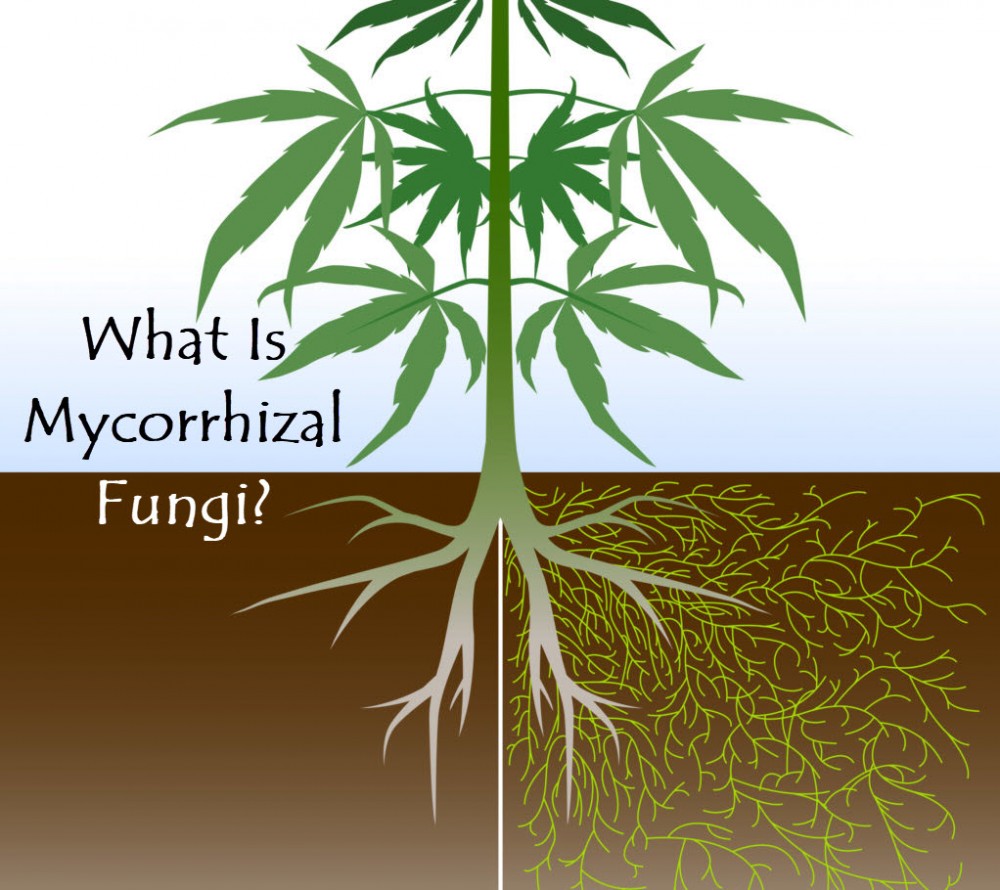
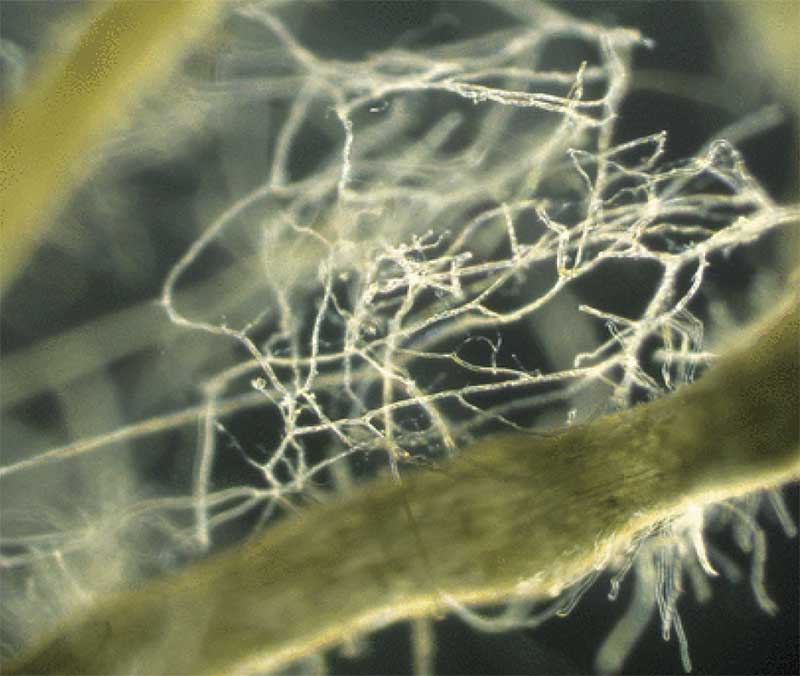
What are Mycorrhizal Fungi and How Do They Help Plants
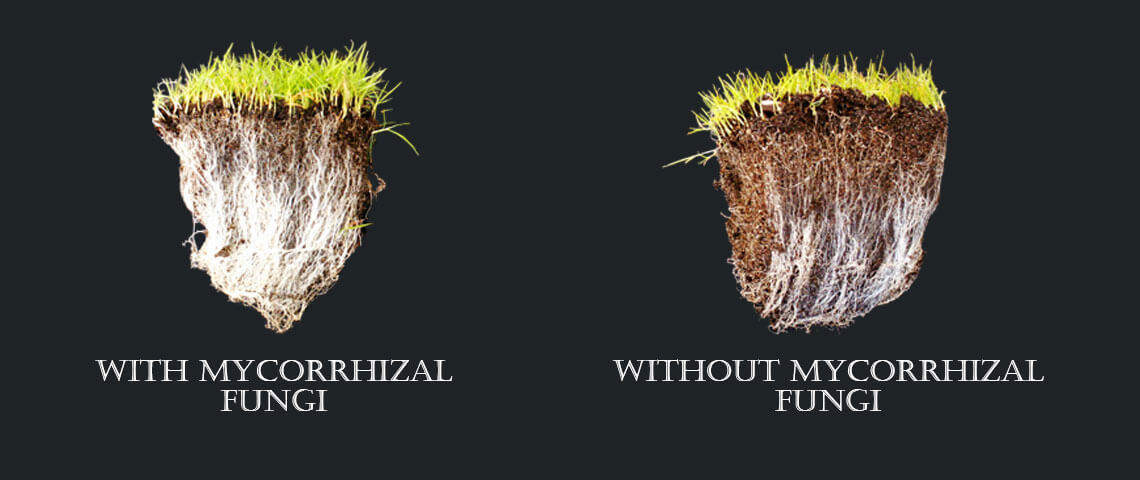
Mycorrhizal fungi are a type of fungi that form symbiotic relationships with plant roots, providing essential nutrients and water in exchange for carbohydrates produced by the plant. This mutually beneficial relationship is crucial for plant growth and development, as it enhances the plant’s ability to absorb water and nutrients from the soil. Mycorrhizal fungi also play a key role in improving soil structure, increasing the soil’s water-holding capacity, and reducing soil erosion.
Plants that benefit from mycorrhizal fungi exhibit improved growth rates, increased yields, and enhanced resistance to diseases and pests. The fungi also help plants to tolerate environmental stresses, such as drought and extreme temperatures. In addition, mycorrhizal fungi can facilitate the transfer of nutrients between plants, promoting a more efficient use of resources within the plant community.
Research has shown that mycorrhizal fungi can increase plant growth by up to 50% and improve crop yields by up to 20%. Furthermore, the use of mycorrhizal fungi in agriculture can reduce the need for synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, promoting a more sustainable and environmentally friendly approach to farming.
When considering which plants benefit from mycorrhizal fungi, it is essential to understand the different types of mycorrhizal fungi and their specific relationships with various plant species. For example, some plants, such as legumes, have a high degree of specificity with certain types of mycorrhizal fungi, while others, such as grasses, can form relationships with a broader range of fungi.
By understanding the complex relationships between mycorrhizal fungi and plants, farmers and gardeners can harness the power of these beneficial microorganisms to improve crop yields, reduce environmental impact, and promote sustainable agriculture practices.
How to Choose the Right Plants for Mycorrhizal Fungi
When selecting plants that benefit from mycorrhizal fungi, it is essential to consider several factors, including plant type, soil conditions, and climate. Different plants have varying levels of compatibility with mycorrhizal fungi, and some may require specific types of fungi to thrive.
