Understanding the Importance of Regular Harvesting
Regular harvesting is a crucial aspect of asparagus cultivation, playing a significant role in maintaining the health and productivity of the plants. Asparagus is a perennial crop that requires careful management to ensure optimal yields and spear quality. One of the primary reasons regular harvesting is essential is that it allows the plants to redirect their energy towards producing new spears, rather than allowing them to mature and go to seed. This process, known as “forcing,” enables the plants to conserve energy and resources, leading to healthier and more productive crowns.
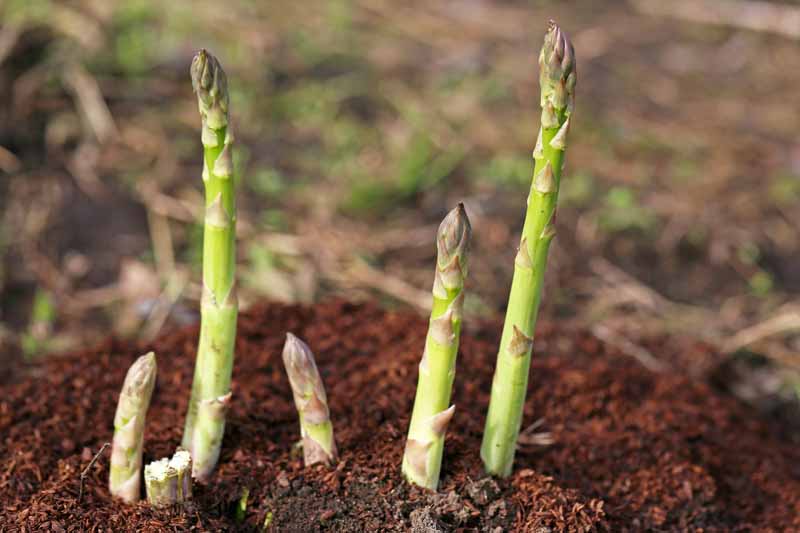
When asparagus is harvested regularly, the spears are typically removed when they reach a height of 6-8 inches, before they have a chance to mature and become tough. This not only ensures that the spears are tender and flavorful but also helps to prevent the plants from becoming leggy and weak. Furthermore, regular harvesting encourages the plants to produce new spears, which can lead to increased yields and a longer harvesting season.
On the other hand, neglecting to harvest asparagus can have negative consequences, including reduced yields, decreased spear size, and increased susceptibility to disease. When asparagus is left unharvested, the spears will eventually mature and go to seed, which can lead to a decrease in plant vigor and productivity. This is because the plants are expending energy on seed production, rather than on producing new spears.
In addition to the physical changes that occur in the plants, neglecting to harvest asparagus can also impact the flavor and texture of the spears. Asparagus that is left unharvested will eventually become tough and fibrous, losing its delicate flavor and crunchy texture. This is because the cell walls of the spears will begin to break down, leading to a loss of texture and flavor.
Overall, regular harvesting is essential for maintaining the health and productivity of asparagus plants. By removing the spears at the optimal time, growers can encourage the plants to produce new spears, leading to increased yields and a longer harvesting season. Conversely, neglecting to harvest asparagus can have negative consequences, including reduced yields, decreased spear size, and increased susceptibility to disease.
