Uncovering the Early Signs of Strawberry Growth
Watching strawberry plants grow can be an exciting experience, especially when you’re able to identify the early signs of sprouting. Recognizing strawberry sprouts is crucial for optimal growth, as it allows you to provide the necessary care and attention to ensure a healthy and bountiful harvest. In this article, we’ll guide you through the process of identifying strawberry sprouts and provide valuable tips for promoting healthy growth.
Strawberry plants are one of the most popular fruits to grow in home gardens, and for good reason. They’re relatively easy to care for, produce delicious fruit, and can thrive in a variety of conditions. However, to get the most out of your strawberry plants, it’s essential to understand what they look like when they sprout. So, what do strawberries look like when they sprout? Let’s take a closer look.
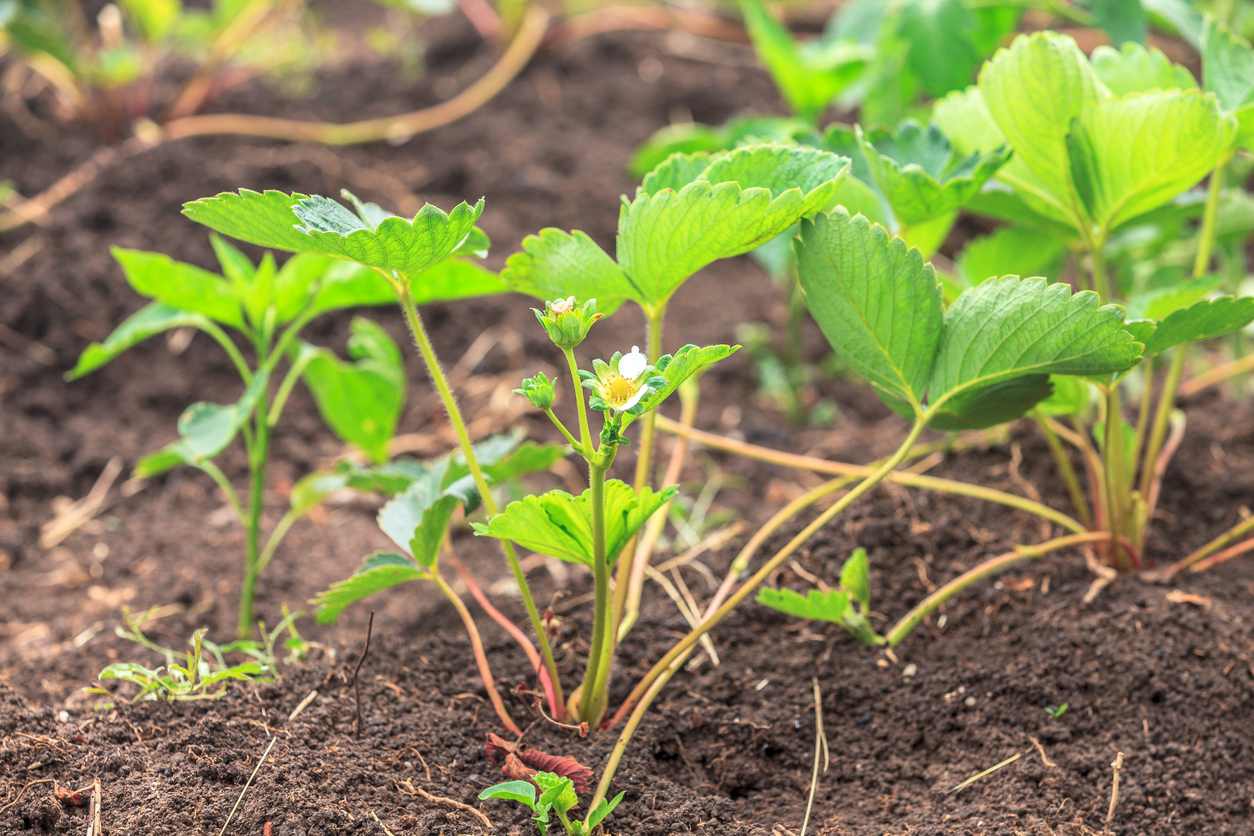
Strawberry sprouts typically emerge from the soil 1-3 weeks after planting, depending on factors such as weather, soil quality, and the specific variety of strawberry. During this time, the seeds germinate, and the first leaves begin to emerge. These initial leaves are usually small, oval-shaped, and a bright green color. As the plant grows, the leaves will become larger and more rounded, with a distinctive serrated edge.
