Soil pH Balancing: The Primary Role of Lime
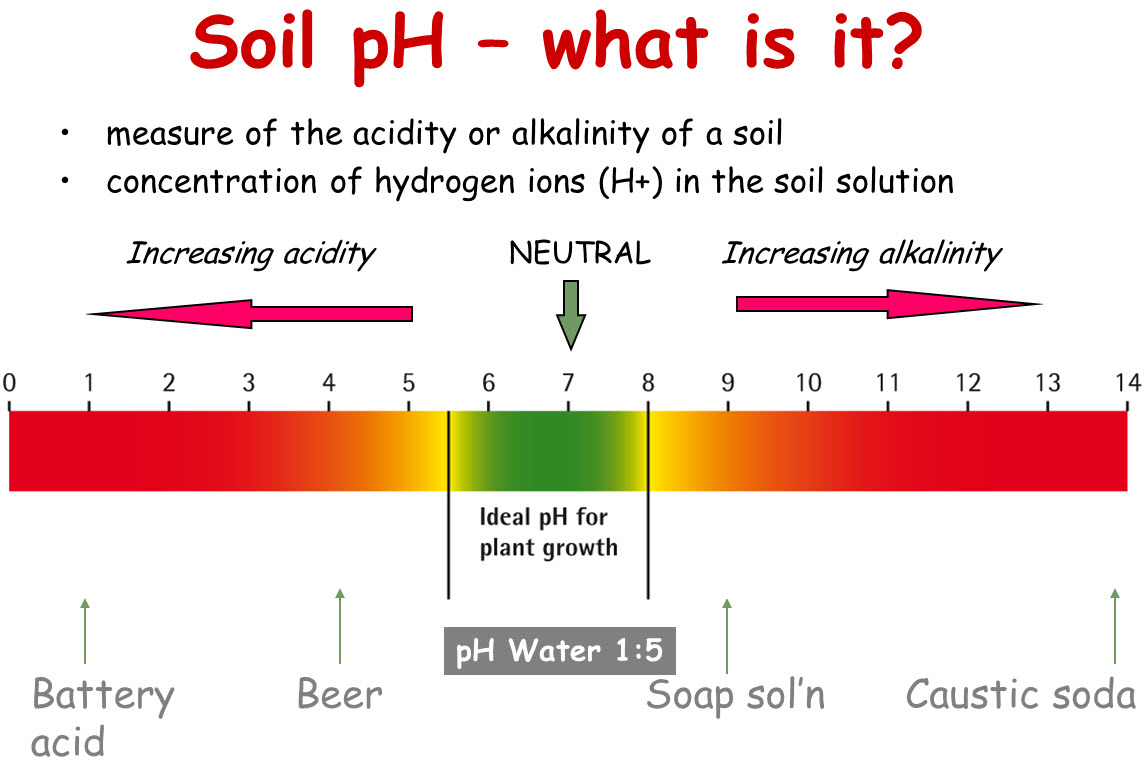
Soil pH, a critical factor in plant growth, plays a vital role in determining the overall health and productivity of crops. It is a delicate balance that can make all the difference in crop yields and plant health. When soil pH becomes imbalanced, it can lead to a range of problems, including poor plant growth, yellowing leaves, and increased susceptibility to disease. Soil pH levels that are too acidic or too alkaline can limit the availability of essential nutrients, hindering plant growth and development. What is lime used for in soil? Lime is used to balance soil pH, making it more conducive to plant growth. By applying lime to acidic soils, farmers and gardeners can create a more balanced pH, leading to improved crop yields and overall plant health. In essence, lime helps to create an environment that fosters healthy plant growth, allowing crops to thrive and reach their full potential. By understanding the importance of soil pH and the role of lime in maintaining optimal levels, farmers and gardeners can unlock the full potential of their soil. This is especially important, as even a slight imbalance in soil pH can have significant consequences for plant growth and productivity. By recognizing the significance of soil pH and the benefits of lime application, farmers and gardeners can take the first step towards creating a more fertile and productive soil environment. Lime’s ability to balance soil pH makes it an essential tool in soil management, allowing farmers and gardeners to optimize soil health and promote healthy plant growth.
