Delving into the World of Plant Classification
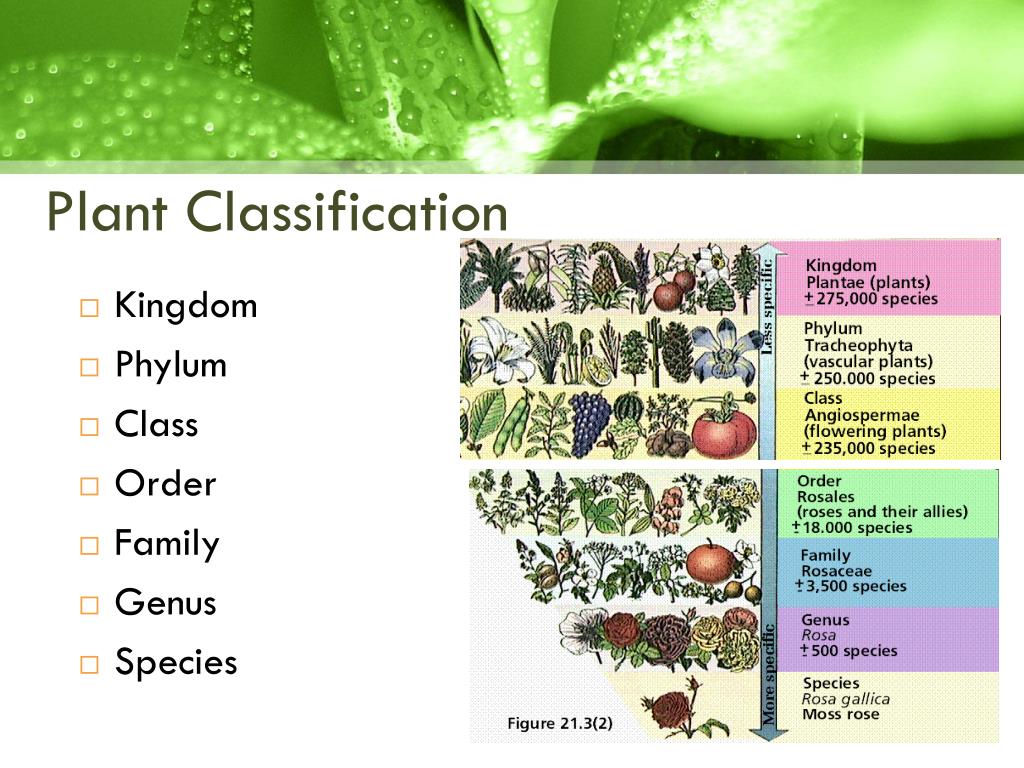
Plant classification is a fundamental concept in botany that helps us understand the relationships between different plant species. By grouping plants into categories based on their shared characteristics, we can better comprehend their properties and behaviors. This system of classification is essential for identifying and studying the vast array of plant species that exist on our planet. When we ask ourselves “what family is the tomato in,” we are, in essence, seeking to understand its place within this complex web of relationships. In the context of plant classification, the family is a critical taxonomic rank that helps us narrow down the identification of a particular species. In the case of tomatoes, understanding their family affiliation is crucial for appreciating their unique characteristics and properties. By recognizing the relationships between different plant species, we can gain a deeper understanding of their evolution, growth habits, and potential uses.
The Solanaceae Family: A Brief Overview
The Solanaceae family, commonly known as the nightshade family, is a diverse and widespread group of plants that comprises over 2,800 species. This family is significant in the plant kingdom, as it includes many economically important crops, such as potatoes, peppers, and eggplants, in addition to tomatoes. The Solanaceae family is characterized by its unique flower structure, which typically features five petals and a distinctive arrangement of stamens. Other well-known plants that belong to this family include tobacco, petunias, and deadly nightshade. Understanding the Solanaceae family is essential for answering the question “what family is the tomato in,” as it provides a framework for exploring the relationships between tomatoes and their relatives. By examining the characteristics and properties of plants within this family, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and diversity of the plant kingdom.