Identifying strawberry sprouts early on allows you to provide the necessary care and attention to promote healthy growth. This includes ensuring the soil is consistently moist, providing adequate sunlight, and fertilizing regularly. By recognizing the early signs of strawberry growth, you can take steps to optimize the growing conditions and set your plants up for success.
In the following sections, we’ll delve deeper into the life cycle of strawberry plants, explore the first signs of strawberry sprouts, and provide expert tips on how to care for your strawberry plants. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just starting out, this guide will help you unlock the secrets of growing delicious and healthy strawberries.
Understanding the Life Cycle of Strawberry Plants
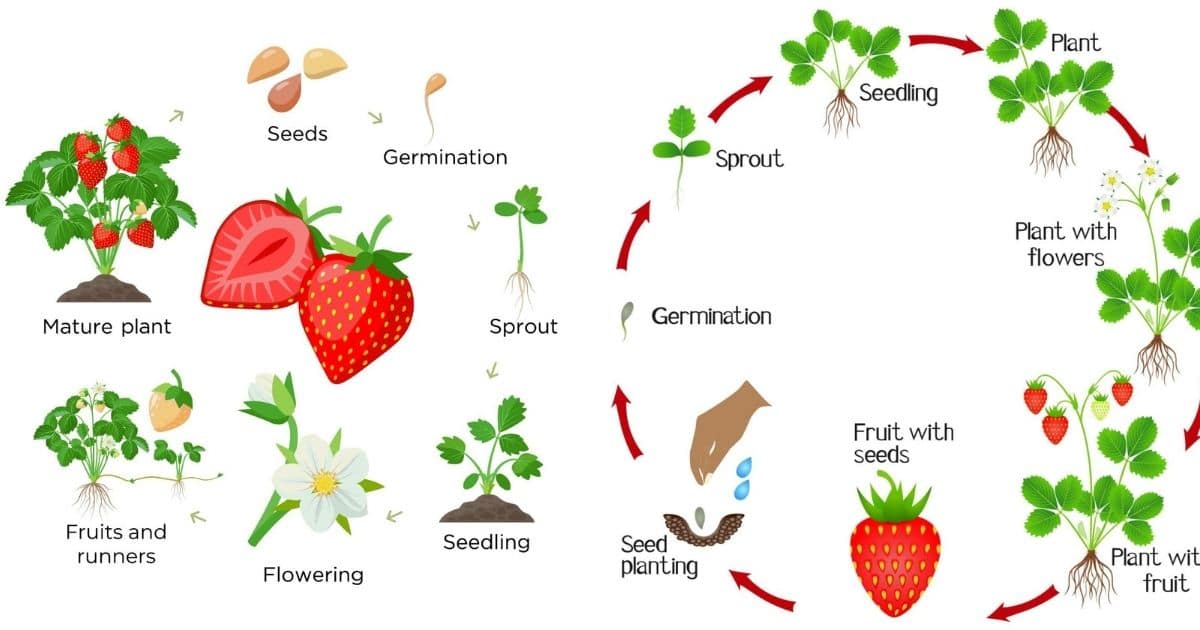
The life cycle of strawberry plants is a complex process that involves several stages of growth, from seed germination to maturity. Understanding these stages is crucial for recognizing the transition from seedling to sprout and providing optimal care for your strawberry plants.
The life cycle of strawberry plants can be divided into five main stages: seed germination, seedling establishment, vegetative growth, flowering, and fruiting. During the seed germination stage, the seeds begin to sprout, and the first leaves emerge. This stage typically lasts around 1-3 weeks, depending on factors such as weather, soil quality, and the specific variety of strawberry.
As the seedling establishes itself, the first leaves grow larger, and the stem begins to develop. This stage is critical for the development of a strong root system, which is essential for the plant’s overall health and productivity. During the vegetative growth stage, the plant produces more leaves, stems, and roots, and begins to produce runners, which are long stems that produce new plants at their tips.
The flowering stage is a critical period in the life cycle of strawberry plants, as it marks the beginning of fruit production. During this stage, the plant produces flowers, which are self-pollinating, meaning they don’t require external pollination to produce fruit. The fruiting stage is the final stage of the life cycle, during which the flowers develop into strawberries.
Recognizing the different stages of growth is essential for providing optimal care for your strawberry plants. By understanding what to expect at each stage, you can take steps to promote healthy growth, prevent common mistakes, and ensure a bountiful harvest. In the next section, we’ll take a closer look at what strawberry sprouts look like and how to identify them in your garden.
When asking what do strawberries look like when they sprout, it’s essential to consider the different stages of growth and how they relate to the overall life cycle of the plant. By understanding these stages, you can better appreciate the complexity of strawberry growth and take steps to promote optimal development.