For example, plants in the legume family, such as beans and peas, have a high degree of specificity with certain types of mycorrhizal fungi. These plants have evolved to form symbiotic relationships with specific fungi, which provide them with essential nutrients in exchange for carbohydrates.
Other plants, such as grasses and cereals, can form relationships with a broader range of mycorrhizal fungi. These plants are often more adaptable and can thrive in a variety of soil conditions.
Soil conditions also play a crucial role in determining which plants benefit from mycorrhizal fungi. Plants that thrive in poor soil conditions, such as those with low nutrient availability, may benefit from mycorrhizal fungi that can provide them with essential nutrients.
Climate is another important factor to consider when selecting plants that benefit from mycorrhizal fungi. Plants that thrive in hot and dry conditions, such as those found in Mediterranean climates, may benefit from mycorrhizal fungi that can provide them with drought tolerance.
Some examples of plants that form symbiotic relationships with mycorrhizal fungi include:
- Legumes (beans, peas, lentils)
- Grasses (wheat, oats, barley)
- Cereals (corn, rice, sorghum)
- Vegetables (tomatoes, peppers, cucumbers)
- Fruits (apples, bananas, strawberries)
By understanding the specific needs of different plants and selecting those that are compatible with mycorrhizal fungi, gardeners and farmers can harness the power of these beneficial microorganisms to improve crop yields and promote sustainable agriculture practices.
When considering which plants benefit from mycorrhizal fungi, it is also important to think about the specific benefits that these fungi can provide. For example, some mycorrhizal fungi can provide plants with increased drought tolerance, while others can improve soil structure and fertility.
By selecting plants that are compatible with mycorrhizal fungi and providing them with the right conditions to thrive, gardeners and farmers can unlock the full potential of these beneficial microorganisms and promote a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future.
Top Plants that Thrive with Mycorrhizal Fungi
Many plants benefit from mycorrhizal fungi, but some species are more responsive to these beneficial microorganisms than others. Here are some of the top plants that thrive with mycorrhizal fungi:
Trees
Trees such as oak, beech, and pine are known to form symbiotic relationships with mycorrhizal fungi. These fungi help trees to absorb water and nutrients from the soil, promoting healthy growth and development.
Shrubs
Shrubs like rose, lavender, and thyme also benefit from mycorrhizal fungi. These fungi help shrubs to tolerate drought and other environmental stresses, making them ideal for gardens and landscapes.
Perennials
Perennials like coneflower, black-eyed Susan, and bee balm are popular among gardeners, and they all benefit from mycorrhizal fungi. These fungi help perennials to absorb nutrients and water, promoting healthy growth and flowering.
Annuals
Annuals like tomatoes, peppers, and cucumbers also benefit from mycorrhizal fungi. These fungi help annuals to absorb nutrients and water, promoting healthy growth and fruiting.
Some examples of plants that are commonly used in gardening and agriculture and benefit from mycorrhizal fungi include:
- Vegetables: carrots, lettuce, spinach, and broccoli
- Fruits: apples, bananas, strawberries, and blueberries
- Herbs: basil, mint, and rosemary
- Grains: wheat, oats, and barley
These plants are all great examples of which plants benefit from mycorrhizal fungi. By incorporating these plants into your garden or agricultural operation, you can harness the power of mycorrhizal fungi to promote healthy growth and development.
It’s worth noting that mycorrhizal fungi can benefit a wide range of plants, and the specific plants that benefit will depend on the type of fungi and the specific growing conditions. By understanding which plants benefit from mycorrhizal fungi, you can make informed decisions about which plants to use in your garden or agricultural operation.
The Science Behind Mycorrhizal Fungi and Plant Relationships
Mycorrhizal fungi are a type of fungi that form symbiotic relationships with plant roots, providing essential nutrients and water in exchange for carbohydrates produced by the plant. This mutually beneficial relationship is crucial for plant growth and development, and is influenced by a variety of factors, including the type of fungi, the plant species, and the environment.
There are several different types of mycorrhizal fungi, including arbuscular mycorrhizal (AM) fungi, ectomycorrhizal (EM) fungi, and ericoid mycorrhizal (ErM) fungi. Each type of fungi has a unique set of characteristics and forms relationships with specific plant species.
