Understanding the Importance of Planting Tomatoes at the Right Time
Planting tomatoes at the right time is crucial for a successful harvest. The timing of tomato planting affects the entire growth cycle, from seed germination to fruit production. Weather, soil temperature, and daylight hours all play a significant role in determining the optimal planting time. In regions with a long growing season, tomatoes can be planted in early spring, while in areas with a shorter growing season, it’s best to wait until the soil has warmed up and the risk of frost has passed.
The ideal time to plant tomatoes varies depending on the specific variety, climate, and region. In general, it’s recommended to plant tomatoes when the soil temperature reaches around 55°F to 60°F (13°C to 15°C). This allows for optimal seed germination and seedling growth. However, in warmer climates, tomatoes can be planted year-round, while in cooler climates, it’s best to wait until the soil has warmed up and the risk of frost has passed.
Daylight hours also play a crucial role in determining the optimal planting time. Tomatoes require at least 6 hours of direct sunlight per day to produce well. In regions with limited daylight hours during the winter months, it’s best to wait until the days get longer before planting tomatoes.
When considering when to plant tomatoes, it’s essential to take into account the specific weather patterns in your region. In areas prone to late frosts, it’s best to wait until the risk of frost has passed before planting. Similarly, in regions with hot summers, it’s best to plant tomatoes in the early spring or late summer to avoid the intense heat.
By understanding the importance of planting tomatoes at the right time, gardeners can set themselves up for success and enjoy a bountiful harvest. Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just starting out, timing is everything when it comes to planting tomatoes.
How to Determine the Ideal Planting Time for Your Region
Determining the ideal planting time for tomatoes in your region requires consideration of several factors, including climate, frost dates, and soil temperature. To ensure a successful harvest, it’s essential to plant tomatoes at the right time for your specific region.
One of the most critical factors to consider is the average frost date for your area. In regions with a high risk of late frosts, it’s best to wait until the risk of frost has passed before planting tomatoes. You can check the average frost dates for your area by visiting the National Weather Service’s website or consulting with a local nursery or gardening expert.
Soil temperature is another crucial factor to consider when determining the ideal planting time for tomatoes. Tomatoes thrive in warm soil, typically above 55°F (13°C). You can use a soil thermometer to determine the soil temperature in your garden. If the soil temperature is too low, it’s best to wait until it warms up before planting.
Climate is also an essential factor to consider when determining the ideal planting time for tomatoes. In regions with a long growing season, tomatoes can be planted in early spring, while in areas with a shorter growing season, it’s best to wait until the soil has warmed up and the risk of frost has passed.
Additionally, you should also consider the specific weather patterns in your region, such as the timing of the last frost, the onset of warm weather, and the duration of the growing season. By taking these factors into account, you can determine the ideal planting time for tomatoes in your region and set yourself up for a successful harvest.
When deciding when to plant tomatoes, it’s also essential to consider the specific variety you are growing. Some tomato varieties are more sensitive to temperature and moisture than others, so it’s crucial to choose a variety that is well-suited to your region’s climate.