The First Signs of Strawberry Sprouts: What to Look For
When asking what do strawberries look like when they sprout, it’s essential to know what to look for. Strawberry sprouts are small, delicate, and can be easily overlooked. However, by recognizing the first signs of growth, you can take steps to promote healthy development and ensure a bountiful harvest.
The first leaves of a strawberry sprout are typically small, oval-shaped, and a bright green color. They are often referred to as “cotyledons” or “seed leaves.” These leaves are an essential part of the plant’s development, as they provide the necessary nutrients and energy for growth.
As the plant grows, the first true leaves emerge. These leaves are larger and more rounded than the cotyledons, with a distinctive serrated edge. The stems of the plant begin to develop, and the roots start to grow, anchoring the plant in the soil.
One of the most distinctive features of strawberry sprouts is the appearance of the crown. The crown is the central part of the plant, from which the leaves and stems emerge. It is typically white or light-colored and can be seen just above the soil surface.
When examining your strawberry plants for signs of growth, look for the following characteristics:
- Small, oval-shaped leaves with a bright green color
- Larger, rounded leaves with a serrated edge
- A white or light-colored crown just above the soil surface
- Delicate stems and roots emerging from the soil
By recognizing these characteristics, you can identify strawberry sprouts in your garden and take steps to promote healthy growth. In the next section, we’ll explore how to care for your strawberry sprouts, including tips on watering, fertilizing, and pruning.
Remember, understanding what strawberries look like when they sprout is crucial for providing optimal care and ensuring a successful harvest. By recognizing the first signs of growth, you can take steps to promote healthy development and enjoy a bountiful crop of delicious strawberries.
How to Care for Your Strawberry Sprouts
Caring for strawberry sprouts requires attention to detail and a commitment to providing optimal growing conditions. By following these tips and advice, you can help your strawberry sprouts thrive and produce a bountiful harvest.
Watering is one of the most critical aspects of caring for strawberry sprouts. Strawberry plants require consistent moisture, especially during the first few weeks after germination. Water your strawberry sprouts gently but thoroughly, making sure the soil is moist but not waterlogged.
Fertilizing is also essential for promoting healthy growth in strawberry sprouts. Use a balanced fertilizer that is high in phosphorus, which promotes root development and fruiting. Apply the fertilizer according to the manufacturer’s instructions, taking care not to over-fertilize, which can damage the plants.
Pruning is another important aspect of caring for strawberry sprouts. Remove any dead or damaged leaves or stems, and trim back the runners to encourage bushy growth and prevent the plants from becoming too leggy.
In addition to watering, fertilizing, and pruning, there are several other things you can do to promote healthy growth in your strawberry sprouts. Make sure they receive full sun to partial shade, and maintain a consistent temperature between 60-70°F (15-21°C).
It’s also essential to provide your strawberry sprouts with good air circulation to prevent disease. Keep the plants at least 12-18 inches apart, and avoid overcrowding, which can lead to fungal diseases and other problems.
By following these tips and advice, you can help your strawberry sprouts thrive and produce a bountiful harvest. Remember, understanding what strawberries look like when they sprout is just the first step in growing delicious and healthy strawberries.
In the next section, we’ll discuss common mistakes to avoid when growing strawberry sprouts, including overwatering, underwatering, and inadequate sunlight. By being aware of these potential pitfalls, you can take steps to prevent them and ensure a successful harvest.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Growing Strawberry Sprouts
While growing strawberry sprouts can be a rewarding experience, there are several common mistakes that can hinder their growth and development. By being aware of these potential pitfalls, you can take steps to prevent them and ensure a successful harvest.
One of the most common mistakes when growing strawberry sprouts is overwatering. Strawberry plants require consistent moisture, but too much water can lead to root rot and other problems. Check the soil regularly to ensure it is moist but not waterlogged, and avoid getting water on the leaves or crown of the plant.
Underwatering is another common mistake that can affect strawberry sprouts. If the soil is too dry for too long, the plants may become stressed and produce fewer fruit. Make sure to water your strawberry sprouts regularly, especially during hot or dry weather.
Inadequate sunlight is another common mistake that can affect strawberry sprouts. Strawberry plants require full sun to partial shade, so make sure to place them in a location that receives at least 6 hours of direct sunlight per day.
