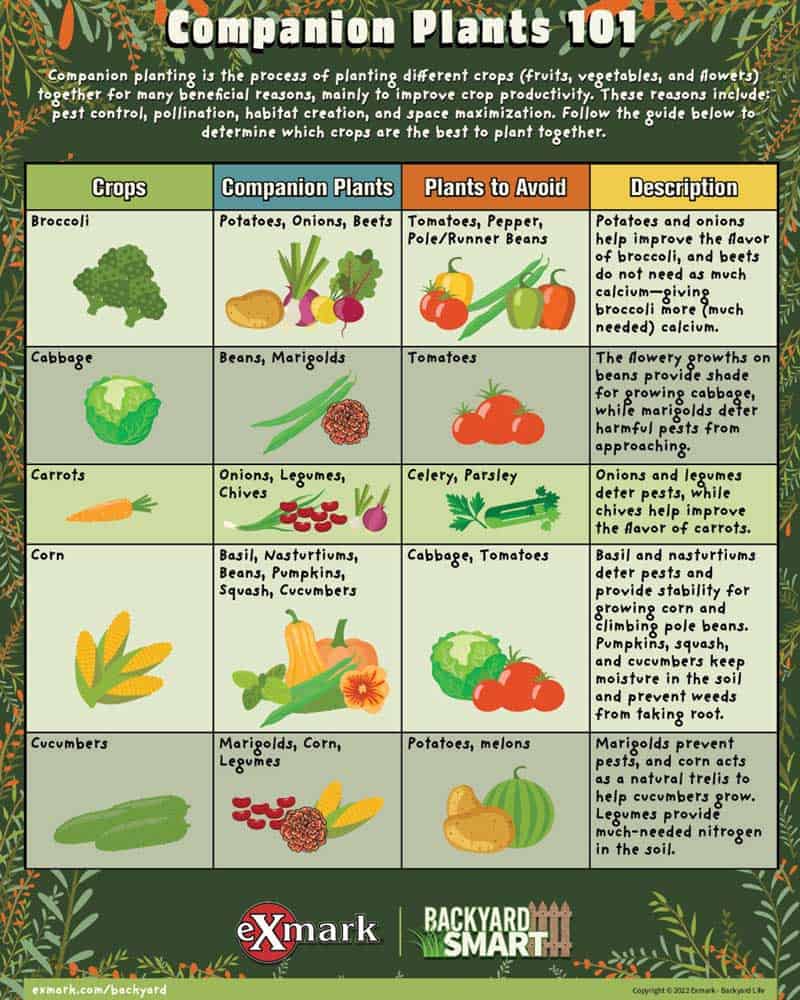
Unlocking the Secrets of Companion Planting
Companion planting is the practice of growing different plants together to improve their growth, health, and productivity. By selecting plants that grow well together, gardeners can create a harmonious and thriving garden ecosystem. This technique has been used for centuries, and its benefits are numerous. Companion planting can help to reduce pests and diseases, improve soil health, and increase biodiversity. For example, planting marigolds with tomatoes can help to deter nematodes, while basil and mint can repel pests that target vegetables. By understanding which plants grow well together, gardeners can create a balanced and resilient garden that requires fewer inputs and maintenance.
In this article, we will explore the concept of companion planting and provide guidance on selecting plants that grow well together. We will discuss the key factors to consider when choosing companion plants, including sunlight requirements, soil type, and watering needs. We will also provide examples of successful plant combinations and offer tips on how to create a balanced ecosystem in your garden. Whether you are a seasoned gardener or just starting out, this article will provide you with the knowledge and inspiration to create a thriving and harmonious garden.
One of the main benefits of companion planting is its ability to improve growth and productivity. By selecting plants that have similar growing requirements, gardeners can create a supportive and nurturing environment that allows each plant to thrive. For example, planting corn, beans, and squash together is a classic example of companion planting. The corn provides a structure for the beans to climb, while the beans fix nitrogen in the soil, and the squash spreads its large leaves to shade the soil and prevent weeds. This combination is often referred to as the “Three Sisters” method and is a great example of how companion planting can improve growth and productivity.
Companion planting is also a great way to reduce pests and diseases in the garden. By selecting plants that repel pests or attract beneficial insects, gardeners can create a balanced ecosystem that requires fewer inputs and maintenance. For example, planting basil and mint together can help to repel pests that target vegetables, while nasturtiums can attract beneficial insects that prey on aphids and whiteflies. By understanding which plants grow well together, gardeners can create a resilient and thriving garden that is better equipped to handle pests and diseases.