The Role of Soil Temperature in Tomato Plant Growth
Soil temperature plays a crucial role in tomato plant growth, and understanding its importance can help you determine when to plant tomatoes for optimal results. Tomato plants thrive in warm soil, and the ideal soil temperature for different stages of growth varies.
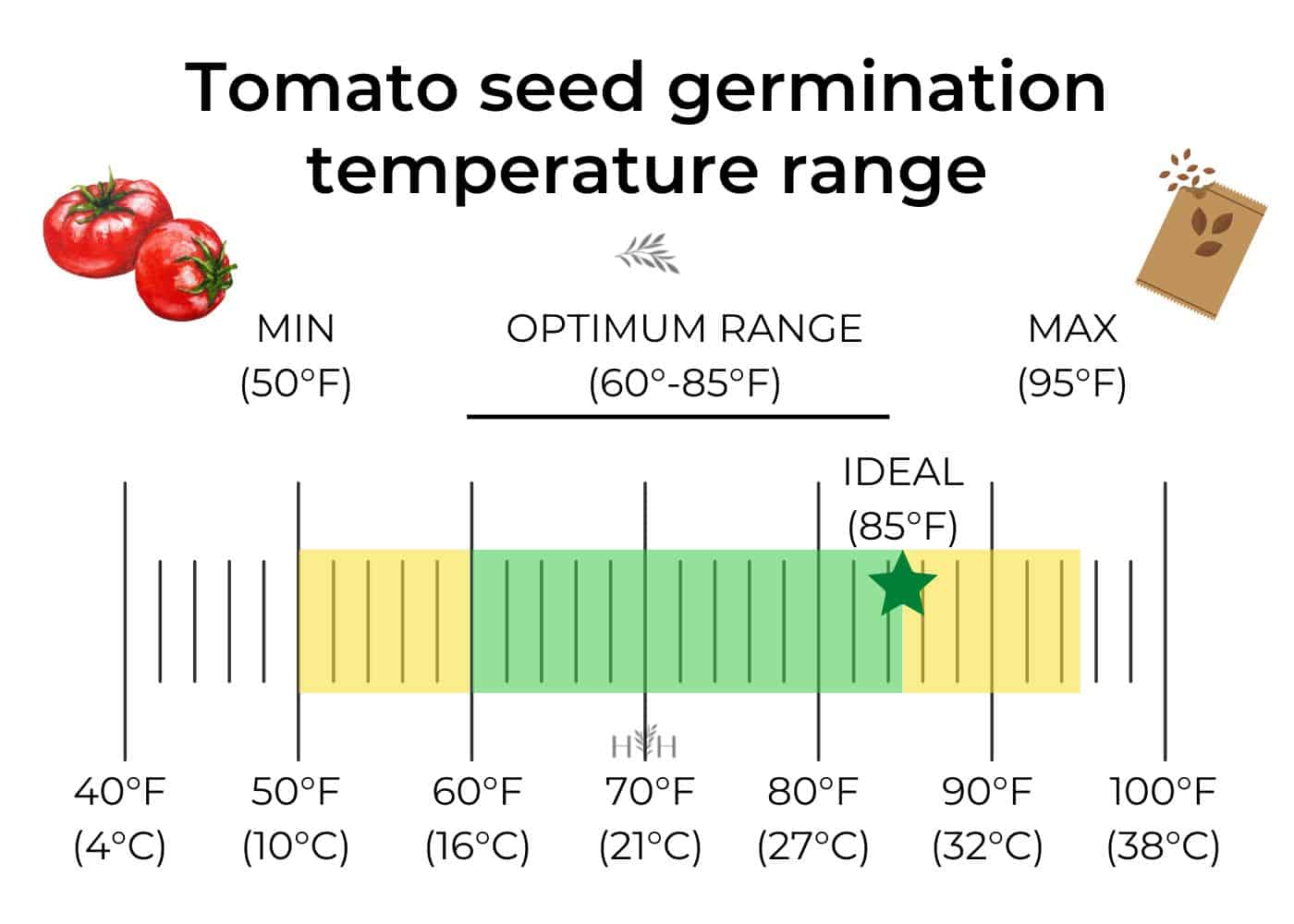
For seed germination, the optimal soil temperature is between 70°F (21°C) and 80°F (27°C). At this temperature range, seeds can germinate within 7-10 days. If the soil temperature is too low, germination may be delayed or inhibited.
For seedling growth, the ideal soil temperature is between 65°F (18°C) and 75°F (24°C). At this temperature range, seedlings can develop a strong root system and grow rapidly. If the soil temperature is too high, seedlings may become stressed and vulnerable to disease.
For fruit production, the optimal soil temperature is between 60°F (16°C) and 70°F (21°C). At this temperature range, fruit can develop and ripen properly. If the soil temperature is too low, fruit production may be reduced or delayed.
It’s essential to note that soil temperature can fluctuate significantly depending on factors such as climate, soil type, and depth. To ensure optimal soil temperature for tomato plant growth, it’s recommended to use a soil thermometer to monitor soil temperature regularly.
Additionally, you can also use mulch or other soil covers to regulate soil temperature and maintain optimal conditions for tomato plant growth. By understanding the role of soil temperature in tomato plant growth, you can make informed decisions about when to plant tomatoes and create a favorable growing environment.
When to Start Tomato Seeds Indoors vs. Direct Sowing Outdoors
When it comes to planting tomatoes, one of the most important decisions you’ll make is whether to start seeds indoors or direct sow them outdoors. Both methods have their pros and cons, and the right choice for you will depend on your specific climate, available space, and personal preference.
Starting tomato seeds indoors can give you a head start on the growing season, allowing you to get a jump on the weather and potentially harvest your tomatoes earlier. This method is especially useful in cooler climates where the growing season is shorter. By starting seeds indoors 4-6 weeks before the last frost date, you can give your seedlings a chance to develop a strong root system and get a head start on the growing season.
However, starting seeds indoors also comes with some risks. One of the biggest risks is transplant shock, which can occur when seedlings are moved from the warm, cozy environment of your home to the outdoors. To minimize this risk, make sure to harden off your seedlings by gradually exposing them to outdoor conditions over the course of 7-10 days.
Direct sowing tomato seeds outdoors can be a more straightforward and low-maintenance option. This method eliminates the need for indoor seed starting and transplanting, and can be a good choice for warmer climates where the growing season is longer. However, direct sowing can also be more unpredictable, as weather conditions and soil temperature can affect germination and seedling growth.
Ultimately, the decision to start tomato seeds indoors or direct sow them outdoors will depend on your specific situation and preferences. If you’re looking for a head start on the growing season and are willing to take on the risks of transplant shock, starting seeds indoors may be the way to go. However, if you prefer a more low-maintenance approach and are willing to wait a bit longer for your tomatoes to mature, direct sowing may be the better choice.