Other common mistakes to avoid when growing strawberry sprouts include:
- Overfertilizing, which can damage the plants and lead to excessive vegetative growth
- Not providing enough space between plants, which can lead to overcrowding and disease
- Not pruning the plants regularly, which can lead to reduced fruit production and plant vigor
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can help your strawberry sprouts thrive and produce a bountiful harvest. Remember, understanding what strawberries look like when they sprout is just the first step in growing delicious and healthy strawberries.
In the next section, we’ll discuss how to recognize pests and diseases in strawberry sprouts, and provide advice on how to prevent and treat these issues.
Recognizing Pests and Diseases in Strawberry Sprouts
Strawberry sprouts can be susceptible to a variety of pests and diseases that can affect their growth and productivity. By recognizing the signs and symptoms of these issues, you can take steps to prevent and treat them, ensuring a healthy and thriving strawberry crop.
Aphids are one of the most common pests that can affect strawberry sprouts. These small, soft-bodied insects feed on the sap of the plant, causing curled or distorted leaves. To control aphids, use neem oil or insecticidal soap, and make sure to remove any infested plants to prevent the spread of the pest.
Slugs and snails are another common pest that can affect strawberry sprouts. These pests feed on the leaves and fruit of the plant, causing holes and damage. To control slugs and snails, use copper tape or crushed eggshells around the plants, and hand-pick any slugs or snails you find.
Powdery mildew is a common disease that can affect strawberry sprouts. This fungal disease causes a white, powdery coating to form on the leaves of the plant, and can lead to reduced growth and productivity. To control powdery mildew, use a fungicide specifically designed for strawberries, and make sure to remove any infected plants to prevent the spread of the disease.
Other common pests and diseases that can affect strawberry sprouts include:
- Spider mites, which cause yellowing or bronzing of the leaves
- Botrytis, a fungal disease that causes gray mold to form on the fruit and leaves
- Root rot, a fungal disease that causes the roots of the plant to rot and decay
By recognizing the signs and symptoms of these pests and diseases, you can take steps to prevent and treat them, ensuring a healthy and thriving strawberry crop. Remember, understanding what strawberries look like when they sprout is just the first step in growing delicious and healthy strawberries.
In the next section, we’ll discuss how to transplant strawberry sprouts for optimal growth, including tips on how to minimize shock and ensure successful transplantation.
How to Transplant Strawberry Sprouts for Optimal Growth
Transplanting strawberry sprouts into larger containers or directly into the garden can be a crucial step in their growth and development. By following these tips and guidelines, you can minimize shock and ensure successful transplantation.
Before transplanting, make sure the strawberry sprouts have at least two sets of leaves and are around 2-3 inches tall. This will ensure they are strong enough to withstand the transplanting process.
Choose a container that is at least 6-8 inches deep and has good drainage holes. Fill the container with a well-draining potting mix, and gently remove the strawberry sprout from its original container.
Plant the strawberry sprout in the new container, making sure the crown (where the roots and leaves meet) is above the soil surface. Water the plant thoroughly, and provide adequate sunlight and nutrients.
When transplanting strawberry sprouts directly into the garden, choose a location that receives full sun to partial shade and has well-draining soil. Plant the strawberry sprout at the same depth as it was in the container, and water thoroughly.
To minimize shock, make sure to:
- Handle the roots gently to avoid damaging them
- Water the plant thoroughly after transplanting
- Provide adequate sunlight and nutrients
- Avoid transplanting during extreme weather conditions
By following these tips and guidelines, you can ensure successful transplantation and optimal growth for your strawberry sprouts. Remember, understanding what strawberries look like when they sprout is just the first step in growing delicious and healthy strawberries.
In the next section, we’ll celebrate the joy of harvesting homegrown strawberries and provide guidance on when to expect fruiting, how to identify ripe strawberries, and tips for enjoying your fresh harvest.
Enjoying the Fruits of Your Labor: Harvesting Your Strawberries
After weeks of careful nurturing, your strawberry plants are finally ready to produce fruit. Harvesting your homegrown strawberries is a rewarding experience, and with these tips, you can enjoy the fruits of your labor.