Understanding Plant Compatibility: Factors to Consider
When selecting plants to grow together, it’s essential to consider their compatibility. Plants that grow well together typically have similar growing requirements, such as sunlight, soil type, and watering needs. By understanding these factors, gardeners can create a harmonious and thriving garden ecosystem.
One of the most critical factors to consider is sunlight requirements. Some plants require full sun, while others prefer partial shade or full shade. For example, tomatoes and peppers require full sun, while lettuce and spinach prefer partial shade. By pairing plants with similar sunlight requirements, gardeners can ensure that each plant receives the right amount of light.
Soil type is another crucial factor to consider. Some plants prefer well-draining soil, while others prefer moist soil. For example, succulents and cacti prefer well-draining soil, while ferns and peace lilies prefer moist soil. By pairing plants with similar soil requirements, gardeners can ensure that each plant receives the right amount of moisture.
Watering needs are also essential to consider. Some plants require frequent watering, while others prefer infrequent watering. For example, tomatoes and cucumbers require frequent watering, while succulents and cacti prefer infrequent watering. By pairing plants with similar watering needs, gardeners can ensure that each plant receives the right amount of water.
Other factors to consider when selecting plants to grow together include temperature, humidity, and nutrient requirements. By understanding these factors, gardeners can create a balanced and thriving garden ecosystem. For example, plants like basil and mint have similar temperature and humidity requirements, making them a great pair for a garden bed.
Some examples of plants that grow well together include:
- Tomatoes and basil: Tomatoes provide shade for basil, while basil repels pests that target tomatoes.
- Marigolds and carrots: Marigolds repel nematodes that target carrots, while carrots provide a structure for marigolds to grow.
- Beans and corn: Beans provide nitrogen for corn, while corn provides a structure for beans to climb.
By considering these factors and pairing plants that grow well together, gardeners can create a harmonious and thriving garden ecosystem that requires fewer inputs and maintenance.
How to Create a Balanced Ecosystem in Your Garden
Creating a balanced ecosystem in your garden is crucial for the health and productivity of your plants. One way to achieve this is by pairing plants that benefit from each other’s growth. This technique is known as companion planting, and it can help to create a harmonious and thriving garden ecosystem.
One of the most well-known examples of companion planting is the “Three Sisters” method of planting corn, beans, and squash together. This method was used by Native American farmers for centuries and is still used today. The corn provides a structure for the beans to climb, while the beans fix nitrogen in the soil, and the squash spreads its large leaves to shade the soil and prevent weeds.
Another example of companion planting is pairing marigolds with tomatoes. Marigolds repel nematodes that target tomatoes, while tomatoes provide shade for marigolds. This pairing can help to improve the growth and productivity of both plants.
When creating a balanced ecosystem in your garden, it’s essential to consider the needs of each plant. For example, some plants require full sun, while others prefer partial shade. By pairing plants with similar sunlight requirements, you can ensure that each plant receives the right amount of light.
Soil type is also an essential factor to consider when creating a balanced ecosystem. Some plants prefer well-draining soil, while others prefer moist soil. By pairing plants with similar soil requirements, you can ensure that each plant receives the right amount of moisture.
Some other examples of plants that grow well together include:
- Radishes and cucumbers: Radishes repel cucumber beetles, while cucumbers provide shade for radishes.
- Basil and peppers: Basil repels pests that target peppers, while peppers provide a structure for basil to grow.
- Carrots and sage: Carrots provide a structure for sage to grow, while sage repels pests that target carrots.
By pairing plants that grow well together, you can create a balanced and thriving garden ecosystem that requires fewer inputs and maintenance. This technique can also help to improve the growth and productivity of your plants, making it a great way to create a harmonious and thriving garden.
Top Plant Combinations for a Low-Maintenance Garden
Busy gardeners often struggle to find the time to maintain their gardens. However, with the right plant combinations, you can create a low-maintenance garden that thrives with minimal care. Companion planting is a great way to achieve this, as it allows you to pair plants that benefit from each other’s growth and reduce the need for pesticides and fertilizers.