AM fungi are the most common type of mycorrhizal fungi and are found in a wide range of plant species, including crops, trees, and grasses. They form relationships with plants by colonizing the root system and providing essential nutrients and water in exchange for carbohydrates.
EM fungi are found in trees and shrubs and form relationships with plants by colonizing the root system and providing essential nutrients and water in exchange for carbohydrates. They are commonly found in forest ecosystems and play a crucial role in the health and productivity of trees.
ErM fungi are found in ericaceous plants, such as blueberries and rhododendrons, and form relationships with plants by colonizing the root system and providing essential nutrients and water in exchange for carbohydrates.
The colonization patterns of mycorrhizal fungi vary depending on the type of fungi and the plant species. Some fungi, such as AM fungi, colonize the root system by forming arbuscules, which are specialized structures that allow for the exchange of nutrients and water. Other fungi, such as EM fungi, colonize the root system by forming ectomycorrhizal structures, which are specialized structures that allow for the exchange of nutrients and water.
The mechanisms of nutrient exchange between mycorrhizal fungi and plants are complex and involve a variety of processes, including the exchange of carbohydrates and nutrients. The fungi provide essential nutrients and water to the plant in exchange for carbohydrates, which are produced by the plant through photosynthesis.
Understanding the science behind mycorrhizal fungi and plant relationships is crucial for harnessing the power of these beneficial microorganisms. By understanding the different types of mycorrhizal fungi, their colonization patterns, and the mechanisms of nutrient exchange, we can better appreciate the importance of these fungi in plant growth and development.
How to Create a Mycorrhizal Fungi-Friendly Environment
Creating an environment that fosters the growth and colonization of mycorrhizal fungi is crucial for harnessing their benefits. Here are some tips and advice on how to create a mycorrhizal fungi-friendly environment:
Soil Preparation
Soil preparation is essential for creating a mycorrhizal fungi-friendly environment. This includes adding organic matter such as compost or manure to the soil, which provides nutrients and habitat for the fungi. Additionally, reducing tillage and using conservation tillage practices can help to preserve the soil’s natural structure and promote the growth of mycorrhizal fungi.
Irrigation
Irrigation is also important for creating a mycorrhizal fungi-friendly environment. Mycorrhizal fungi thrive in moist environments, so ensuring that the soil is consistently moist can help to promote their growth. However, over-irrigation can be detrimental to the fungi, so it’s essential to strike a balance.
Fertilization
Fertilization can also impact the growth of mycorrhizal fungi. While fertilizers can provide essential nutrients for plant growth, they can also harm the fungi. Using organic fertilizers or reducing the amount of fertilizer used can help to promote the growth of mycorrhizal fungi.
Other factors to consider when creating a mycorrhizal fungi-friendly environment include:
- Using cover crops to provide habitat for the fungi
- Reducing the use of pesticides and herbicides, which can harm the fungi
- Creating a diverse and complex ecosystem, which can promote the growth of mycorrhizal fungi
By following these tips and advice, you can create an environment that fosters the growth and colonization of mycorrhizal fungi, which can help to promote plant growth and health.
It’s also important to note that different plants have different requirements for mycorrhizal fungi, so it’s essential to research the specific needs of the plants you are growing. By understanding which plants benefit from mycorrhizal fungi and how to create a mycorrhizal fungi-friendly environment, you can harness the power of these beneficial microorganisms to promote plant growth and health.
Common Challenges and Solutions for Working with Mycorrhizal Fungi
While mycorrhizal fungi can be a powerful tool for improving plant growth and health, there are several common challenges that gardeners and farmers may face when working with these beneficial microorganisms. Here are some of the most common challenges and solutions:
Contamination
One of the most common challenges when working with mycorrhizal fungi is contamination. This can occur when other microorganisms, such as bacteria or fungi, are present in the soil and compete with the mycorrhizal fungi for resources. To avoid contamination, it’s essential to use sterile equipment and follow proper handling and storage procedures.
Competition
Another challenge when working with mycorrhizal fungi is competition from other microorganisms. This can occur when other microorganisms, such as bacteria or fungi, are present in the soil and compete with the mycorrhizal fungi for resources. To overcome this challenge, it’s essential to create an environment that favors the growth of mycorrhizal fungi, such as by adding organic matter to the soil.
