serums, and toners to brighten and even out skin tone, reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, and protect against environmental stressors.
- Dietary supplements: Orange-derived supplements, such as vitamin C tablets and powder, are used to support immune function, reduce inflammation, and promote overall health and wellness.
Some brands that use orange-derived ingredients in their products include Aesop, Lush, and The Ordinary. These brands are known for their commitment to natural, sustainable, and ethical practices, and are popular choices for consumers who are looking for high-quality, effective products.
Sustainable Orange Farming: Protecting the Environment and Supporting Local Communities
Orange farming has a long and rich history, but it is not without its challenges. In recent years, there has been a growing awareness of the need for sustainable orange farming practices that protect the environment and support local communities. Here are some examples of organizations and initiatives that promote sustainable orange farming:
- Fairtrade International: Fairtrade International is a global organization that works to ensure fair prices, decent working conditions, and sustainable livelihoods for farmers and workers in developing countries. Fairtrade-certified orange farmers receive a fair price for their crops, as well as a premium that is used to invest in community development projects, such as schools, healthcare facilities, and clean water systems.
- Rainforest Alliance: The Rainforest Alliance is a nonprofit organization that works to conserve biodiversity and ensure sustainable livelihoods by transforming land-use practices, business practices, and consumer behavior. Rainforest Alliance-certified orange farms must meet strict standards for environmental protection, social responsibility, and economic viability. These standards include reducing pesticide use, conserving water, and supporting fair labor practices.
- Regenerative Organic Certified: Regenerative Organic Certified is a new certification program that aims to promote regenerative agriculture practices that improve soil health, sequester carbon, and promote biodiversity. Regenerative Organic Certified orange farms must meet strict standards for soil health, animal welfare, and social responsibility. These standards include reducing pesticide use, conserving water, and supporting fair labor practices.
By supporting sustainable orange farming practices, consumers can help protect the environment, support local communities, and enjoy high-quality, delicious oranges. Look for certified oranges at your local grocery store or market, and consider supporting organizations and initiatives that promote sustainable orange farming.