How to Identify Soil pH Imbalance and the Need for Lime
Soil pH imbalance can have devastating effects on plant growth and productivity. Identifying the signs of imbalance is crucial in determining the need for lime application. Some common indicators of soil pH imbalance include poor plant growth, yellowing leaves, and increased susceptibility to disease. If plants are struggling to thrive, or if crops are not yielding as expected, it may be a sign that the soil pH is out of balance. Another indicator is the presence of weeds, such as sorrel or plantain, which thrive in acidic soils. To confirm soil pH imbalance, it is essential to test the soil pH. This can be done using a pH meter or by sending a soil sample to a laboratory for analysis. If the test reveals that the soil pH is too acidic or too alkaline, lime application may be necessary to balance the pH and create a more conducive environment for plant growth. What is lime used for in soil? Lime is used to neutralize soil acidity and raise the pH, making it more suitable for plant growth. By identifying the signs of soil pH imbalance and testing the soil pH, farmers and gardeners can determine the need for lime application and take the necessary steps to optimize soil health.
The Science Behind Lime’s Soil Amelioration Properties
Lime’s ability to neutralize soil acidity and improve soil structure is rooted in its chemical composition. When lime is applied to acidic soils, it reacts with the hydrogen ions to form water and calcium carbonate, effectively raising the pH. This process is known as neutralization, and it is the primary mechanism by which lime improves soil health. There are several types of lime, each with its own unique characteristics and uses. Calcium oxide, also known as quicklime, is a highly reactive form of lime that is often used to rapidly raise soil pH. Calcium hydroxide, or slaked lime, is a slower-acting form of lime that is often used in situations where a more gradual pH adjustment is desired. Dolomitic lime, a type of lime that contains both calcium and magnesium, is often used to provide additional nutrients to plants. What is lime used for in soil? Lime is used to neutralize soil acidity, improve soil structure, and provide essential nutrients to plants. By understanding the chemistry behind lime’s soil amelioration properties, farmers and gardeners can make informed decisions about the type and amount of lime to apply to their soils. This knowledge is essential for optimizing soil health and promoting healthy plant growth.
Lime’s Impact on Soil Microbiology and Nutrient Availability
Lime’s benefits extend beyond pH balancing, as it also has a profound impact on soil microbiology and nutrient availability. When lime is applied to soil, it creates an environment that fosters the growth of beneficial microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi. These microorganisms play a crucial role in decomposing organic matter, fixing nitrogen, and solubilizing minerals, making them more available to plants. Additionally, lime helps to suppress pathogens, such as fungal diseases, that can harm plants. By promoting a healthy soil microbiome, lime enables plants to absorb essential nutrients more efficiently, leading to improved growth and productivity. What is lime used for in soil? Lime is used to create a favorable environment for beneficial microorganisms to thrive, which in turn, enhances nutrient availability and uptake by plants. Furthermore, lime’s ability to improve soil structure and increase the water-holding capacity of soil also contributes to better nutrient availability. By understanding the complex relationships between lime, soil microbiology, and nutrient availability, farmers and gardeners can optimize their soil management strategies to achieve better crop yields and healthier plants.
Practical Applications of Lime in Agriculture and Horticulture
Lime is a versatile soil amendment with a wide range of practical applications in agriculture and horticulture. In crop production, lime is used to optimize soil pH, improve soil structure, and increase crop yields. For example, in acidic soils, lime can help to increase the availability of essential nutrients like calcium and magnesium, leading to healthier and more productive crops. In lawn care, lime is used to maintain optimal soil pH, reduce soil compaction, and promote healthy turf growth. In gardening, lime is used to improve soil fertility, increase the water-holding capacity of soil, and support the growth of a diverse range of plants. What is lime used for in soil? Lime is used to create a favorable soil environment that supports healthy plant growth, improves soil fertility, and increases crop yields. By understanding the various practical applications of lime, farmers and gardeners can optimize their soil management strategies to achieve better results. For instance, in orchards, lime can be used to improve soil fertility and reduce the incidence of diseases like apple scab. In vineyards, lime can be used to optimize soil pH and improve grape quality. By recognizing the diverse benefits of lime, agricultural and horticultural practitioners can unlock its full potential and achieve greater success in their endeavors.