How to Identify Tomato Relatives in the Solanaceae Family
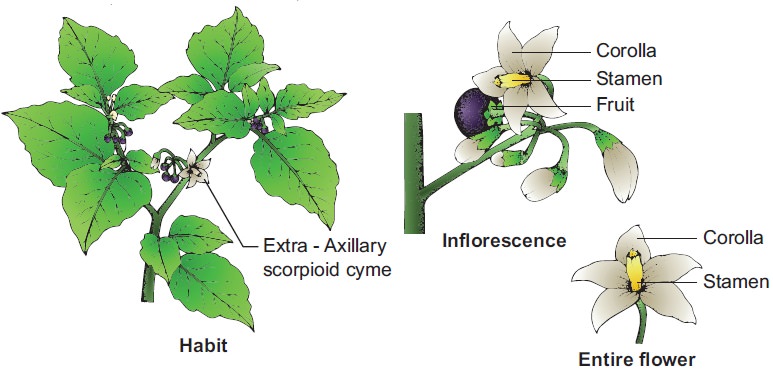
When trying to identify plants that are closely related to tomatoes within the Solanaceae family, there are several key characteristics to look for. One of the most distinctive features of Solanaceae plants is their flower shape, which typically consists of five petals and a central cluster of stamens. Leaf structure is another important identifier, with many Solanaceae plants featuring alternate, simple leaves with a pointed tip. Fruit type is also a crucial characteristic, as Solanaceae plants often produce berries, such as tomatoes, or capsules, like those found on petunias. By examining these features, it becomes clear that plants like peppers, eggplants, and potatoes are all closely related to tomatoes, answering the question “what family is the tomato in.” Additionally, other plants like tobacco and deadly nightshade, although not as closely related, still share many characteristics with tomatoes and are part of the Solanaceae family. By recognizing these patterns and relationships, we can better understand the diversity and complexity of the plant kingdom.
The Evolutionary History of Tomatoes and Their Closest Relatives
The evolutionary history of tomatoes and their closest relatives is a fascinating story that spans millions of years. Through fossil records and genetic analysis, scientists have been able to reconstruct the history of the Solanaceae family, including the tomato’s ancestors. It is believed that the Solanaceae family originated in the Andes Mountains of South America, where the earliest known relatives of tomatoes, such as the wild tomato (Solanum lycopersicum var. cerasiforme), can still be found. Over time, these early tomato relatives diverged and evolved into distinct species, adapting to different environments and developing unique characteristics. For example, the potato, another member of the Solanaceae family, evolved from a common ancestor with tomatoes around 7-10 million years ago. Understanding the evolutionary history of tomatoes and their closest relatives provides valuable insights into the development of their unique characteristics and properties, ultimately helping us better comprehend what family is the tomato in and its significance in the plant kingdom.
What Makes Tomatoes Unique within the Solanaceae Family
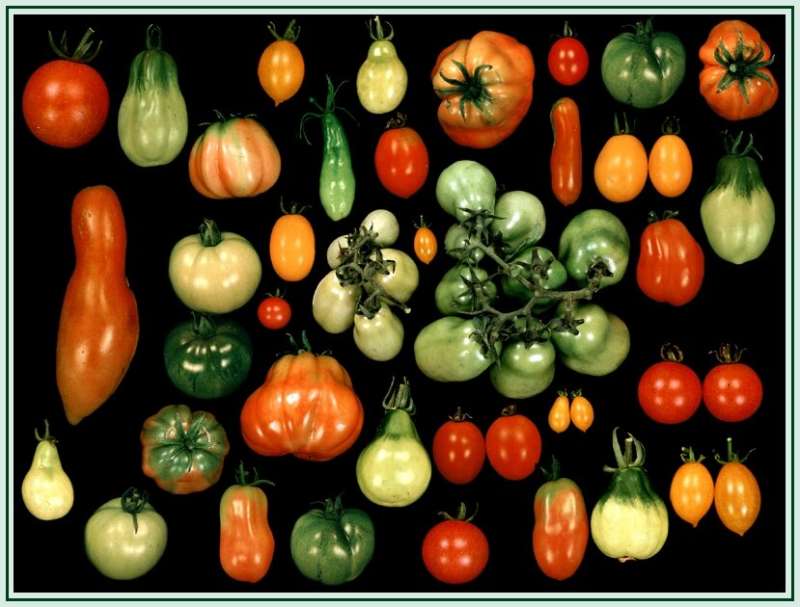
While tomatoes share many characteristics with their relatives in the Solanaceae family, they possess several distinct features that set them apart. One of the most notable differences is their fruit type. Tomatoes are a type of berry, specifically a “true berry,” which means that the fruit comes from a single ovary in the flower. This is in contrast to other Solanaceae plants like peppers, which are technically a type of fruit known as a capsule. Tomatoes are also unique in their growth habits, with many varieties being indeterminate, meaning they will continue to grow and produce fruit throughout the season. Additionally, tomatoes have adapted to thrive in a wide range of environments, from the hot and dry to the cool and wet. This adaptability has made them a staple crop in many parts of the world, and has contributed to their widespread cultivation and consumption. Understanding what makes tomatoes unique within the Solanaceae family provides valuable insights into their characteristics and properties, ultimately helping us better comprehend what family is the tomato in and its significance in the plant kingdom.