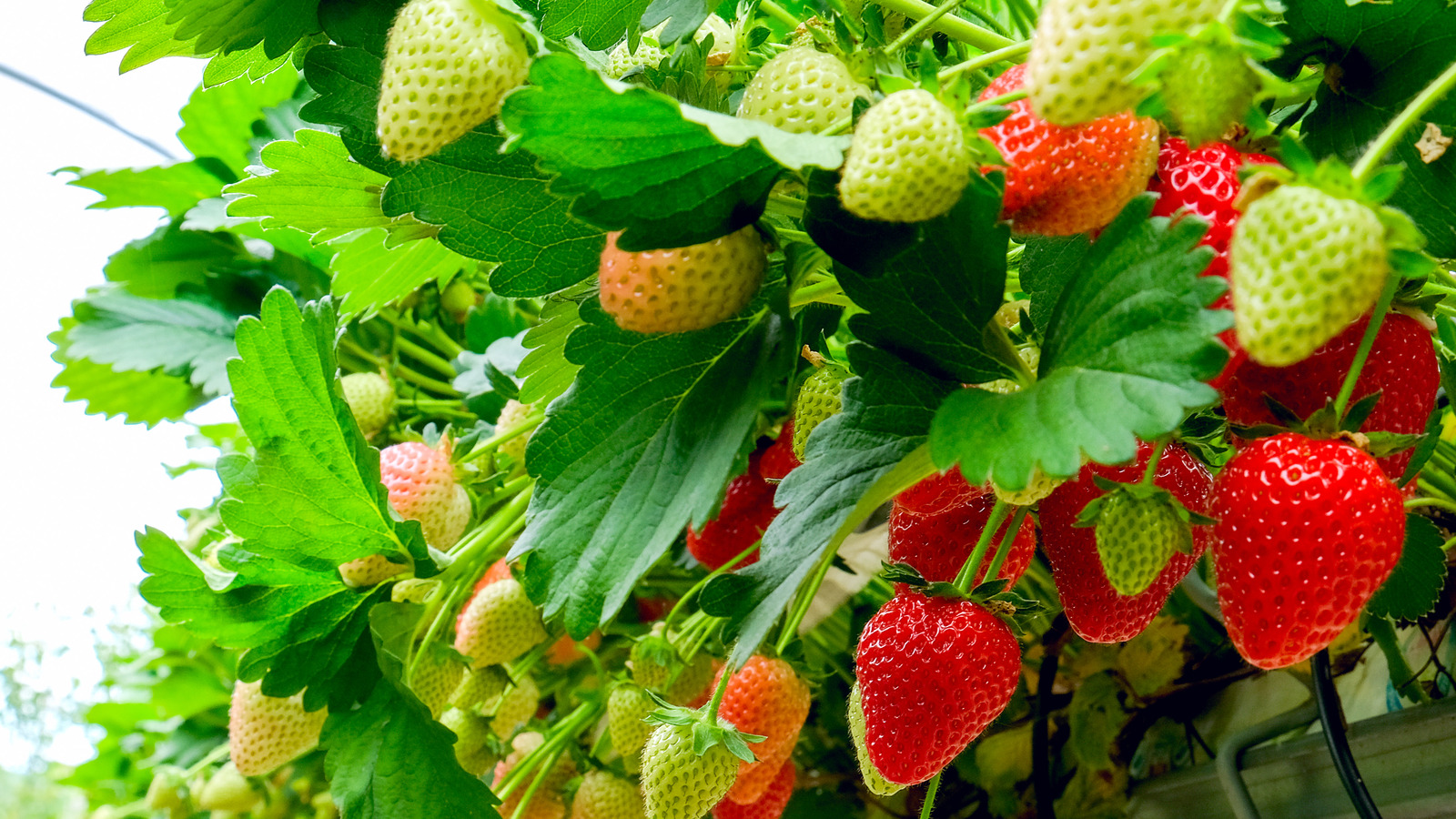
Strawberries are typically ready to harvest about 60 days after planting. Check your plants regularly for ripe fruit, which will be bright red and slightly soft to the touch. Avoid picking strawberries that are not yet ripe, as they will not continue to ripen after being picked.
To harvest your strawberries, gently grasp the fruit and twist it from the stem. Make sure to leave a small piece of stem attached to the fruit to help it stay fresh. You can also use scissors to cut the stem, leaving about 1 inch of stem attached to the fruit.
Strawberries are a delicate fruit and should be handled with care. Avoid squeezing or bruising the fruit, as this can cause damage and reduce its shelf life.
Once you’ve harvested your strawberries, you can enjoy them fresh, use them in recipes, or preserve them for later use. Some popular ways to enjoy strawberries include:
- Eating them fresh, either on their own or with whipped cream or ice cream
- Using them in salads, smoothies, or other recipes
- Preserving them through freezing, canning, or dehydrating
By following these tips and guidelines, you can enjoy the fruits of your labor and savor the delicious taste of homegrown strawberries. Remember, understanding what strawberries look like when they sprout is just the first step in growing delicious and healthy strawberries.
With these tips and guidelines, you’re now ready to start growing your own strawberries and enjoying the fruits of your labor. Happy growing!