One of the best plant combinations for a low-maintenance garden is succulents and creeping thyme. Succulents are drought-tolerant and require minimal watering, while creeping thyme is a low-growing, spreading plant that can help to suppress weeds. This combination is perfect for busy gardeners who want to create a beautiful and thriving garden with minimal maintenance.
Another great plant combination is marigolds and tomatoes. Marigolds repel nematodes that target tomatoes, while tomatoes provide shade for marigolds. This combination is not only low-maintenance but also provides a natural pest control method.
Other low-maintenance plant combinations include:
- Radishes and cucumbers: Radishes repel cucumber beetles, while cucumbers provide shade for radishes.
- Basil and peppers: Basil repels pests that target peppers, while peppers provide a structure for basil to grow.
- Carrots and sage: Carrots provide a structure for sage to grow, while sage repels pests that target carrots.
When selecting plant combinations for a low-maintenance garden, it’s essential to consider the growing requirements of each plant. Look for plants that have similar sunlight, soil, and watering needs, and pair them together to create a harmonious and thriving garden ecosystem.
Some other tips for creating a low-maintenance garden include:
- Using drought-tolerant plants to reduce watering needs.
- Implementing a mulching system to suppress weeds and retain moisture.
- Using natural pest control methods, such as companion planting, to reduce the need for pesticides.
By following these tips and selecting the right plant combinations, you can create a low-maintenance garden that thrives with minimal care.
Maximizing Space: Vertical Gardening with Companion Plants
Vertical gardening is a great way to maximize space in your garden, and when combined with companion planting, it can be a highly effective way to grow a variety of plants in a small area. By using a trellis or other support system, you can train plants to grow upwards, making the most of your available space.
One of the benefits of vertical gardening with companion plants is that it allows you to grow a variety of plants in a small area. For example, you can plant strawberries and borage together, with the strawberries growing on the ground and the borage growing up a trellis. This not only makes the most of your space but also provides a beautiful and thriving garden ecosystem.
Another great example of vertical gardening with companion plants is peas and mint. Peas can be trained to grow up a trellis, while mint can be planted at the base of the trellis. The peas will provide shade for the mint, while the mint will help to repel pests that target the peas.
Other examples of companion plants that thrive in vertical gardens include:
- Cucumbers and dill: Cucumbers can be trained to grow up a trellis, while dill can be planted at the base of the trellis. The dill will help to repel pests that target the cucumbers.
- Carrots and sage: Carrots can be planted in a vertical garden, while sage can be planted at the top of the garden. The sage will help to repel pests that target the carrots.
- Radishes and nasturtiums: Radishes can be planted in a vertical garden, while nasturtiums can be planted at the top of the garden. The nasturtiums will help to repel pests that target the radishes.
When creating a vertical garden with companion plants, it’s essential to consider the growing requirements of each plant. Look for plants that have similar sunlight, soil, and watering needs, and pair them together to create a harmonious and thriving garden ecosystem.
Some other tips for creating a vertical garden with companion plants include:
- Using a trellis or other support system to train plants to grow upwards.
- Planting a variety of plants in a small area to maximize space.
- Using companion planting to reduce the need for pesticides and fertilizers.
By following these tips and selecting the right companion plants, you can create a thriving and productive vertical garden that makes the most of your available space.
Companion Planting for Pest Control: Natural Solutions
Companion planting is a natural and effective way to control pests in your garden. By pairing plants that repel pests or attract beneficial insects, you can create a balanced ecosystem that reduces the need for pesticides and other chemicals.
One of the most well-known examples of companion planting for pest control is the use of basil and mint to repel pests. Basil repels aphids, whiteflies, and other pests that target vegetables, while mint repels ants, aphids, and other pests that target herbs and flowers.
Another example of companion planting for pest control is the use of nasturtiums to attract beneficial insects. Nasturtiums attract lacewings, hoverflies, and other beneficial insects that prey on aphids, whiteflies, and other pests.
Other examples of companion plants that repel pests include:
- Marigolds: Repel nematodes, whiteflies, and other pests that target vegetables.
- Radishes: Repel cucumber beetles and other pests that target cucumbers.
- Garlic: Repels aphids, spider mites, and other pests that target vegetables.
Some other tips for using companion planting for pest control include:
- Planting a variety of plants together to create a diverse and balanced ecosystem.
- Using physical barriers, such as row covers, to prevent pests from reaching your plants.