Limited Colonization
Limited colonization is another common challenge when working with mycorrhizal fungi. This can occur when the mycorrhizal fungi are not able to colonize the plant roots effectively, which can limit their ability to provide benefits to the plant. To overcome this challenge, it’s essential to ensure that the soil is conducive to mycorrhizal fungi growth and that the plant roots are healthy and able to form symbiotic relationships with the fungi.
Other solutions for overcoming common challenges when working with mycorrhizal fungi include:
- Using a diverse range of mycorrhizal fungi species to promote colonization and reduce competition
- Adding organic matter to the soil to promote mycorrhizal fungi growth and reduce contamination
- Using conservation tillage practices to reduce soil disturbance and promote mycorrhizal fungi growth
By understanding the common challenges and solutions for working with mycorrhizal fungi, gardeners and farmers can harness the power of these beneficial microorganisms to improve plant growth and health.
It’s also important to note that different plants have different requirements for mycorrhizal fungi, so it’s essential to research the specific needs of the plants you are growing. By understanding which plants benefit from mycorrhizal fungi and how to create a mycorrhizal fungi-friendly environment, you can overcome common challenges and promote plant growth and health.
Real-World Examples of Mycorrhizal Fungi in Action
Mycorrhizal fungi have been used in a variety of real-world applications, including agriculture, forestry, and conservation. Here are some examples of mycorrhizal fungi in action:
Agriculture
In agriculture, mycorrhizal fungi have been used to improve crop yields and reduce the need for fertilizers and pesticides. For example, a study in the United States found that using mycorrhizal fungi in corn production increased yields by 20% and reduced the need for fertilizers by 30%.
Forestry
In forestry, mycorrhizal fungi have been used to improve tree growth and reduce the need for fertilizers and pesticides. For example, a study in Canada found that using mycorrhizal fungi in tree plantations increased tree growth by 15% and reduced the need for fertilizers by 25%.
Conservation
In conservation, mycorrhizal fungi have been used to restore degraded ecosystems and promote biodiversity. For example, a study in Australia found that using mycorrhizal fungi in restoration efforts increased plant diversity by 50% and improved soil health by 30%.
Other examples of mycorrhizal fungi in action include:
- Using mycorrhizal fungi to improve soil health and reduce erosion in vineyards
- Using mycorrhizal fungi to improve tree growth and reduce the need for fertilizers in urban forestry
- Using mycorrhizal fungi to promote biodiversity and improve ecosystem health in wetlands
These examples demonstrate the potential of mycorrhizal fungi to contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future. By understanding which plants benefit from mycorrhizal fungi and how to create a mycorrhizal fungi-friendly environment, we can harness the power of these beneficial microorganisms to improve plant growth and health.
It’s also important to note that mycorrhizal fungi can be used in a variety of different applications, including agriculture, forestry, and conservation. By exploring the different ways that mycorrhizal fungi can be used, we can unlock their full potential and promote a more sustainable future.
Conclusion: Harnessing the Power of Mycorrhizal Fungi for a Sustainable Future
Mycorrhizal fungi are a powerful tool for improving plant growth and health, and have the potential to contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future. By understanding which plants benefit from mycorrhizal fungi and how to create a mycorrhizal fungi-friendly environment, we can harness the power of these beneficial microorganisms to improve plant growth and health.
The benefits of mycorrhizal fungi are numerous, and include increased water and nutrient uptake, improved soil structure, and enhanced disease resistance. Additionally, mycorrhizal fungi can help to promote biodiversity and improve ecosystem health, making them a valuable tool for conservation and sustainability efforts.
While there are challenges to working with mycorrhizal fungi, such as contamination, competition, and limited colonization, these can be overcome with proper planning and management. By understanding the common challenges and solutions for working with mycorrhizal fungi, we can unlock their full potential and promote a more sustainable future.
Real-world examples of mycorrhizal fungi in action demonstrate their potential to improve plant growth and health, and promote sustainability. From agriculture to forestry to conservation, mycorrhizal fungi are being used to improve ecosystem health and promote biodiversity.
In conclusion, mycorrhizal fungi are a powerful tool for improving plant growth and health, and have the potential to contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future. By understanding which plants benefit from mycorrhizal fungi and how to create a mycorrhizal fungi-friendly environment, we can harness the power of these beneficial microorganisms to promote a more sustainable future.