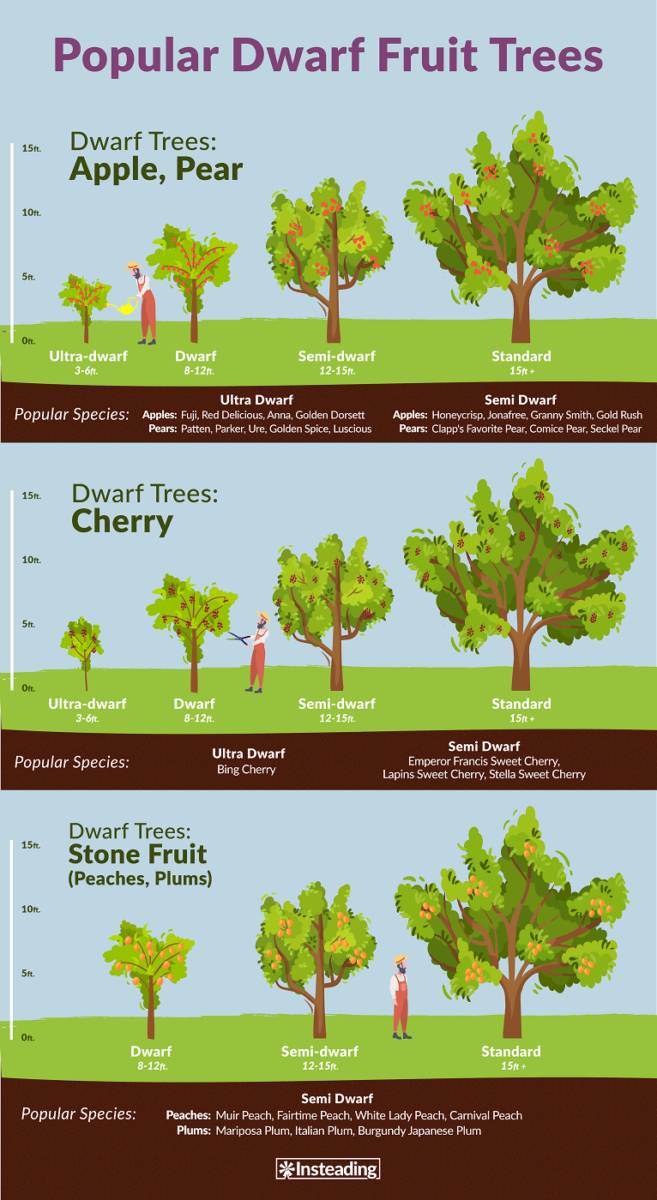
Understanding Cherry Tree Climate Requirements
When it comes to growing cherry trees, climate plays a crucial role in determining the tree’s growth and fruit production. Cherry trees require a specific set of climate conditions to thrive, making it essential to understand these requirements before deciding where to grow cherry trees. Temperature, humidity, and sunlight are the three primary climate factors that affect cherry tree growth.
Temperature is a critical factor in cherry tree growth, with most varieties requiring a certain number of chill hours to break dormancy. Chill hours refer to the amount of time the tree spends in temperatures between 32°F and 45°F (0°C and 7°C). The ideal temperature range for cherry trees is between 35°F and 75°F (2°C and 24°C), with optimal growth occurring in temperatures around 60°F to 70°F (15°C to 21°C).
Humidity is another essential climate factor for cherry trees. These trees prefer a relatively low humidity environment, with an ideal range of 40% to 60%. High humidity can lead to disease issues, such as powdery mildew and brown rot, which can significantly impact fruit production.
Sunlight is also crucial for cherry tree growth, with most varieties requiring full sun to produce well. Cherry trees need at least six hours of direct sunlight per day, with eight hours or more being ideal. Insufficient sunlight can lead to reduced fruit production and poor tree growth.