- Encouraging beneficial insects, such as bees and butterflies, by planting flowers that attract them.
By using companion planting as a natural pest control method, you can create a healthy and balanced ecosystem in your garden that reduces the need for pesticides and other chemicals.
Some popular companion planting combinations for pest control include:
- Tomatoes and basil: Basil repels pests that target tomatoes, such as aphids and whiteflies.
- Cucumbers and dill: Dill repels aphids and other pests that target cucumbers.
- Carrots and sage: Sage repels pests that target carrots, such as carrot flies and rabbits.
By incorporating these companion planting combinations into your garden, you can create a natural and effective pest control system that promotes a healthy and balanced ecosystem.
Seasonal Plant Pairings: Making the Most of Your Garden Year-Round
Seasonal plant pairings are a great way to ensure a thriving garden year-round. By selecting plants that grow well together during different seasons, you can create a diverse and resilient garden ecosystem that provides a constant source of fresh produce and beauty.
Winter is a great time to plant cool-season crops like kale, spinach, and garlic. These plants thrive in the cooler temperatures and can be paired with other plants like Brussels sprouts, broccoli, and cauliflower. For example, planting kale and garlic together can help to repel pests that target kale, while Brussels sprouts and broccoli can be planted together to create a diverse and nutritious winter garden.
Spring is a time of renewal and growth, and it’s a great time to plant warm-season crops like tomatoes, peppers, and eggplants. These plants can be paired with other plants like basil, mint, and lemongrass to create a fragrant and flavorful garden. For example, planting tomatoes and basil together can help to repel pests that target tomatoes, while peppers and eggplants can be planted together to create a diverse and nutritious spring garden.
Summer is a great time to plant warm-season crops like zinnias, cosmos, and sunflowers. These plants can be paired with other plants like marigolds, nasturtiums, and calendulas to create a colorful and vibrant garden. For example, planting zinnias and cosmos together can help to attract beneficial insects, while marigolds and nasturtiums can be planted together to create a diverse and resilient summer garden.
Fall is a great time to plant cool-season crops like broccoli, cauliflower, and kale. These plants can be paired with other plants like carrots, beets, and radishes to create a diverse and nutritious fall garden. For example, planting broccoli and cauliflower together can help to repel pests that target broccoli, while carrots and beets can be planted together to create a diverse and resilient fall garden.
Some other seasonal plant pairing suggestions include:
- Winter: Kale and garlic, Brussels sprouts and broccoli, cauliflower and carrots.
- Spring: Tomatoes and basil, peppers and eggplants, zinnias and cosmos.
- Summer: Zinnias and cosmos, marigolds and nasturtiums, sunflowers and calendulas.
- Fall: Broccoli and cauliflower, carrots and beets, kale and radishes.
By incorporating these seasonal plant pairings into your garden, you can create a diverse and resilient garden ecosystem that provides a constant source of fresh produce and beauty year-round.
Putting it all Together: Creating a Companion Planting Plan
Creating a companion planting plan is a great way to ensure a thriving and harmonious garden. By considering the needs and benefits of different plants, you can create a personalized plan that meets your specific gardening goals.
The first step in creating a companion planting plan is to assess your garden’s conditions. Consider the amount of sunlight, soil type, and watering needs of your garden. This will help you determine which plants will thrive in your garden and which plants to pair together.
Next, select the plants you want to include in your companion planting plan. Consider the benefits and needs of each plant, as well as their growth habits and space requirements. Make sure to choose plants that grow well together and provide a diverse range of benefits.
Once you have selected your plants, design a harmonious garden layout. Consider the mature size of each plant and leave enough space for proper growth and air circulation. Also, consider the visual appeal of your garden and create a layout that is aesthetically pleasing.
Some tips for creating a companion planting plan include:
- Start small and gradually add more plants to your garden.
- Consider the mature size of each plant and leave enough space for proper growth and air circulation.
- Choose plants that grow well together and provide a diverse range of benefits.
- Design a harmonious garden layout that is aesthetically pleasing.
Some popular companion planting plans include:
- The “Three Sisters” method of planting corn, beans, and squash together.
- Planting marigolds and tomatoes together to repel nematodes and attract beneficial insects.
- Planting basil and mint together to repel pests and attract beneficial insects.
By following these tips and creating a personalized companion planting plan, you can create a thriving and harmonious garden that meets your specific gardening goals.