What Happens When Asparagus Goes Unharvested
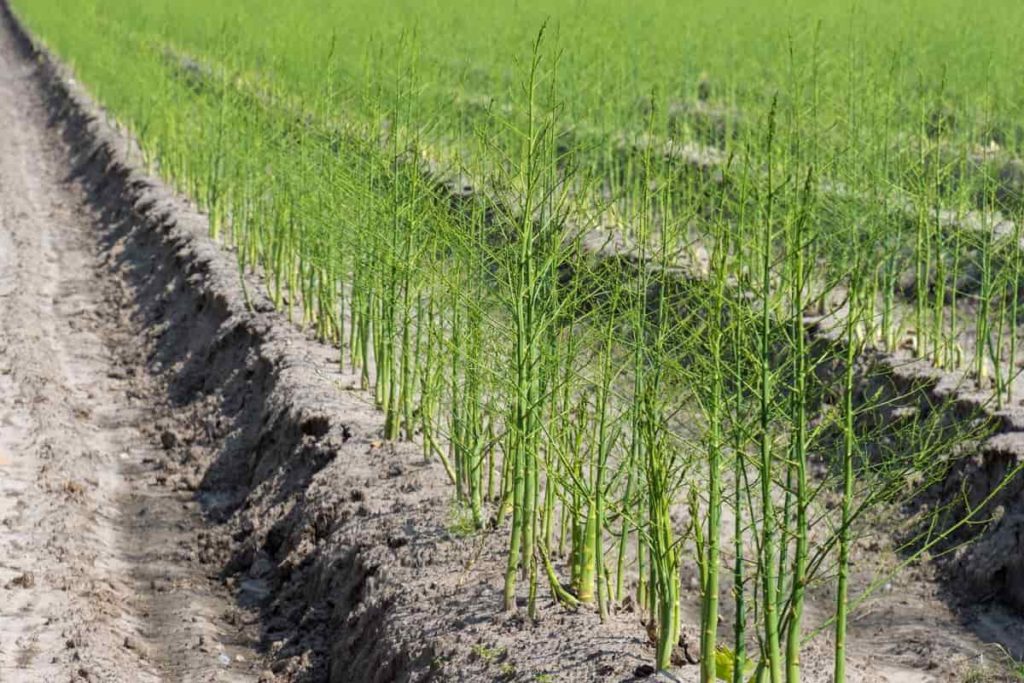
When asparagus is left unharvested, it undergoes a series of physical changes that can significantly impact its quality and edibility. One of the most noticeable changes is the transition from tender shoots to tough, woody stems. This is because the cell walls of the spears begin to break down, leading to a loss of texture and flavor.
As the spears mature, they will eventually reach a height of 3-4 feet, at which point they will begin to produce seeds. This process, known as “bolting,” can lead to a decrease in plant vigor and productivity, as the plants are expending energy on seed production rather than on producing new spears.
Another consequence of neglecting to harvest asparagus is the development of a tough, fibrous texture. This is because the spears will begin to produce lignin, a complex organic compound that provides structural support to the plant. While lignin is essential for the plant’s growth and development, it can make the spears unpalatable and difficult to digest.
In addition to the physical changes that occur in the spears, neglecting to harvest asparagus can also impact the plant’s crown. The crown is the underground stem that produces the spears, and it is essential for the plant’s survival. When asparagus is left unharvested, the crown can become weakened, leading to a decrease in plant productivity and an increased susceptibility to disease.
It’s worth noting that the consequences of neglecting to harvest asparagus can be long-lasting, and may impact future crops. For example, if asparagus is left unharvested for an extended period, it can lead to a decrease in plant vigor and productivity, making it more challenging to produce high-quality spears in subsequent years.
Overall, neglecting to harvest asparagus can have significant consequences for the plant’s quality, productivity, and overall health. By understanding what happens when asparagus goes unharvested, growers can take steps to ensure that their plants receive the care and attention they need to thrive.
The Impact on Future Crops: How Neglecting Harvest Affects Yield
Neglecting to harvest asparagus can have a significant impact on future crops, affecting not only the yield but also the quality of the spears. When asparagus is left unharvested, the plants will continue to produce seeds, which can lead to a decrease in plant vigor and productivity. This is because the plants are expending energy on seed production rather than on producing new spears.
One of the most significant consequences of neglecting to harvest asparagus is reduced yields. When asparagus is left unharvested, the plants will produce fewer spears, and the spears that are produced will be smaller and less flavorful. This is because the plants are not receiving the necessary stimulation to produce new spears, and the energy is being diverted to seed production.
In addition to reduced yields, neglecting to harvest asparagus can also lead to decreased spear size. When asparagus is left unharvested, the spears will continue to grow, but they will not be as tender or flavorful as they would be if they were harvested regularly. This is because the cell walls of the spears will begin to break down, leading to a loss of texture and flavor.
Neglecting to harvest asparagus can also increase the susceptibility of the plants to disease. When asparagus is left unharvested, the plants will be more prone to disease, as the energy is being diverted to seed production rather than to producing new spears. This can lead to a decrease in plant productivity and an increased risk of disease.
Furthermore, neglecting to harvest asparagus can also impact the crown health of the plants. The crown is the underground stem that produces the spears, and it is essential for the plant’s survival. When asparagus is left unharvested, the crown can become weakened, leading to a decrease in plant productivity and an increased susceptibility to disease.