Understanding these climate requirements is essential when deciding where to grow cherry trees. By selecting a location with the ideal temperature, humidity, and sunlight conditions, growers can optimize cherry tree growth and fruit production. In regions with less-than-ideal climate conditions, growers can use techniques such as providing supplemental chill hours or using row covers to modify the microclimate and promote healthy tree growth.
By considering these climate factors, growers can create an optimal environment for their cherry trees to thrive, leading to improved fruit production and a healthier tree. Whether growing cherry trees in a commercial orchard or a backyard garden, understanding the climate requirements is crucial for success.
Choosing the Right Soil for Cherry Trees
Soil quality and composition play a vital role in the growth and development of cherry trees. When deciding where to grow cherry trees, it’s essential to consider the soil conditions to ensure optimal growth and fruit production. Cherry trees prefer well-draining, fertile soil with a pH between 6.0 and 6.5.
The ideal soil pH for cherry trees is slightly acidic to neutral, with a pH range of 6.0 to 6.5. Soil pH outside this range can lead to nutrient deficiencies and reduced tree growth. For example, soil with a pH below 6.0 can cause manganese toxicity, while soil with a pH above 6.5 can lead to iron deficiency.
In addition to pH, cherry trees require a balanced nutrient profile to thrive. The essential nutrients for cherry tree growth include nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and micronutrients like boron and zinc. Soil with adequate nutrient levels can promote healthy tree growth, fruit production, and disease resistance.
Soil drainage is also crucial for cherry tree growth. Cherry trees prefer well-draining soil to prevent waterlogged soil conditions, which can lead to root rot and other diseases. Soil with good drainage allows for healthy root development, which is essential for tree growth and fruit production.
When evaluating soil quality for cherry tree growth, consider the following factors:
- Soil texture: Cherry trees prefer a mix of sand, silt, and clay, with a well-balanced texture that allows for good drainage and aeration.
- Soil organic matter: Incorporating organic matter like compost or manure can improve soil fertility, structure, and overall health.
- Soil nutrient levels: Regular soil testing can help identify nutrient deficiencies and inform fertilization strategies.
By selecting a location with suitable soil conditions, growers can create an optimal environment for their cherry trees to thrive. Whether growing cherry trees in a commercial orchard or a backyard garden, understanding the importance of soil quality and composition is crucial for success.
In regions where soil conditions are less than ideal, growers can use techniques like soil amendments, mulching, and cover cropping to improve soil health and fertility. By taking a proactive approach to soil management, growers can create a thriving environment for their cherry trees and optimize fruit production.
How to Select the Perfect Spot for Your Cherry Tree
When deciding where to grow cherry trees, selecting the right location is crucial for optimal growth and fruit production. Cherry trees require specific conditions to thrive, and choosing the perfect spot can make all the difference. Here are some tips to help you select the best location for your cherry tree:
Sunlight is essential for cherry tree growth, and selecting a location with full sun is ideal. Cherry trees require at least six hours of direct sunlight per day, with eight hours or more being optimal. When evaluating potential locations, consider the amount of sunlight the area receives and whether any obstructions, such as buildings or trees, may block sunlight.
Wind protection is also crucial for cherry trees, as strong winds can damage the tree and reduce fruit production. Selecting a location with natural wind protection, such as a hill or a group of trees, can help shield your cherry tree from harsh winds. Alternatively, you can create a windbreak using a fence or a row of trees.
Proximity to water sources is another important consideration when selecting a location for your cherry tree. Cherry trees require consistent moisture, especially during the first year after planting. Selecting a location with easy access to a water source, such as a hose or a irrigation system, can make it easier to keep your tree watered.
Soil quality and composition are also essential factors to consider when selecting a location for your cherry tree. Cherry trees prefer well-draining, fertile soil with a pH between 6.0 and 6.5. Evaluating the soil conditions at potential locations can help you determine whether the soil is suitable for cherry tree growth.
Other factors to consider when selecting a location for your cherry tree include:
- Space: Cherry trees can grow quite large, so selecting a location with enough space for the tree to mature is essential.