How to Prepare Your Soil for Tomato Planting
Preparing your soil for tomato planting is crucial for a successful harvest. Tomatoes require a well-draining, fertile soil with a pH between 6.0 and 6.8. To achieve this, you’ll need to test your soil and make any necessary adjustments.
Start by testing your soil pH using a soil testing kit or by sending a sample to a laboratory for analysis. If your soil pH is too low or too high, you can adjust it by adding lime or sulfur. Additionally, you’ll want to check your soil’s nutrient levels, including nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
Tomatoes also require a significant amount of organic matter to thrive. You can add compost, manure, or other soil amendments to your soil to increase its fertility and structure. Compost is particularly beneficial, as it adds nutrients, improves soil structure, and supports beneficial microorganisms.
Another important consideration is soil texture. Tomatoes prefer a well-draining soil with a mix of sand, silt, and clay. If your soil is too dense or too sandy, you can amend it by adding organic matter or perlite.
Finally, consider using cover crops or crop rotation to improve your soil’s fertility and structure. Cover crops, such as clover or rye, can add nutrients and organic matter to your soil, while crop rotation can help break disease and pest cycles.
By preparing your soil properly, you can create a fertile growing environment that will support healthy tomato plants and a bountiful harvest. Remember to test your soil regularly and make adjustments as needed to ensure optimal growing conditions.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Planting Tomatoes
When planting tomatoes, there are several common mistakes to avoid in order to ensure a successful harvest. One of the most critical mistakes is planting too early or too late. Planting too early can expose your tomato plants to frost, while planting too late can result in a reduced harvest.
Another common mistake is not providing enough space between plants. Tomatoes need adequate space to grow and receive sufficient air circulation, sunlight, and water. Planting them too close together can lead to disease and pest issues, as well as reduced fruit production.
Not supporting indeterminate varieties is also a common mistake. Indeterminate tomato varieties will continue to grow and produce fruit throughout the season, but they require support to keep them upright and promote healthy growth. Using tomato cages, trellises, or stakes can help keep your indeterminate varieties healthy and productive.
Additionally, not rotating your tomato crop can lead to soil-borne diseases and pest issues. Tomatoes should be rotated every year to a new location to avoid depleting the soil of nutrients and to reduce the risk of disease.
Finally, not monitoring your tomato plants regularly can lead to pest and disease issues going unnoticed. Regularly inspect your plants for signs of pests or disease, and take action promptly to prevent the issue from spreading.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can help ensure a successful tomato harvest and enjoy a bountiful crop of delicious, juicy tomatoes.
Regional Variations: Planting Tomatoes in Different Climates
When it comes to planting tomatoes, regional variations in climate can play a significant role in determining the best time to plant. In general, tomatoes are a warm-season crop and thrive in temperatures between 65°F and 85°F (18°C and 30°C). However, different climates present unique challenges and opportunities for tomato planting.
In cool-season climates, such as those found in the northern United States or Canada, tomatoes should be planted after the last frost date. This allows the soil to warm up and reduces the risk of frost damage. In these climates, it’s also important to choose tomato varieties that mature quickly, typically within 60 to 70 days.
In warm-season climates, such as those found in the southern United States or California, tomatoes can be planted in the early spring or late summer. In these climates, it’s essential to choose heat-tolerant and disease-resistant varieties to ensure a successful harvest.
In regions with a Mediterranean climate, such as those found in parts of California or Italy, tomatoes can be planted in the early spring or late summer. In these climates, it’s essential to choose varieties that are resistant to heat stress and drought.
Regardless of the climate, it’s essential to consider the specific weather patterns in your region when planting tomatoes. This includes factors such as temperature, rainfall, and sunlight. By understanding the unique challenges and opportunities of your region’s climate, you can make informed decisions about when to plant tomatoes and ensure a successful harvest.
Conclusion: Timing is Everything for a Successful Tomato Harvest
Timing is everything when it comes to planting tomatoes. Planting at the right time can make all the difference in the success of your harvest. By understanding the importance of weather, soil temperature, and daylight hours on plant growth and productivity, you can make informed decisions about when to plant tomatoes in your region.
Whether you’re a seasoned gardener or just starting out, it’s essential to consider the unique challenges and opportunities of your region’s climate when planting tomatoes. By choosing the right variety, preparing your soil, and avoiding common mistakes, you can set yourself up for a successful harvest.
Remember, the key to a successful tomato harvest is timing. Planting too early or too late can result in reduced yields, poor fruit quality, and increased susceptibility to disease and pests. By planting at the right time, you can ensure a bountiful harvest of delicious, juicy tomatoes.
So, when should tomato plants be planted? The answer depends on your region, climate, and specific weather patterns. By following the guidelines outlined in this article, you can determine the best time to plant tomatoes in your area and enjoy a successful harvest.
Happy gardening!