Understanding Camellia’s Climate Requirements
Camellia plants are highly sensitive to their environment, and understanding their climate requirements is crucial for their growth and development. Temperature, humidity, and sunlight all play a significant role in determining the health and success of camellia plants. In order to provide the best conditions for these plants, it’s essential to know what zone does camellia grow in and how to replicate those conditions in your garden. By doing so, you can ensure your camellia plant receives the necessary care to thrive. For instance, camellias grown in zones with high temperatures may require more frequent watering, while those in zones with low humidity may need additional misting. By understanding these climate requirements, you can tailor your care routine to meet the specific needs of your camellia plant.
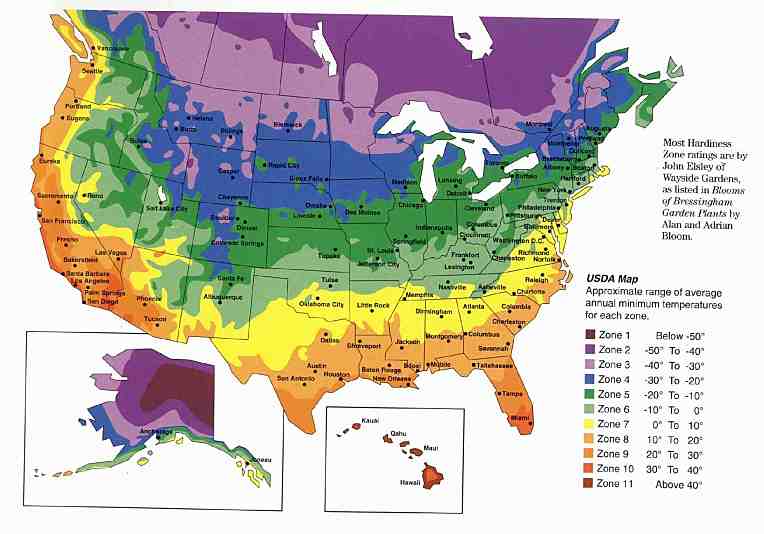
What Hardiness Zone is Best for Camellia?
Hardiness zones are a crucial factor in determining the ideal climate conditions for growing camellia plants. The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map divides North America into 11 zones, each representing a specific range of temperatures. Camellias, being sensitive to temperature fluctuations, thrive in zones with mild winters and cool summers. Generally, camellias grow best in zones 6-9, where the average annual extreme minimum temperature ranges from -10°F to 20°F (-23°C to -7°C). However, some species and varieties can tolerate warmer or cooler temperatures, making it essential to know what zone does camellia grow in and choose the right variety for your specific zone. For instance, Camellia japonica and Camellia sasanqua are popular varieties that thrive in zones 7-9, while Camellia hiemalis is more tolerant of colder temperatures and can grow in zones 6-8.
How to Determine Your Local Hardiness Zone
Determining your local hardiness zone is a crucial step in growing healthy and thriving camellia plants. To find your specific zone, follow these simple steps: First, visit the USDA’s interactive map online, which provides a detailed breakdown of hardiness zones across North America. Enter your zip code or city and state to find your zone. Alternatively, you can check the USDA’s Plant Hardiness Zone Map, which is available for download or purchase. Another option is to consult with local nurseries or gardening experts, who can provide valuable insights into the specific climate conditions in your area. Knowing what zone does camellia grow in and understanding your local hardiness zone will help you choose the right camellia variety and provide the necessary care for optimal growth.
The Impact of Microclimates on Camellia Growth
Microclimates play a significant role in camellia growth, and understanding their impact is crucial for creating an ideal environment for these plants. A microclimate refers to a small, localized area with unique climate conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and sunlight, that differ from the surrounding area. Camellias are sensitive to these variations, and even a slight change in microclimate can affect their growth and development. For instance, a camellia plant growing in a spot with full sun may require more frequent watering than one growing in a shaded area. To create a microclimate conducive to camellia growth, consider the following tips: provide shade during the hottest part of the day, especially in warmer hardiness zones; use mulch to retain moisture and regulate soil temperature; and avoid planting in low-lying areas where cold air may settle. By understanding and manipulating microclimates, camellia growers can create an optimal environment for their plants to thrive, regardless of what zone does camellia grow in.
Camellia Care Tips for Different Hardiness Zones
Camellia plants require specific care tailored to their hardiness zone to thrive. In zones 6-7, where camellias are more sensitive to cold temperatures, provide extra protection during harsh winters by mulching around the base and covering the plant with a frost cloth. In warmer zones 8-9, camellias require more frequent watering and fertilization to promote healthy growth. In coastal regions, such as those in zone 10, camellias benefit from regular pruning to maintain shape and promote air circulation. Regardless of what zone does camellia grow in, it’s essential to choose a well-draining soil with a slightly acidic pH, and to water camellias regularly, but avoid overwatering. Additionally, camellias in all zones benefit from regular fertilization, especially during the growing season. By understanding the specific needs of camellias in different hardiness zones, growers can provide the necessary care to promote healthy and thriving plants.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Growing Camellia in Your Zone
When growing camellias in their ideal hardiness zone, it’s essential to avoid common mistakes that can hinder their growth and development. One common mistake is underestimating the importance of soil quality. Camellias require well-draining, acidic soil to thrive, and neglecting to provide this can lead to root rot and other problems. Another mistake is overwatering, which can be detrimental to camellias in any zone. It’s crucial to monitor soil moisture and adjust watering schedules accordingly. Additionally, failing to provide adequate protection from extreme temperatures, wind, and frost can be detrimental to camellia growth. In zones with harsh winters, camellias may need to be protected with mulch or brought indoors to ensure their survival. By being aware of these common mistakes, camellia growers can take steps to avoid them and create an optimal environment for their plants to thrive, regardless of what zone does camellia grow in. Furthermore, understanding the specific needs of camellias in different hardiness zones can help growers tailor their care and avoid mistakes that can impact plant health.
Camellia Varieties for Specific Hardiness Zones
When it comes to growing camellias, choosing the right variety for your hardiness zone is crucial. In zones 6-7, camellia varieties like ‘Pink Perfume’ and ‘Winter’s Star’ thrive, producing vibrant flowers and compact growth. In warmer zones 8-9, varieties like ‘Debutante’ and ‘Cleopatra’ excel, showcasing larger blooms and more vigorous growth. In coastal regions, such as those in zone 10, camellia varieties like ‘Professor Sargent’ and ‘Mathotiana’ perform well, tolerating salt spray and high humidity. Regardless of what zone does camellia grow in, understanding the unique characteristics and growing requirements of different varieties can help growers select the best camellias for their specific climate. By choosing a camellia variety that is well-suited to their hardiness zone, growers can enjoy healthy, thriving plants that provide beauty and interest to their gardens.
Conclusion: Growing Camellia in Your Ideal Zone
In conclusion, understanding the ideal climate conditions for growing camellias is crucial for their success. By recognizing the importance of hardiness zones, microclimates, and specific care requirements, growers can create an optimal environment for their camellia plants to thrive. Whether you’re growing camellias in zone 6 or zone 10, knowing what zone does camellia grow in and selecting the right variety for your region can make all the difference. By avoiding common mistakes and providing the right care, camellia growers can enjoy beautiful, blooming plants that bring joy and elegance to their gardens. With the right knowledge and attention, camellias can flourish in any hardiness zone, providing a stunning display of color and beauty for years to come.