- Soil depth: Cherry trees prefer deep soil with a depth of at least 3 feet to accommodate their root system.
- Drainage: Cherry trees prefer well-draining soil to prevent waterlogged soil conditions.
By considering these factors, you can select the perfect spot for your cherry tree and create an optimal environment for growth and fruit production. Whether you’re growing cherry trees in a commercial orchard or a backyard garden, choosing the right location is crucial for success.
When evaluating potential locations, remember to consider the specific needs of your cherry tree variety. Different varieties have unique growing requirements, and selecting a location that meets those needs can help ensure optimal growth and fruit production.
Regional Considerations for Growing Cherry Trees
When deciding where to grow cherry trees, regional climate and soil conditions play a significant role in determining the tree’s growth and fruit production. Different regions have unique climate and soil characteristics that can affect cherry tree growth, and understanding these regional differences is crucial for optimal growth.
In the United States, the Pacific Northwest is one of the most suitable regions for growing cherry trees. The region’s mild winters, cool summers, and well-distributed rainfall create an ideal climate for cherry tree growth. Washington state, in particular, is renowned for its cherry production, with many commercial orchards located in the Yakima Valley and Lake Chelan areas.
The Northeast region is another area well-suited for growing cherry trees. The region’s cool winters and warm summers provide the necessary chill hours for cherry tree growth, and the soil is often rich in nutrients. New York, Michigan, and Pennsylvania are among the top cherry-producing states in the Northeast.
In contrast, the Southern states have a more challenging climate for growing cherry trees. The region’s hot and humid summers can lead to disease issues, and the soil is often too sandy or too clayey for optimal growth. However, some cherry tree varieties, such as the ‘Bing’ and ‘Rainier’, are more tolerant of the Southern climate and can thrive in states like Georgia and North Carolina.
California is also a significant cherry-producing state, with many commercial orchards located in the San Joaquin Valley and Lake County. The state’s Mediterranean climate, with warm summers and cool winters, is well-suited for cherry tree growth, and the soil is often rich in nutrients.
When growing cherry trees in different regions, it’s essential to consider the specific climate and soil conditions. For example:
- In regions with hot summers, providing shade for the trees during the hottest part of the day can help prevent sunburn and reduce stress.
- In regions with cold winters, selecting cherry tree varieties with high chill hour requirements can help ensure optimal growth and fruit production.
- In regions with poor soil quality, incorporating organic matter like compost or manure can help improve soil fertility and structure.
By understanding the regional differences in climate and soil conditions, growers can select the most suitable cherry tree varieties and create an optimal environment for growth and fruit production. Whether growing cherry trees in a commercial orchard or a backyard garden, considering the regional factors can help ensure success.
When deciding where to grow cherry trees, it’s also essential to consider the specific growing requirements of the chosen variety. Different varieties have unique climate and soil requirements, and selecting a variety that is well-suited to the regional conditions can help ensure optimal growth and fruit production.
Microclimates and Cherry Tree Growth
When deciding where to grow cherry trees, understanding the concept of microclimates is essential for optimal growth and fruit production. A microclimate refers to the unique climate conditions that exist in a specific area, such as a garden or orchard, which can differ from the surrounding climate. Microclimates can be influenced by various factors, including topography, soil type, and vegetation.
Microclimates can have a significant impact on cherry tree growth, as they can affect the tree’s temperature, humidity, and sunlight exposure. For example, a microclimate with a south-facing slope can receive more sunlight and warmth than a north-facing slope, which can affect the tree’s growth and fruit production.
To identify microclimates in your area, consider the following factors:
- Topography: Hills, valleys, and slopes can create microclimates with unique temperature and sunlight patterns.
- Soil type: Different soil types can retain or release heat, affecting the microclimate.
- Vegetation: Trees, shrubs, and other vegetation can provide shade, block winds, and affect the microclimate.
- Water sources: Proximity to water sources, such as rivers or lakes, can affect the microclimate.