It’s worth noting that the impact of neglecting to harvest asparagus can be long-lasting, and may affect future crops. For example, if asparagus is left unharvested for an extended period, it can lead to a decrease in plant vigor and productivity, making it more challenging to produce high-quality spears in subsequent years.
Overall, neglecting to harvest asparagus can have significant consequences for future crops, affecting not only the yield but also the quality of the spears. By understanding the impact of neglecting to harvest asparagus, growers can take steps to ensure that their plants receive the care and attention they need to thrive.
How to Harvest Asparagus for Optimal Results
Harvesting asparagus is a crucial step in its cultivation, and it requires careful attention to detail to ensure optimal results. To harvest asparagus correctly, follow these steps:
1. Timing: Asparagus is typically ready to harvest in the spring, when the spears are 6-8 inches tall and about 1/2 inch in diameter. The exact timing will depend on the specific variety, weather conditions, and soil temperature.
2. Technique: To harvest asparagus, grasp the spear at the base and gently twist it back and forth until it comes loose from the crown. Avoid pulling or tugging on the spear, as this can damage the crown and reduce future yields.
3. Tool selection: Use a sharp, clean knife or asparagus snips to cut the spear at the base, just above the soil line. This will help to prevent damage to the crown and promote healthy regrowth.
4. Harvest frequency: Asparagus should be harvested every 2-3 days, or when the spears are 6-8 inches tall. This will help to encourage the plants to produce new spears and prevent them from becoming too woody.
5. Handling: Handle the harvested asparagus spears with care, as they can be easily damaged. Store them in a cool, dry place, or refrigerate them immediately to preserve their freshness and flavor.
By following these steps, you can ensure that your asparagus is harvested correctly and that you get the best possible results from your crop. Remember to always prioritize the health and well-being of your plants, and to take steps to prevent damage and disease.
In addition to these steps, there are a few other things to keep in mind when harvesting asparagus. For example, it’s essential to avoid over-harvesting, as this can weaken the plants and reduce future yields. It’s also important to avoid under-harvesting, as this can lead to a decrease in plant productivity and an increased risk of disease.
By taking the time to learn how to harvest asparagus correctly, you can enjoy a bountiful and delicious crop, while also promoting the health and well-being of your plants.
The Role of Asparagus Crowns in Regeneration
Asparagus crowns play a crucial role in the regeneration of new spears, and neglecting to harvest asparagus can impact crown health. The crown is the underground stem that produces the spears, and it is essential for the plant’s survival. When asparagus is harvested regularly, the crown is stimulated to produce new spears, which helps to maintain the plant’s productivity and overall health.
However, when asparagus is left unharvested, the crown can become weakened, leading to a decrease in plant productivity and an increased susceptibility to disease. This is because the energy that would normally be directed towards producing new spears is instead diverted towards seed production, which can weaken the crown and reduce its ability to regenerate new spears.
Furthermore, neglecting to harvest asparagus can also lead to a decrease in crown size, which can impact the plant’s ability to produce new spears. When asparagus is harvested regularly, the crown is able to maintain its size and continue to produce new spears, but when it is left unharvested, the crown can shrink, leading to a decrease in plant productivity.
It’s worth noting that the impact of neglecting to harvest asparagus on crown health can be long-lasting, and may affect future crops. For example, if asparagus is left unharvested for an extended period, it can lead to a decrease in plant vigor and productivity, making it more challenging to produce high-quality spears in subsequent years.
To maintain healthy crowns and promote regeneration, it’s essential to harvest asparagus regularly. This will help to stimulate the crown to produce new spears, maintain its size, and reduce the risk of disease. By prioritizing regular harvesting, growers can ensure that their asparagus plants remain healthy and productive, and that they continue to produce high-quality spears for years to come.
In addition to regular harvesting, there are several other ways to promote crown health and regeneration. For example, providing adequate soil preparation, fertilization, and pest management can help to maintain crown health and promote regeneration. By taking a holistic approach to asparagus cultivation, growers can ensure that their plants remain healthy and productive, and that they continue to produce high-quality spears.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Harvesting Asparagus
Harvesting asparagus can be a delicate process, and making mistakes can impact the quality and quantity of the spears. Here are some common mistakes to avoid when harvesting asparagus:
Over-harvesting: Harvesting too many spears at once can weaken the plant and reduce future yields. It’s essential to harvest asparagus regularly, but not to overdo it. Leave some spears to mature and produce seeds, as this will help to maintain the plant’s health and productivity.