Exploring the Culinary and Cultural Significance of Tomatoes
Tomatoes have had a profound impact on human culture and cuisine, playing a starring role in many traditional dishes around the world. From the rich flavors of Italian pasta sauces to the vibrant colors of Mexican salsas, tomatoes have become an integral part of our culinary heritage. But their significance extends beyond the kitchen, with tomatoes also holding important cultural and symbolic meanings in many societies. In some cultures, tomatoes are seen as a symbol of love and fertility, while in others they are associated with good luck and prosperity. The nutritional benefits of tomatoes have also been well-documented, with high levels of vitamins A and C, potassium, and lycopene making them a valuable addition to a healthy diet. As we continue to explore the botanical relationships between tomatoes and their relatives within the Solanaceae family, it’s clear that understanding what family is the tomato in is crucial to appreciating the full significance of this beloved fruit. By examining the cultural and culinary significance of tomatoes, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complex and fascinating world of plant classification.
Tomatoes in Modern Times: Breeding, Genetics, and Beyond
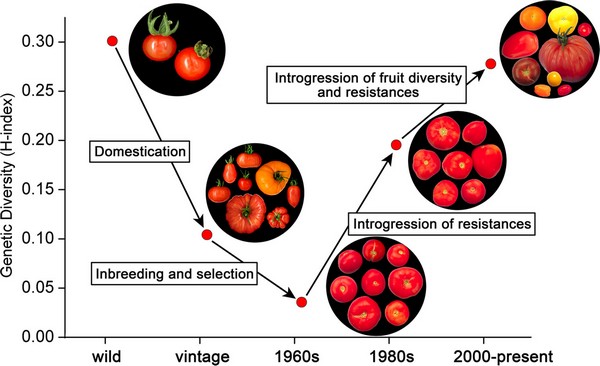
In modern times, tomato breeding and genetics have become increasingly sophisticated, driven by advances in technology and our understanding of plant biology. Today, scientists are working to develop new tomato varieties with desirable traits, such as improved disease resistance, increased yield, and enhanced nutritional content. This is achieved through a combination of traditional breeding techniques and cutting-edge genetic engineering methods. By understanding what family is the tomato in and its relationships with other plants in the Solanaceae family, researchers can identify and exploit genetic variations that will benefit tomato cultivation. For example, scientists have developed tomatoes with increased resistance to diseases such as verticillium and fusarium wilt, which can devastate tomato crops. Additionally, efforts are being made to develop tomatoes with improved flavor profiles, textures, and colors, catering to the diverse preferences of consumers around the world. As our knowledge of tomato genetics and breeding continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more innovative and exciting developments in the world of tomatoes.
Conclusion: Unraveling the Tomato’s Family Ties
In conclusion, our botanical exploration of tomatoes has revealed the fascinating world of plant classification and the significance of understanding the relationships between different plant species. By examining the Solanaceae family, we have gained insight into the characteristics and properties of tomatoes and their relatives, including their evolutionary history, unique features, and cultural significance. As we continue to explore the complexities of plant biology, it is essential to recognize the importance of understanding what family is the tomato in and its relationships within the Solanaceae family. This knowledge has far-reaching implications for tomato breeding, genetics, and cultivation, ultimately benefiting our ability to grow and enjoy this beloved fruit. By unraveling the tomato’s family ties, we can deepen our appreciation for the intricate web of relationships within the plant kingdom and continue to uncover the secrets of this remarkable fruit.