Creating microclimates that promote healthy cherry tree growth can be achieved through various techniques, including:
- Using windbreaks: Planting trees or shrubs to block winds and create a more sheltered microclimate.
- Providing shade: Using shade cloth or planting trees to provide shade and reduce heat stress.
- Improving soil quality: Adding organic matter or fertilizers to improve soil fertility and structure.
- Installing irrigation systems: Providing consistent moisture levels to promote healthy growth.
By understanding and creating microclimates that promote healthy cherry tree growth, growers can optimize fruit production and tree health. Whether growing cherry trees in a commercial orchard or a backyard garden, considering microclimates is essential for success.
When deciding where to grow cherry trees, it’s also essential to consider the specific microclimate requirements of the chosen variety. Different varieties have unique microclimate requirements, and selecting a variety that is well-suited to the local microclimate can help ensure optimal growth and fruit production.
In addition to creating microclimates, growers can also use other techniques to promote healthy cherry tree growth, such as pruning, pest management, and fertilization. By combining these techniques with an understanding of microclimates, growers can create an optimal environment for their cherry trees to thrive.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Planting Cherry Trees
When planting cherry trees, it’s essential to avoid common mistakes that can impact the tree’s growth and fruit production. By understanding these mistakes, growers can take steps to prevent them and create an optimal environment for their cherry trees to thrive.
Inadequate soil preparation is one of the most common mistakes people make when planting cherry trees. Cherry trees require well-draining, fertile soil with a pH between 6.0 and 6.5. Failure to prepare the soil properly can lead to poor tree growth, reduced fruit production, and increased susceptibility to disease.
Poor watering habits are another common mistake. Cherry trees require consistent moisture, especially during the first year after planting. Overwatering or underwatering can lead to stress, disease, and pest issues. It’s essential to water cherry trees regularly, but avoid overwatering, which can lead to root rot and other problems.
Insufficient pruning is also a common mistake. Pruning is essential for maintaining the tree’s shape, promoting fruiting, and removing diseased or damaged branches. Failure to prune cherry trees regularly can lead to reduced fruit production, increased disease susceptibility, and a less attractive tree shape.
Other common mistakes to avoid when planting cherry trees include:
- Planting trees too close together: Cherry trees require adequate space to grow and produce fruit. Planting trees too close together can lead to reduced fruit production, increased disease susceptibility, and a less attractive tree shape.
- Not providing support: Cherry trees may require support, especially when they’re young. Failure to provide support can lead to branch breakage, reduced fruit production, and a less attractive tree shape.
- Not monitoring for pests and diseases: Cherry trees are susceptible to various pests and diseases, such as aphids, spider mites, and powdery mildew. Failure to monitor for these issues can lead to reduced fruit production, increased disease susceptibility, and a less attractive tree shape.
By avoiding these common mistakes, growers can create an optimal environment for their cherry trees to thrive. Whether growing cherry trees in a commercial orchard or a backyard garden, understanding these mistakes can help ensure success.
When deciding where to grow cherry trees, it’s also essential to consider the specific growing requirements of the chosen variety. Different varieties have unique growing requirements, and selecting a variety that is well-suited to the local climate and soil conditions can help ensure optimal growth and fruit production.
In addition to avoiding common mistakes, growers can also use other techniques to promote healthy cherry tree growth, such as fertilization, pest management, and irrigation management. By combining these techniques with an understanding of common mistakes, growers can create an optimal environment for their cherry trees to thrive.
Cherry Tree Varieties and Their Specific Growing Requirements
When deciding where to grow cherry trees, it’s essential to consider the specific growing requirements of the chosen variety. Different cherry tree varieties have unique growing requirements, and selecting a variety that is well-suited to the local climate and soil conditions can help ensure optimal growth and fruit production.
Some popular cherry tree varieties include:
- ‘Bing’: This variety is known for its large, sweet fruit and is well-suited for growing in regions with mild winters and cool summers.