Under-harvesting: On the other hand, under-harvesting can also be a problem. If the spears are not harvested regularly, they can become too large and woody, making them unpalatable. Regular harvesting will help to encourage the plant to produce new spears, ensuring a continuous supply of fresh, tender asparagus.
Damaging the crowns: The crowns are the underground stems that produce the spears, and damaging them can impact the plant’s ability to produce new spears. When harvesting asparagus, be careful not to damage the crowns, as this can reduce future yields and impact the plant’s overall health.
Harvesting at the wrong time: Harvesting asparagus at the wrong time can impact the quality and quantity of the spears. Asparagus is typically ready to harvest in the spring, when the spears are 6-8 inches tall and about 1/2 inch in diameter. Harvesting too early or too late can result in spears that are too small or too large, making them unpalatable.
Using the wrong tools: Using the wrong tools can damage the spears and the crowns, impacting the plant’s ability to produce new spears. Use a sharp, clean knife or asparagus snips to harvest the spears, and avoid using tools that can damage the crowns or the spears.
Not handling the spears correctly: Handling the spears incorrectly can impact their quality and freshness. Handle the spears gently, and avoid bruising or damaging them. Store the spears in a cool, dry place, or refrigerate them immediately to preserve their freshness and flavor.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can ensure that your asparagus harvest is successful and that you get the best possible results from your crop.
Maximizing Asparagus Production: Tips for a Bountiful Harvest
To maximize asparagus production and achieve a bountiful harvest, it’s essential to focus on several key factors, including soil preparation, fertilization, and pest management. Here are some expert tips to help you optimize your asparagus cultivation:
Soil Preparation: Asparagus prefers well-draining, fertile soil with a pH between 6.5 and 7.5. To prepare the soil, add a 2-inch layer of compost or well-rotted manure, and mix it in to a depth of 8-10 inches. This will help to improve soil structure, fertility, and drainage.
Fertilization: Asparagus is a heavy feeder and requires regular fertilization to promote healthy growth and production. Apply a balanced fertilizer (10-10-10 NPK) in early spring, following the manufacturer’s instructions. You can also side-dress with a high-phosphorus fertilizer (10-20-10 NPK) to promote root development and spear production.
Pest Management: Asparagus is susceptible to several pests, including aphids, spider mites, and asparagus beetles. To manage these pests, use integrated pest management (IPM) techniques, such as introducing beneficial insects, practicing good sanitation, and using organic or chemical controls as needed.
Irrigation: Asparagus requires consistent moisture, especially during the first year after planting. Water the plants regularly, providing about 1 inch of water per week. Avoid overwatering, which can lead to root rot and other problems.
Support: Asparagus spears can grow quite tall, so provide support using a trellis or stake to keep them upright and promote better growth.
Mulching: Mulching around the plants can help to retain moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature. Use a 2-3 inch layer of organic mulch, such as straw or wood chips, and keep it a few inches away from the plant stems.
By following these tips, you can maximize your asparagus production and achieve a bountiful harvest. Remember to prioritize regular harvesting, as this will help to promote healthy growth and encourage the plants to produce new spears.
Conclusion: The Importance of Regular Asparagus Harvest
In conclusion, regular asparagus harvest is a crucial step in asparagus cultivation that should not be neglected. Neglecting to harvest asparagus can lead to a range of negative consequences, including reduced yields, decreased spear size, and increased susceptibility to disease.
By understanding the importance of regular harvesting and following the tips outlined in this article, growers can maximize their asparagus production and achieve a bountiful harvest. Remember to prioritize regular harvesting, as this will help to promote healthy growth and encourage the plants to produce new spears.
Regular asparagus harvest is not just important for the current crop, but also for future crops. By harvesting asparagus regularly, growers can help to maintain the health and productivity of their plants, ensuring a consistent supply of fresh, tender spears for years to come.
In addition to the benefits for the plants, regular asparagus harvest also has benefits for the environment. By promoting healthy growth and reducing the risk of disease, regular harvesting can help to reduce the need for pesticides and other chemicals, creating a more sustainable and environmentally friendly growing practice.
So, if you’re looking to maximize your asparagus production and achieve a bountiful harvest, remember to prioritize regular harvesting. With the right techniques and a little bit of knowledge, you can enjoy a delicious and sustainable asparagus crop for years to come.