Environmental Considerations: The Responsible Use of Lime in Soil Management
While lime is a valuable tool in soil management, its use can have environmental implications if not applied responsibly. One of the primary concerns is soil salinization, which occurs when lime is over-applied, leading to an increase in soil salt levels. This can have devastating effects on soil fertility, plant growth, and overall ecosystem health. Another potential issue is water pollution, which can result from lime runoff into waterways, affecting aquatic life and ecosystems. To minimize these risks, it is essential to adopt responsible lime application practices. This includes conducting thorough soil tests to determine the optimal lime application rate, avoiding over-liming, and incorporating lime into the soil to reduce runoff. Additionally, farmers and gardeners can adopt conservation tillage practices, use cover crops, and implement integrated pest management strategies to reduce the environmental impact of lime use. What is lime used for in soil? Lime is used to improve soil fertility and structure, but it is crucial to do so in a way that prioritizes environmental sustainability. By adopting responsible lime use practices, agricultural and horticultural practitioners can ensure the long-term health and productivity of their soils while minimizing the environmental footprint of their operations.
Lime vs. Other Soil Amendments: A Comparative Analysis
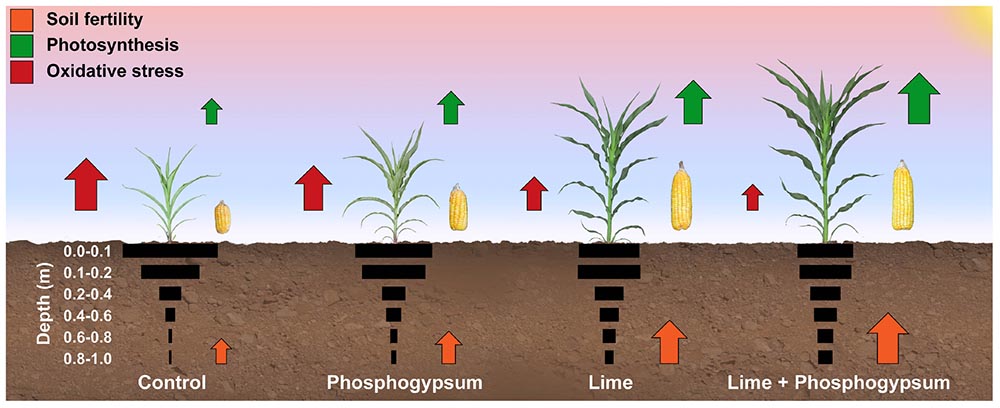
In the realm of soil management, various amendments are available to improve soil fertility and structure. While lime is a popular choice, it is essential to understand its relative effectiveness and suitability compared to other options. Sulfur, gypsum, and wood ash are three common soil amendments that are often used in conjunction with or as an alternative to lime. Sulfur, for instance, is an effective acidifying agent, making it an ideal choice for alkaline soils. Gypsum, on the other hand, is a natural source of calcium and sulfur, which can help to improve soil structure and fertility. Wood ash, a byproduct of wood combustion, can provide a slow release of nutrients and improve soil pH. What is lime used for in soil? Lime is used to neutralize soil acidity and improve soil structure, but it may not be the most suitable option for all soil types and conditions. In comparison to these alternatives, lime is often more effective in acidic soils, while sulfur and gypsum may be more suitable for alkaline soils. Wood ash, with its slow release of nutrients, may be a better choice for soils that require a more gradual improvement. By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each soil amendment, agricultural and horticultural practitioners can make informed decisions about the most effective strategies for their specific soil management needs. Ultimately, a comprehensive approach that incorporates a combination of soil amendments may be the most effective way to optimize soil health and fertility.
Conclusion: Optimizing Soil Health with Lime
In conclusion, lime is a vital component of soil management, playing a crucial role in balancing soil pH, improving soil structure, and promoting healthy plant growth. By understanding the importance of lime in soil management, agricultural and horticultural practitioners can unlock its full potential and reap the benefits of optimized soil health. What is lime used for in soil? Lime is used to neutralize soil acidity, improve soil fertility, and promote beneficial microorganisms, ultimately leading to healthier plants and increased crop yields. By adopting responsible lime application practices and considering the unique needs of their soil, farmers and gardeners can create a thriving soil ecosystem that supports long-term sustainability and productivity. As a key component of a comprehensive soil care strategy, lime can help to unlock the full potential of the soil, leading to a more resilient and productive agricultural and horticultural industry.