- ‘Rainier’: This variety is known for its light-colored fruit and is well-suited for growing in regions with warm summers and cold winters.
- ‘Montmorency’: This variety is known for its sour fruit and is well-suited for growing in regions with cold winters and cool summers.
Each of these varieties has specific growing requirements, including:
- Temperature: Cherry trees require a certain number of chill hours to break dormancy, and the specific temperature requirements vary by variety.
- Soil: Cherry trees prefer well-draining, fertile soil with a pH between 6.0 and 6.5, but some varieties may require more specific soil conditions.
- Water: Cherry trees require consistent moisture, especially during the first year after planting, but some varieties may be more drought-tolerant than others.
When selecting a cherry tree variety, consider the specific growing requirements and how they align with the local climate and soil conditions. This will help ensure optimal growth and fruit production.
In addition to considering the specific growing requirements of the chosen variety, it’s also essential to consider the overall climate and soil conditions of the region. Cherry trees are generally hardy in USDA zones 5-9, but some varieties may be more tolerant of extreme temperatures or soil conditions.
Some regions that are well-suited for growing cherry trees include:
- The Pacific Northwest: This region has a mild climate and rich soil, making it an ideal location for growing cherry trees.
- The Northeast: This region has a cool climate and well-draining soil, making it an ideal location for growing cherry trees.
- California: This region has a warm climate and well-draining soil, making it an ideal location for growing cherry trees.
By considering the specific growing requirements of the chosen variety and the overall climate and soil conditions of the region, growers can create an optimal environment for their cherry trees to thrive.
Creating a Thriving Cherry Tree Orchard
Creating a thriving cherry tree orchard requires careful planning, attention to detail, and a commitment to providing optimal growing conditions. By following these tips, you can create a healthy and productive cherry tree orchard that will provide delicious fruit for years to come.
Tree Spacing:
One of the most important factors in creating a thriving cherry tree orchard is tree spacing. Cherry trees should be spaced at least 20-25 feet apart to allow for proper air circulation and sunlight penetration. This will also help prevent disease and pest issues.
Pruning:
Pruning is essential for maintaining the health and productivity of your cherry tree orchard. Prune your trees annually to remove any dead, diseased, or damaged branches. This will help promote healthy growth and fruit production.
Pest Management:
Pests can be a major problem in cherry tree orchards, so it’s essential to have a pest management plan in place. Use integrated pest management (IPM) techniques, such as introducing beneficial insects, practicing good sanitation, and using organic pesticides, to minimize the risk of pest damage.
Soil Care:
Soil care is critical for creating a thriving cherry tree orchard. Test your soil regularly to determine its pH and nutrient levels. Add organic matter, such as compost or manure, to improve soil fertility and structure.
Irrigation:
Cherry trees require consistent moisture, especially during the first year after planting. Use drip irrigation or soaker hoses to deliver water directly to the roots of the trees, reducing evaporation and runoff.
Fertilization:
Fertilize your cherry trees annually with a balanced fertilizer that contains nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. Avoid over-fertilizing, as this can damage the trees and the environment.
By following these tips, you can create a thriving cherry tree orchard that will provide delicious fruit for years to come. Remember to always follow best practices for tree care and maintenance to ensure the health and productivity of your orchard.
When deciding where to grow cherry trees, consider the specific growing requirements of the variety you are planting. Different varieties have unique growing requirements, and selecting a variety that is well-suited to the local climate and soil conditions can help ensure optimal growth and fruit production.
Some popular cherry tree varieties for orchards include:
- ‘Bing’: This variety is known for its large, sweet fruit and is well-suited for growing in regions with mild winters and cool summers.
- ‘Rainier’: This variety is known for its light-colored fruit and is well-suited for growing in regions with warm summers and cold winters.
- ‘Montmorency’: This variety is known for its sour fruit and is well-suited for growing in regions with cold winters and cool summers.
By selecting the right variety for your orchard and following these tips, you can create a thriving cherry tree orchard that will provide delicious fruit for years to come.